![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
50 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What veins join to form the external jugular vein?
|
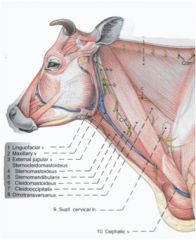
The maxillary and linguofacial veins
|
|
|
What is Viborg's triangle?
|
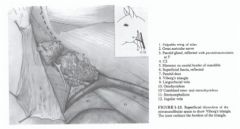
The surgical landmark for access to an enlarged guttural pouch.
Normal guttural pouches do not extend this far ventrally Boundaries: Linguofacial v. Ramus of the mandible Sternocephalicus (sternomandibularis) tendon |
|
|
Where in the external jugular vein is venipuncture of the horse normally performed?
Why? (3 reasons) |
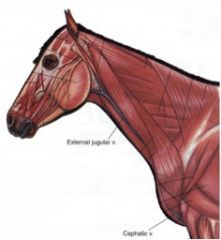
In the cranial third of the neck.
External jugular vein is not obscured by the cutaneous colli m. in this region External jugular vein is lateral to the common carotid artery in this region Omohyoideus muscle may provide protection for the common carotid artery in this region |
|
|
Where is venipuncture of the external jugular vein in the llama performed? What position must the llama be in?
|
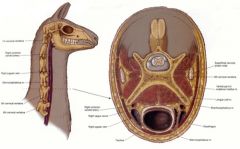
The transverse processes of the caudal cervical vertebrae cover the external jugular vein
Venipuncture is performed in the cranial third of the neck from a craniodorsal standing position |
|
|
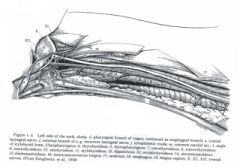
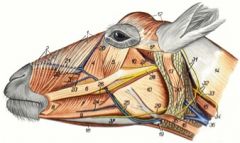
What structures are within the carotid sheath in the horse? in the ox?
|
Horse:
common carotid a. vagosympathetic trunk tracheal trunk Ox: Common carotid a. Internal jugular v. (usually absent in small ruminants) Vagosympathetic trunk Tracheal trunk |
|
|
What are the lymph nodes in the cervical section of the horse and ox?
|
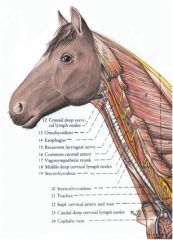
cranial, middle, and caudal
|
|
|
What are the main nerves you'll find in the cervical region of the horse and ox?
|
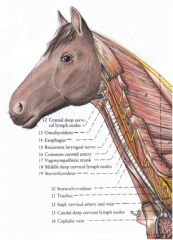
Recurrent laryngeal nn. and vagosympathetic trunk (in the carotid sheath)
|
|
|
T/F the thymus in the horse and ox is in the neck
|
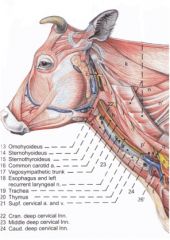
True
|
|
|
T/F the esophagus is on the right side of the neck in the horse
|
False, it is on the left side.
|
|
|
Where is the thyroid gland in the horse?
|
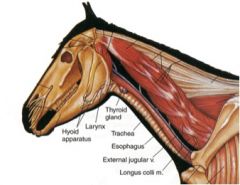
In the cranial neck, dorsal to the trachea.
|
|
|
Where is the thryoid gland located in small ruminants?
|
In the cranial part of the neck, lateral to the trachea, connected with the other side.
|
|
|
What is the location of the thymus in the calf?
|
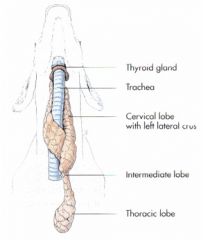
In the neck, wrapped all up around the trachea.
|
|
|
Where is the esophagus in relation to the trachea at C1 in the horse?
|
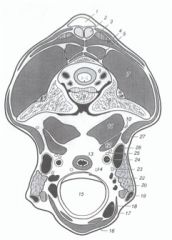
It is directly dorsal to it.
|
|
|
Where is the esophagus in relation to the trachea at C4 in the horse?
|
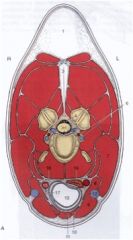
It is sliding to the left.
