![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
93 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Staphylococcus aureus |
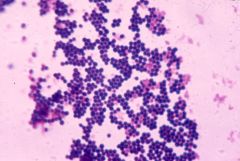
Gram Positive Bacteria, Skin & Respiratory Infections, (clusters of grapes) |
|
|
bacillus antracis |
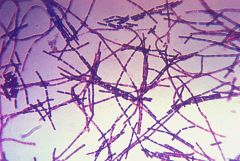
gram positive, anthrax, chains of rods, bracteria |
|
|
Klebsiella pneumoniae |
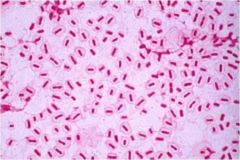
Bacterial infections, gram negative |
|
|
treponema pallidum |
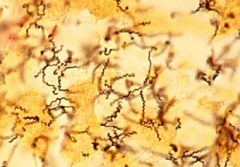
Syphilis, gram negative, bacteria |
|
|
Streptococcus pyogenes |
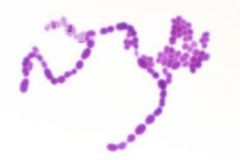
bacteria strept throat, cocci chains, gram positive
|
|
|
candida albicans |
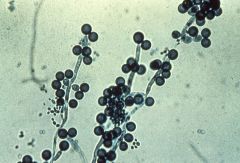
yeast infections, lives inmucosal membranes fungus |
|
|
rhizopus nigricans |
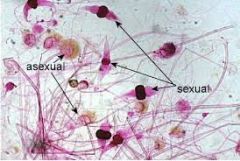
spoiled food, bread molds and allergies, fungus
|
|
|
aspergillus niger |
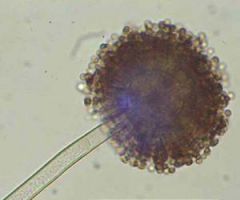
molds, spoiled fruits and vegetables fungus
|
|
|
penicillium notatum |
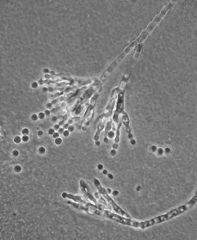
fungus, antibiotic |
|
|
Trypanosoma gambiense |
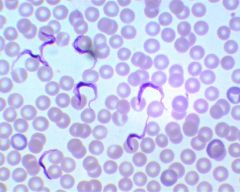
african sleeping sickness, by the tsetse fly, protozoan
|
|
|
Spirogyra |

algae in freshwater
|
|
|
volvox |

algae in freshwater |
|
|
Sterilization |
process used to destroy all life forms |
|
|
three methods of sterilization |
autoclaving, dry heat and filitration |
|
|
Semi-Solids are used |
to determine motility, and contains less agar |
|
|
defined or synthetic medium |
known ingredidents, reproducile recipe
|
|
|
complex or nonsynthetic medium |
undefined ingredients, each batch is different |
|
|
culture medium |
any medium which will support growth of microorganisms |
|
|
autoclaving |
121 degrees C at 15 pounds of pressure for 15 minutes |
|
|
Dry heat |
160-170 degrees C for 2 hours |
|
|
filitration |
passage through filters with pore sizes no greater than .22 lm |
|
|
Why are petri dishes inverted after they cool |
so the agar will not get too dry via evaporation |
|
|
why is culture medium cooled before it is poured into petri plates |
cool enough to be handled and is still iquid to minimize condenstation |
|
|
What is a buffer? |
buffers are used so that the pH of the medium will remain constant even if the microorganisms produces acidic or basic metabolites |
|
|
Serological Pipette |
is completely emptied to deliver the correct amount of liquid |
|
|
Purpose of flmaing in the aseptic tehcnique |
to kill incident microorganims on the transfer tools and the sterile tubes |
|
|
purpose of subculturing |
to transfer cultures from one medium to anothe, to study the maintenace of the cultures |
|
|
Signs of growth in a liquid medium |
cloudiness, a fluffy precipitate, colony formation, and a change in color |
|
|
Difference between inoculating loop and needle |
the needle can be used to lift individual colonies and isolate a pure culture of a single organism |
|
|
why use oil immersion |
more light will enter the viewers eye, and oil decreases distortion |
|
|
function of the condenser |
focuses maximum light upon the object on the side |
|
|
bacilli |
rods |
|
|
coccus |
round |
|
|
sprilla |
spiral
|
|
|
how to increase resolution |
keeping the lens clean and adjusting the diaphragm and condenser correctly |
|
|
Objective lens on a microscope |
4X 10X 40X 100X |
|
|
Selective Media |
adds chemicals that limit growth of some bacteria, it selects what can and cant grow |
|
|
Differential media |
allows everything to grow but shows some difference, |
|
|
MSA Mannitol salt agar |
selective for staph and differential for manitol fermentation |
|
|
Eosin Methylene Blue |
inhibits growth of gram postive bacteria and differntiate lactose fermenters (selective for gram negative bacteria) |
|
|
Purpose of ethanol in the spread plate technique |
burns at low temperature and sterilizes glass rod while not being to hot to use |
|
|
why use only diluted culutres in the spread plate technique |
to be able to distinguish between colonies, and so there wont be to much growth of the microorganisms |
|
|
purpose of spread plate technique |
to allow maximum separation of cells |
|
|
spread plate technique |
easy to use, unreliable results, uses a glass rod to spread an even amount on to the media |
|
|
why are petri plates labeled on the bottom |
