![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
68 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What two layers make up the integument?
|
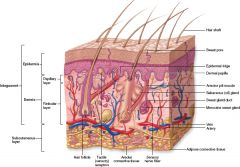
Epidermis, dermis
|
|
|
What are the three layers of skin?
|
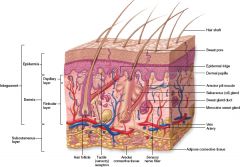
Epidermis, dermis, subcutaneous layer
|
|
|
What is the portion of the hair that exits out of the skin?
|
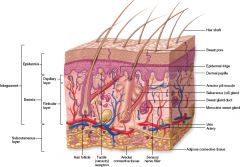
Hair shaft
|
|
|
Ventral is synonymous with what other term?
|
Anterior
|
|
|
Dorsal is synonymous with what other word?
|
Posterior (for bipeds)
|
|
|
_______ is closer to the trunk in relation to something else.
|
Proximal
|
|
|
________ is further from the trunk in relation to something else.
|
Distal
|
|
|
_____ is closer to the midline
|
Medial
|
|
|
_____ is further away from the midline
|
Lateral
|
|
|
What body cavities are lined by a serous membrane?
|
Ventral
|
|
|
What does serous mean?
|
Thin, watery fluid
|
|
|
What is a serous membrane?
|
thin membrane that secretes serous fluid in order to lubricate between internal organs and reduce friction
|
|
|
What is the purpose of a serous membrane?
|
Lubrication, reduce friction
|
|
|
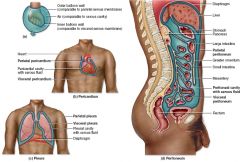
Which serous membrane lines the cavity wall and which serous membrane lines the organ? Why is the space between the two membranes potential space?
|
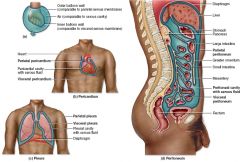
Parietal membrane lines cavity wall
Visceral membrane lines the organ The space is potential space because it's not empty, it is filled with serous fluid |
|
|
What is the lining directly on the lungs called? What is the lining on the thoracic cavity around the lungs? What is the space between the two called?
|
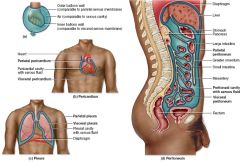
Visceral pleura
Parietal pleura Serous cavity |
|
|
What body cavities have serous membranes?
|
Ventral
|
|
|
Which serous membrane layer is on the outside, against the cavity wall?
|
Parietal
|
|
|
Which serous membrane is on the organ?
|
Visceral layer
|
|
|
What does the word "viscera" mean?
|
Organ
|
|
|
What is another word for organ?
|
Viscera
|
|
|
Name the nine abdominopelvic regions
|
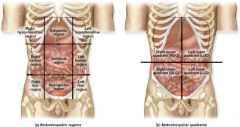
Right hypochondriac
Right lumbar Right iliac epigastric umbilical hypogastric Left hypochondriac Left lumbar left iliac |
|
|
What does "epi" mean?
|
above
|
|
|
Which cavity type is encased completely in bone?
|
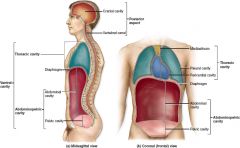
Posterior aspect or dorsal body cavity
|
|
|
What are the two subdivisions of the posterior aspect?
|
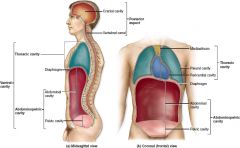
Cranial, which houses the brain and is also called endocranium, and the vertebral canal, which is formed by the bones of the vertebral column and houses the spinal cord.
|
|
|
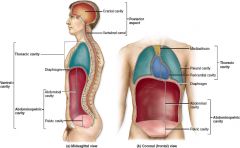
What are the two main cavities that are part of the ventral cavity?
|
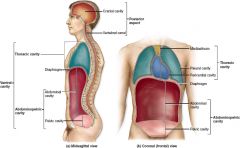
Thoracic cavity and abdominopelvic cavity
|
|
|
What organ separates the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities?
|
Diaphragm
|
|
|
What organ separates the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities?
|
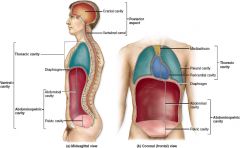
Diaphragm
|
|
|
Are the cavities of the posterior aspect lined with serous membranes?
|
No
|
|
|
What three cavities are part of the thoracic cavity?
|
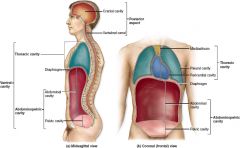
Mediastinum, pleural, and pericardial
|
|
|
What two cavities are part of the abdominopelvic cavity?
|
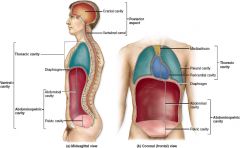
Abdominal, pelvic
|
|
|
What kind of fluid is secreted by serous membranes?
|
Serous fluid
|
|
|
The median space in the thoracic cavity is called the _____?
|
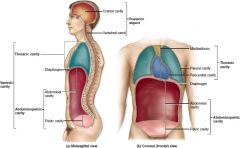
Mediastinum
|
|
|
What is contained in the mediastinum?
|
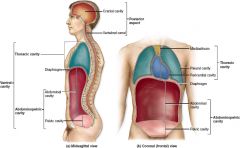
heart, thymus, esophagus, trachea and major blood vessels that connect to the heart
|
|
|
The pericardium is composed of two _____ membranes called the _______ membrane and the ______ membrane, making the pericardial cavity.