|
|
|
Where is the esophagus in relation to the trachea at the level of C6 in the horse?
|
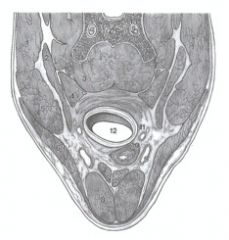
It has slid around the left and is coming ventrally
|
|
|
What special skull facial structure does a sheep have?
|
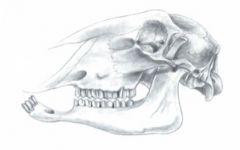
Cutaneous infraorbital sinus
|
|
|
What special skull structure do goats have?
|

horn glands
|
|
|
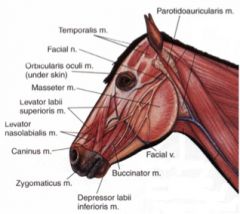
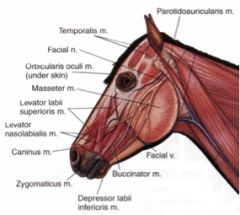
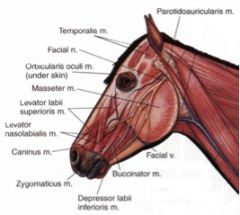
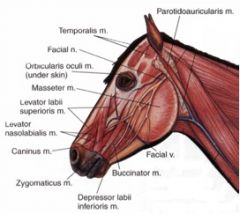
What nerve innervates the muscles of facial expression in the horse and ox?
|
CN VII
|
|
|
What superficial muscle extends from the laryngeal region to the commissure of the mouth in the ox and horse?
|
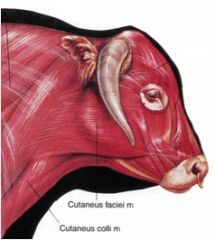
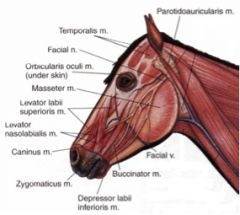
The cutaneous faciei m.
It's the facial part of the platysma |
|
|
Where does the parotidoauricularis muscle course between in the horse and ox? What is its function?
|
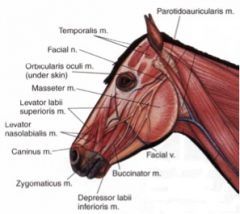
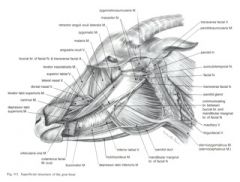
From fascia on the ventral part of the parotid salivary gland to the auricular cartilage of the ear
Draws the ear ventrally and caudally (one of the muscles involved in laying back the ears) |
|
|
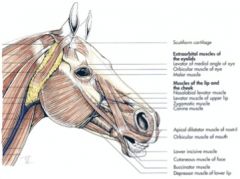
Where does the orbicularis oculi muscle course between in the horse and ox? What is its function?
|
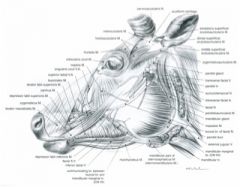
From the medial palpebral ligament to the superior and inferior palpebrae
Acts as a sphincter to close the palpebral fissure |
|
|
Where does orbicularis oris m. course between in the horse and ox?
What is its function? |
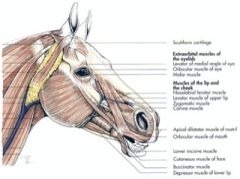
Located inside the stroma of the lips
Acts as a sphincter to close the lips |
|
|
Where does the zygomaticus muscle course from and to in the horse and ruminant (they are different)?
What is its function? |
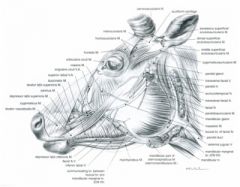
Horse – from the fascia covering the masseter muscle (masseteric fascia) below the facial crest to the commissure of the lips; blends with buccinator
Ruminant – from masseteric fascia and the temporal process of the zygomatic bone to the commissure of the lips; blends with buccinator Retracts and raises the angle of the mouth |
|
|
Where does the levator nasolabialis muscle course from and to in the horse? What is its action?
|
Originates from the frontal and nasal bones, then divides into two branches which course to: 1) the superior lip and the lateral wing of the nostril and 2) the commissure of the lips
Actions: Elevates the superior lip and commissure; dilates the nostril |
|
|
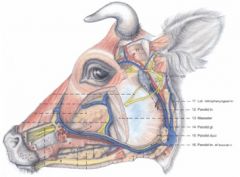
Where does the levator nasolabialis muscle course from and to in the ruminant?
