![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
63 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Suppression Ratio |
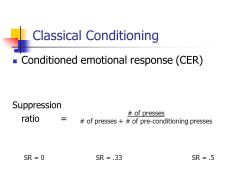
Studies the relationship between an overt response and the covert behavior that may be oppressed |
|
|
Interstimulus Interval |
The time between the presentation of the NS, and the presentation of the US |
|
|
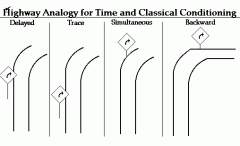
Delayed Conditioning |
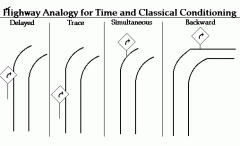
The onset of the NS precedes the US, but the presentation of the US overlaps with the NS. |
|
|
Neutral Stimulus |
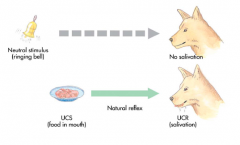
A stimulus which initially produces no specific response other than focusing attention. |
|
|
Conditioned Stimulus |
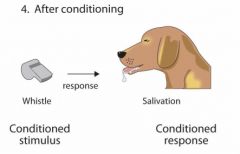
A natural response, that is paired with a neutral stimulus, to create a new, learned stimulus |
|
|
Conditioned Response |
A pairing of a conditioned stimulus with a certain event to create a predictable behavior |
|
|
Unconditioned Stimulus |
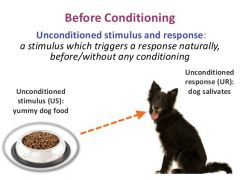
A natural appetitive or aversive stimulus |
|
|
Trace Conditioning |
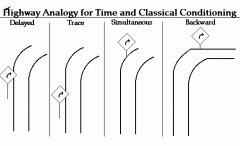
A form of conditioning where the NS precedes the US, but is removed before US is presented. |
|
|
Simultaneous Conditioning |
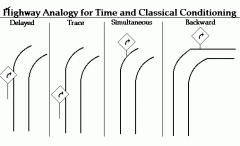
A type of conditioning where the NS and US are presented at the same time. |
|
|
Backward Conditioning |
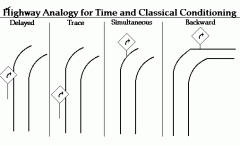
A type of conditioning where the US precedes the NS, and creates no predictive value |
|
|
Temporal Conditioning |
A type of conditioning where the specific time interval is the CS |
|
|
Occasion Setting |
The idea that the predictive value of a CS is conditional, and based on the setting/situation |
|
|
Acquisition |
The shift from NS to CS as a gradual increase of associative strength. This is affected by the intensity. |
|
|
Unconditioned Stimulus Inflation |
A type of acquisition curve where there is a quick, strong association |
|
|
Unconditioned Stimulus Deflation |
A type of acquisition curve where there is a slow, and gradual weakening of association |
|
|
Extinction |
A conditioned stimulus occurs, but no longer with the unconditioned stimulus, and therefore no longer predicts the US |
|
|
Adversive Conditioning |

If CS is avoided, extinction will not occur, because nothing is being unlearned, just avoided |
|
|
Dis-inhibition |
Changes to the environment during extinction trials will also result in the sudden re-appearance of a conditioned response. |
|
|
External Inhibition |

A novel stimulus may distract or interrupt the appearance of a conditioned response. (external interruption) |
|
|
Experimental Neurosis |

This is an abnormal behavior condition produced in an experimental setting where the subject is typically placed in a frustrating situation that then induces erratic altered behavior that mimics a mental disorder |
|
|
Rescorla-Wagner Theory |
A theory that says: the potential for conditioning is limited |
|
|
Latent Learning |