|
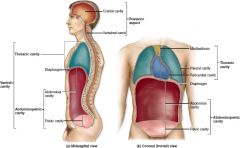
serous; visceral pericardium, parietal pericardium
|
|
|
What types of membranes are associated with the lungs?
|
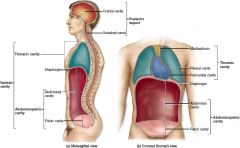
Parietal pleura, visceral pleura, creating the pleural cavity.
|
|
|
Where do the abdominal and pelvic cavities subdivide?
|
plane at the level of the superior aspects of the ilia
|
|
|
The two-layered serous membrane that lines the abdominopelvic cavity
|
Peritoneum
|
|
|
Which body cavity is associated with the lungs, and what are the names of its serous membranes?
|
Pleural cavity; parietal pleura and visceral pleura
|
|
|
Homeostasis means what? (break the word down)
|
ABOUT the same
homeo means about stasis means state |
|
|
The body's ability to maintain a relatively stable internal environment in response to changing internal or external conditions.
|
Homeostasis
|
|
|
Describe the homeostasis process.
|
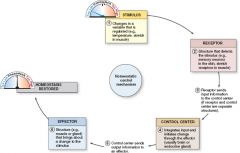
Change from baseline, or stimulus.
Receptors are structures that detect the stimulus Receptors send a signal to the control center Control centers include the brain and endocrine system Control center sends output information to effector An effector is a muscle or gland that brings about a change to the stimulus Homeostasis is restored |
|
|
What system includes a stimulus, receptor, control center, and effector?
|
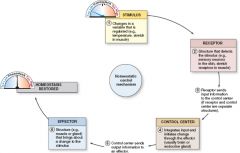
Homeostasis
|
|
|
List and describe three components of a homeostatic system and give examples of each in the human body.
|
Stimulus, receptor, control center, effector.
receptor, control center, and effector are the same when the pancreas detects the sugar levels in the blood and adjusts insulin accordingly. |
|
|
Most processes in the body are controlled by (positive/negative) feedback?
|
Negative
|
|
|
What is the baseline called for homeostasis around which positive and negative feedback revolve?
|
Set point
|
|
|
Body temperature is regulated by what part of the brain?
|
Hypothalamus
|
|
|
Describe how the hypothalamus reacts to low external temperatures.
|
The hypothalamus can be alerted to the external drop in temperature by nerve sensors in the skin, or by the lowered temperature of the blood that passes through it. The hypothalamus then alters nerve impulses to the vessels in the skin to decrease the lumen diameter, reducing the amount of blood near the surface of the skin that is radiating heat and shunting the blood to the core of the body.
|
|
|
Examining the superficial anatomic markings and internal body structures as they relate to the covering skin is called:
a. regional anatomy b. surface anatomy c. pathologic anatomy d. comparative anatomy |
b. surface anatomy
|
|
|
The _______ level of organization is composed of two or more tissue types that work together to perform a common function.
a. cellular b. molecular c. organ d. organismal |
c. organ
|
|
|
The term _______ refers to the sum of all chemical reactions in the body.
a. metabolism b. responsiveness c. stimulus d. reproduction |
a. metabolism
|
|
|
anabolism/catabolism is the building up of a molecule from small to large and anabolism/catabolism is the breaking down of a molecule from large to small
|
anabolism
catabolism |
|
|
A midsagittal plane separates the body into
a. anterior and posterior portions b. superior and inferior portions c. right and left halves d. unequal right and left portions |
c. right and left halves
|
|
|
The term used to describe an appendage structure that is closest to its point of attachment to the trunk is
a. distal b. lateral c. superior d. proximal |
d. proximal
|
|
|
The _______ region is the anterior part of the knee.
a. patellar b. popliteal c. pes d. inguinal |
b. Popliteal
|
|
|
Which body cavity is located inferior to the diaphragm and superior to a horizontal line drawn between the superior edges of the hip bones?
a. abdominal cavity b. pelvic cavity c. pleural cavity d. pericardial cavity |
a. abdominal cavity
|
|
|
The _____ is the serous membrane layer that covers the surface of the lungs.
a. parietal pleura b. visceral pericardium c. visceral peritoneum d. visceral pleura |
d. visceral pleura
|
|
|
The state of maintaining a constant internal environment within an organism is called
a. reproduction b. homeostasis c. imbalance d. life |
b. homeostasis
|
|
|
In a negative feedback mechanism, which of the following events does NOT occur?
a. a stimulus is a change in some variable (eg rise in blood glucose levels) b. a receptor perceives a stimulus c. the control center sends output to an effector d. the effector stimulates or increases the stimulus, so the cycle continues |
d. the effector stimulates or increases the stimulus, so the cycle continues
|
|
|
what is the storage form of glucose in animals?
|
glycogen, stored in the liver and some in the muscles
|
|
|
The study of cells
|
cytology
|
|
|
Name three modified versions of the plasma membrane
|
Microvilli, flagella, cilia
|
|
|
What is the largest structure within the cell?
|
Nucleus
|
|
|
What is the fluid inside the nucleus called?
|
Nucleoplasm
|
|
|
What is intracellular fluid called?
|
Cytosol also called cytoplasmic matrix
|
|
|
What does the prefix cyto- mean?
|
Cell
|
|
|
What are the primary components of the cytoplasm?
|
Cytosol, inclusions, and organelles
|
|
|
Name two categories of organelles
|
Membrane-bound, non-membrane-bound
|
|
|
Name some membrane-bound organelles
|
endoplasmic reticulum, golgi apparatus, lysosomes, peroxisomes, and mitochondria
|