How many parts does it have? What is its action? |
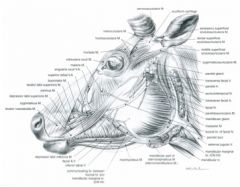
Originates from the rostral part of the frontal bone and the frontalis m., then in the ox, divides into superficial and deep parts
Superficial part courses to the nostril and superior lip and the deep portion courses to the lateral nasal cartilages, incisive bone and the lateral part of the nostril Actions: Elevates the superior lip and dorsolateral portion of the nostril |
|
|
Where does levator labii superioris muscle course from and to in the horse?
What is its action? |
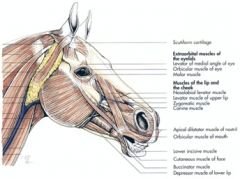
From lacrimal, zygomatic and maxillary bones at their junction to the superior lip, by a common tendon with its fellow of the opposite side
Elevates the superior lip |
|
|
Where does the levator labii superioris m. course between in the small ruminant?
What is its action? Is it the O/I in the ox? |
From the facial tuberosity to the central portion of the superior lip by a common tendon with its fellow of the opposite side
Elevates the superior lip In the ox this muscle courses between the superficial and deep portions of levator nasolabialis m. |
|
|
Where does the caninus m. in the horse course from and to?
What is its action? |
Horse – from the maxilla, near the rostral extent of the facial crest, to the lateral wing of the nostril; courses between the two branches of levator nasolabialis m.
Dilates the nostril |
|
|
Where does the caninus muscle course from and to in the ruminant? What is its action?
|
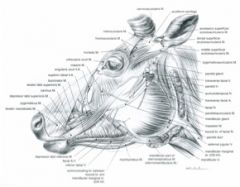
Ruminant – from the facial tuberosity to the lateral part of the nostril; in the ox this muscle courses between the superficial and deep portions of levator nasolabialis m.
Dilates the nostril |
|
|
Where does the depressor labii superioris muscle course between in the ruminant?
What is its function? |
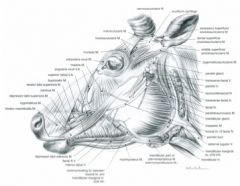
From the maxilla and facial tuberosity to the superior lip and the ventral portion of the nostril
Retracts the rostral portion of the superior lip and ventrolateral portion of the nostril |
|
|
Which depressor labii muscle is not present in horses, dogs, and cats?
|
The depressor labii superioris muscle.
|
|
|
Where does the depressor labii inferioris muscle course between in the horse and ox?
What is its function? |
From the alveolar border of the mandible to the inferior lip
Depresses and retracts the inferior lip |
|
|
Where does the malaris m. in the horse course between?
What is its function? |
Also referred to as depressor palpebrae inferioris m.
From fascia rostral to the orbit to the inferior palpebra – very thin Depresses the inferior palpebra |
|
|
What does the malaris muscle course between in the ox? How many portions does it have?
What are the functions of each portion? |
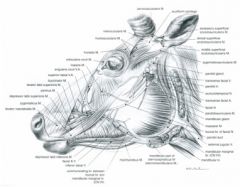
Rostral portion – from facial part of lacrimal bone to buccal fascia in the region of the dorsal border of the buccinator
Elevates the caudal part of the cheek Caudal portion – from the masseteric fascia to the inferior palpebra Depresses the inferior palpebra and widens the palpebral fissure |
|
|
What are the rostral and caudal portions of the malaris muscle of the small ruminant called?
|
Rostral portion is referred to as malaris m. (4)
Caudal portion is referred to as depressor palpebrae inferioris m. (5) |
|
|
Which species is the frontalis m. best developed in?
|
The ox
|
|
|
Where does the frontalis m. course between? What is its function?
|
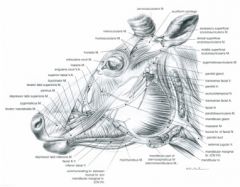
From the base of the horn and intercornual process to the superior palpebra and frontal region
Elevates the superior palpebra and medial angle of the eye |
|
|
What three species have the frontalis m.?
|
The carnivore, ruminant and pig
|
|
|
Does the sternomandibularis m. cover the facial a. in the sheep?
|
No, because sheep don't have sternomandibularis m. It does cover facial a. in the ox.
|
|
|
What are the five muscles of mastication in domestic animals?
|
Masseter m.