Learning is taking place, but isn't detected, and can be expressed later depending on the situation/environment |
|
|
Over expectation Effect |
When two NS are conditioned independently, but when paired together, there is overestimation, and can result in a decreased CR |
|
|
Heritability |
Relative contribution of genetic predisposition in relation to the environment |
|
|
Phobia |
Overwhelming fear association out of proportion to the actual threat. Is not weakened over time, does not require repeated conditioning, and does not respond well to coping mechanisms - Often involves extreme overgeneralizations |
|
|
Incubation |
Avoidance of a feared stimulus reduces the opportunity for extinction |
|
|
Selective Sensitization |
Emotional and physiological states that are heightened will increase the likelihood of a threat & increase the likelihood of developing a phobia |
|
|
Overshadowing |
The possibility of extinguishing an association due to a long inter stimulus interval |
|
|
Material Behavioral Perspective |
Behavioral perspective based on neurological and physiological processes |
|
|
Formal Behavioral Perspective |
Behavioral perspective using descriptive models explaining pathways and processes in the body |
|
|
Efficient Behavioral Perspective |
Behavioral Perspective focusing on triggers (the input which causes the output) |
|
|
Final Behavior perspecive |
Behavioral Perspective the focuses on evolutionary perspectives |
|
|
Preparedness |
Relative ease with which an association can be made. It's an inherited predisposition and most animals display forms of this when it comes to species specific behavior. |
|
|
Correlation |
Can provide useful information but cannot be directly attributed to any individual. Mis-attributions of this type of info can be faulty, suggestive, and self fullfilling |
|
|
US Revaluation |
Accumulation of fear- Increasingly unpleasant experiences compound the associated fear |
|
|
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy |
A psychotherapy treatment that takes a hands-on, practical approach to problem-solving. Its goal is to change patterns of thinking or behavior that are behind people's difficulties, and so change the way they feel.
|
|
|
Behaviorism |
The theory that human and animal behavior can be explained in terms of conditioning, without appeal to thoughts or feelings, and that psychological disorders are best treated by altering behavior patterns.
|
|
|
Counter Conditioning |
Type of treatment conditioning where the feared stimulus is presented w/o aversive consequence and in conjunction with something appetitive |
|
|
Reciprocal Inhibition |
A negative association is not eliminated but is incompatible with the newer, stronger positive association |
|
|
Flooding |
Prolonged, intense but controlled exposure to aversive stimuli |
|
|
Therapist Modeled Interaction Therapy |
Therapist models an interaction in front of patient with the aversive stimuli in a controlled and safe setting |
|
|
Therapist Facilitated Patient Approach |
Therapist models an interaction with aversive stimuli, & asks the patient to mirror actions. Or, both interact with aversive stimuli together. |
|
|
Aversion Therapy |
Type of therapy that uses counter appetitive with alternative aversion association - Used in therapy when detrimental behavior is perceived as enjoyable or 'rewarding' (such as alcoholism) |
|
|
Covert Sensitization |
An imagery-based procedure. The technique consists of having the client imagine himself or herself engaging in an undesirable behavior (e.g., overeating or excessive alcohol consumption).
|
|
|
Instinctive Drift |
The emergence of a fixed action pattern instead of an operant behavior - Often happens when trying to teach an operant behavior, and replaces it |
|
|
Sign Tracking |
The expression of directed behavior toward a signal (cue) |
|
|
Autoshaping |
The sign tracking behavior emerges naturally with pairing and can then serve as an operant response in further training. |
|
|
Negative Auto Maintenance |
As with instinctive tracking, the expression of sign tracking can be so strong as to impede access to the desired consequence - Both instinctive drift and sign tracking can override the animal's ability to perform the rewarded behavior/response |
|
|
Fixed Interval Schedules |
Intervals of provided reward for a given behavior only following a set passage of time after each response. |
|
|
Interreinforcement Intervals |
Subject know that the behavior will not be rewarded again until a set amount of time |
|
|
Adjunctive Behavior |
A behavior repetitive behavior pattern type which emerges under intermittent schedules (time gaps) of reinforcement - Fills time between opportunities for reinforcement of operant hebavior |
|
|
Displacement Behaviors |
Preventing abandonment of a frustrating but ultimately rewarding process can improve self control |
|
|
Activity Anorexia |
A restrictive eating schedule combined with high levels of activity can cause eating disorders and extreme weightloss |
|
|
Operant Conditioning |
Occurrence of a behavior contingent on an outcome, reward or punishment |
|
|
Discriminitive Stimulus |
A signaling stimulus that cues the availability og a reinforcer for a given response |
|
|
Positive Reinforcer |
Adding something appetitive |
|
|
Positive Punishment |
Adding something aversive |
|
|
Negative Reinforcer |
Removing something aversive |
|
|
Negative Punishment |
Removing something appetitive |
|
|
Secondary Reinforcer |
A situation in which a stimulus reinforces a behavior after it has been associated with a primary reinforcer |
|
|
Generalized Secondary Reinforcer |
A situation where a learned reinforcer can be widely exchanged for other reinforcers - Money |
|
|
Intrinsic Reinforcement |
When a behavior itself is reinforcing enough - Playing an instrument - Learning a sport |
|
|
Extrinsic Reinforcement |
When a behavior itself isnt reinforcing enough, it needs outside reinforcement to make it appetitive |

