![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is epithelium? |
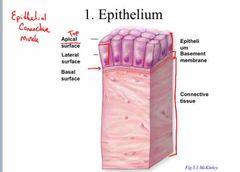
Types of Tissue #1 : Epithelium Epithelial Connective Tissue |
|
|
1A. Covering and Lining Epithelium what are the 3 names of epithelial according to SHAPE ? |
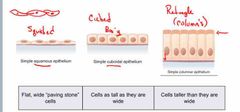
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Covering and Lining Epithelium
3 Naming Epithelia according to ARRANGEMENT ? |
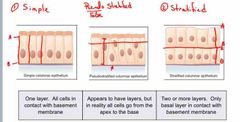
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Covering and Lining Epithelium: SIMPLE SQUAMOUS |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Covering and Lining Epithelium SIMPLE CUBOIDAL |
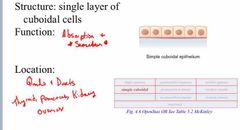
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Covering and Lining Epithelium SIMPLE COLUMNAR (non-ciliated) |
Structure: single layer of columnarcells, no cilia on microvilli Function: absorption and secretion and the majority of themare absorption Location: microvilli in theintestines, non-ciliated in intestinesCiliated -trachea |
|
|
Covering and Lining Epithelium SIMPLE COLUMNAR (ciliated) |
Structure: single layer of columnarcells, microvilli have cilia Function: has protection level andmucus production. Location: found in the trachea |
|
|
Covering and Lining Epithelium PSEUDOSTRATIFIED COLUMNAR |
Structure: single layer of columnar cells,nuclei at different levels Function: protection Location: lines the larger airways(bronchi). |
|
|
Covering and Lining Epithelium STRATIFIED SQUAMOUS |
Structure: many layers of thincells
Function: protection Abrasive substances
Location: Keratonized(outside of the skin) and not-keritonized(found in esophagus and mouth) |
|
|
Covering and Lining Epithelium STRATIFIED CUBOIDAL |
Structure: many layers of cuboidalcells Function:Protection and mainly secretion (#1function) Location: •Ducts of exocrine glands •In male urethra •Ovarian Follicle |
|
|
Covering and Lining Epithelium STRATIFIED COLUMNAR |
Structure: basal layers irregularly shaped, the apical layer has columnar cells Function:Protection and secretion Location: Ductsof the salivary glands and themembranous of the male urethra |
|
|
Covering and Lining Epithelium TRANSITIONAL |
Structure: variable appearance . •Polyhedralshape multiple layers Function: distention and relaxation Location: Urinary Bladder (the very tipof the ureters) |
|
|
GLANDULAR EPITHELIUM What is the purpose of Epithelial Glands? What are the 4 Epithelial Glands? |
•Epithelialglands – function for secretion Exocrine Merocrine glands Apocrine glands Holocrine |
|
|
GLANDULAR EPITHELIUM EXOCRINE GLANDS |
•have ducts! |
|
|
GLANDULAR EPITHELIUM MEROCRINE GLANDS |
•Merocrine glands: package secretions intosecretory vesicle and release via exocytosis (ceremonious: your earwax) sweat, saliva and lacrimal |
|
|
GLANDULAR EPITHELIUM APPOCRINE GLANDS |
•Apocrine glands: apical membrane aroundthe glandular cell’s cytoplasm –pinches itself off and become the secretion |
|
|
GLANDULAR EPITHELIUM HALOCRINE GLANDS |
•Halocrine: from cells , accumulate, disintegratesebaceous |
|
|
Compound Ducts |
Compound Tubuloalveolar Salivary Glands; glands of respiratory passages; and pancreas |

