![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What does the phloem transport and in which direction? |
Sugars, down the plant |
|
|
What does the xylem transport and in which direction? |
Water, up the plant |
|
|
What is in-between the xylem and the phloem in the vascular bundle? |
Vascular Cambium |
|
|
What surrounds the xylem, phloem and vascular cambium? |
Bundle Sheath |
|
|
What is closest to the middle of the plant? (xylem or phloem) |
Xylem |
|
|
What is closest to the outside of the plant? (xylem or phloem) |
Phloem |
|
|
During secondary growth, do the phloem crush together or the xylem? |
Phloem |
|
|
During secondary growth, do the xylem make rings or the phloem? |
Xylem |
|
|
Where in the vascular bundle does the secondary growth occur? |
Vascular Cambium |
|
|
What does the waxy cuticle do in a leaf? |
It is a clear waterproof layer that stops water from leaking out. |
|
|
Why is the waxy cuticle transparent? |
To allow photosynthesis to occur within the leaf. |
|
|
What does the Palisade Mesophyll do in a leaf? |
Absorbs light using the chloroplasts (which contain chlorophyll). |
|
|
Why is the Palisade layer packed lengthways? |
For optimum chance of light hitting the chlorophyll inside. |
|
|
What does the Upper Epidermis do in a leaf? |
They protect the palisade cells. |
|
|
Why is the Upper Epidermis transparent? |
To allow photosynthesis to occur within the leaf. |
|
|
What does the Spongy Mesophyll do in a leaf? |
They reflect light back into the palaside layer. |
|
|
Why does the Spongy Mesophyll have lots of empty space? |
So CO2 can reach the palisade layer for photosynthesis to occur. |
|
|
What does the Lower Epidermis do in a leaf? |
Releases O2, brings in CO2, and controls water leakage. It contains the stomata and guard cells. |
|
|
What do the guard cells do in a leaf? |
Control the opening and closing of the stomata. |
|
|
What does the stoma do in a leaf? |
Allow gases to difuse (or liquids) in and out of the plant. |
|
|
What does the vascular bundle do in a leaf? |
Transports water needed for photosynthesis (via xylem) and sugars to areas of growth (via phloem). |
|
|
What is the correct leaf structure order? 1. Spongy Mesophyll 2. Lower Epidermis 3. Waxy Cuticle 4. Palisade Mesophyll 5. Vascular Bundle 6. Upper Epidermis |
1. Waxy Cuticle 2. Upper Epidermis 3. Palisade Mesophyll 4. Spongy Mesophyll 5. Vascular Bundle 6. Lower Epidermis |
|
|
What layers are in the wrong place? 1. Waxy Cuticle 2. Upper Epidermis 3. Spongy Mesophyll 4. Palisade Mesophyll 5. Vascular Bundle 6. Lower Epidermis |
3. Palisade Mesophyll 4. Spongy Mesophyll |
|
|
What is wrong with this leaf structure? 1. Waxy Cuticle 2. Upper Epidermis 3.Palisade Mesophyll 4. Spongy Mesophyll 5. Lower Epidermis |
Missing the Vascular Bundle between Spongy Mesophyll and Lower Epidermis. |
|
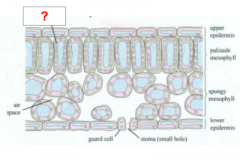
|
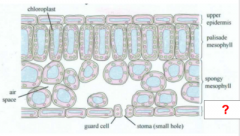
Chloroplast |
|
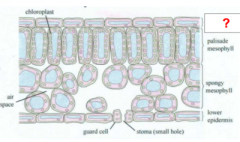
|
Upper Epidermis |
|
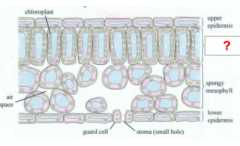
|
Palisade Layer/ Mesophyll |
|
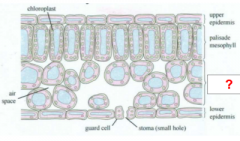
|
Spongy Mesophyll |
|
|
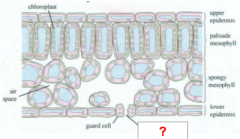
Lower Epidermis |
|
|
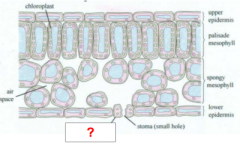
Stoma |
|
|
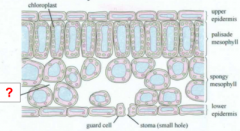
Guard Cell |
|
|
Air Space |
|
|
Vascular Bundle |