because they are incubated in the inverted postion, bottom side up so condenstation does not affect the culture, and so the label will be visible |
|
|
Streak plate technique |
most relibale and commonly used method, applying bacteria to media on four different quadrants and sterilizing loop each time |
|
|
EMB & MSA |
are both selective and differintial |
|
|
Pour Plate Technique |
relies on multiple dilutions of the culture |
|
|
Negative Stains |
background stains, uses acidic dies because the negative charge is repelled by the cell |
|
|
when is negative staining used |
when baceria will not stain well or not at all |
|
|
three stains used for negative stainging |
India ink nigrosin and eosin |
|
|
Purpose of simple staining |
observe size shape and arrangments of microorganisms |
|
|
Dyes used to staning bacteria |
basic dyes, the positive outer surface of bacteria attracts to the negative charged cell |
|
|
example of basic dies |
methylene blue, carbofuchin and crystal violet |
|
|
when making smears from a solid media |
use a innoculating needle to pick up less culture and avoid putting to much on the slide |
|
|
when making smears from a liquid media |
use the innoculating loop |
|
|
Gram Stain |
the mose useful differntial stain |
|
|
gram negative |
shows pink or red, will see color of the counter stian because of the thin cell wall
|
|
|
Gram positve |
will show purple because the thick cell wall retains teh primary stain |
|
|
Steps in Gram staining |
Crystal Violet stain, rinse, Iodine, rinse, Decolorizer, rinse, and counterstain with safarin, rain
|
|
|
what is the decolorizer in the gram stain |
alcohol, removes the crystal violet from the gram negative cell walls |
|
|
purpose of the mordant |
attaches the crystal violet tighlty to the wall of the gram postitive cells |
|
|
purpose of the counterstain |
to stain the cells that have been decolorized |
|
|
poor restults in the gram stain may be from |
too much or too little decolorizer |
|
|
why must young cultures be used during gram staining |
old cultures appear to be gram negative due to ell wall deterioration
|
|
|
gram variable |
when cells of the same organism stain both postive and negative |
|
|
Acid-fast staingin |
used for cells that have mycolic acid in the cell walls and does not stain well, involves heat to melt lipid coat |
|
|
acid fast staining steps |
Simple stain carbofuchsin, rinse, acid-alcohol, rinse, methleyne blue counterstain, rinse
|
|
|
Steps of endospore staining |
malachite green and steam, rinse, safarin, rinse, |
|
|
why must heat be applied in endospore staining
|
so the dye will penetrate into the spores |
|
|
causes endospores |
bacillius antracis and clostriudim tetani |
|
|
purpose of endospore |
protect the organism during periods when the normal vegitatve cell would die |
|
|
endospore staining is a |
differentials staining technique |
|
|
obligate anerobes |
require oxygen |
|
|
facultative anaerobes |
better with oxygen but does not need it |
|
|
obligate anerobes |
harmed by the presence of oxygen |
|
|
aerotolerant anaerobes |
cannot use oxygen but will not be harmed by it |
|
|
microaerophiles |
need a small amount of oxygen but normal levels inhibit it |
|
|
Anerobic broth |
thioglycollate |
|
|
Wrights tube |
uses NaOH and pyrogallol to remove oxygenn |
|
|
anaerobe jar/pouch with gas pack |
uses palladium catalyst to make water from oxygen and hydrogen
|
|
|
oxyrase |
reduces oxygen |
|
|
Standard plate count |
grows bacterial and counts colonies using multiple dilutions of the original sample, ony mesaures live bacteria, requires an incubation period |
|
|
spectrophotometric analyss |
measures the amount of light that travels through sample or how turbid (cloudy) the sample is (dead and alive), immediate results |
|
|
%T = Percent Transmittance |
measures the amount of light passing through the test suspension |
|
|
Absorbance |
measures the amount of light absorbed by the susepension |
|
|
Calibration Curve |
can be used as a standard curve for future reference, and allows a estimation of cell numbers immediately after the reading` |
|
|
CFU |
colony forming unit |
|
|
how would u prepare a series of dilutions to get a final diulution of 10^(-10) |
use 1/10 increments 9 times |
|
|
biomass |
the amount of organic material in a cellular at any given time |
|
|
color of endospore in endospore staning |
green |
|
|
color of vegitative cell in endospore staning |
pink |
|
|
Absorbance formula |
2-log(%T) |