Temporalis m. Digastricus m. Medial pterygoideus m. Lateral pterygoideus m. |
|
|
reproach
|
(v) Express disapproval or disappointment, criticize
(n) express of disapproval, rebuke, blame |
|
|
How many portions does the masseter of domestic species have? Which way do the fibers run?
|
Has superficial and deep portions – superficial fibers course predominantly horizontally; deep fibers course predominantly vertically
|
|
|
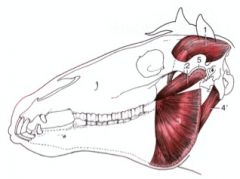
Where does the temporalis m. course between in the horse?
What is the action? |
From the temporal fossa and the crests surrounding the fossa to the coronoid process of the mandible
Raises the mandible |
|
|
Where does the temporalis m. course between in the ruminant?
What is its action? |
From the temporal fossa to the coronoid process of the mandible
In the ox the temporalis m. fills the temporal fossa and is entirely lateral in position (17) Raises the mandible |
|
|
What are the rostral and caudal bellies of digastricus m. joined by in the horse and ox? What extra part does the caudal belly have in the horse?
|
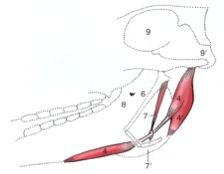
Rostral and caudal bellies are joined by an intermediate tendon; caudal belly has an occipitomandibular part
|
|
|
Where does the medial pterygoideus m. course between in the horse? What is the action?
|
O: The crest formed by the pterygoid processes of the basisphenoid and palatine bones
I: Medial surface of the ramus and ventral border of the mandible Action: Together – raise the mandible; singly – lateral movement of the jaw |
|
|
where does the lateral pterygoideus muscle course between in the horse?
What is the action? |
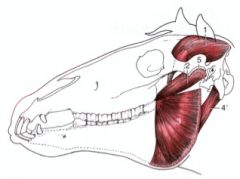
O: Lateral surface of the pterygoid process of the basisphenoid bone
I: Medial surface of ramus and condyle of the mandible Action: Together – draw mandible rostrally; singly – move jaw to side opposite to the muscle contracting Smaller than medial pterygoideus m. |
|
|
Which is smaller: medial pterygoideus or lateral pterygoideus m.?
|
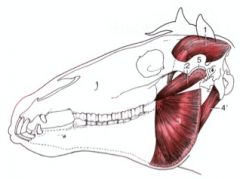
Lateral pterygoideus m. (2) is smaller than medial pterygoideus m. (3)
|
|
|
Where does medial pterygoideus m. course between in the ruminant?
Action? |
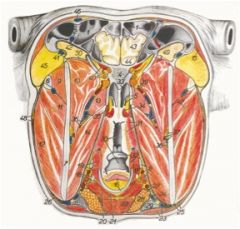
O: The lateral surface of the perpendicular part of the palatine bone and the pterygoid process of the basisphenoid bone
I: Medial surface of the mandible ventral and caudal to the mandibular foramen and the angle of the mandible Action: Together – raise the mandible; singly – one muscle moves the ramus toward the median plane |
|
|
Where does the lateral pterygoideus m. course between?
Action? |
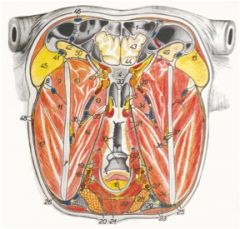
O: Pterygopalatine fossa and the pterygoid process of the basisphenoid bone
I: Rostromedial border of the mandibular condyle and the adjacent part of the neck of the mandible Action: Together – draw mandible rostrally; singly – pronounced lateral movement of the mandible |

