![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Pic of surface anatomy (legs) |
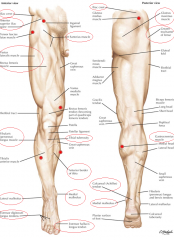
|
|
|
Pic of surface anatomy (pelvic girdle - anterior) |
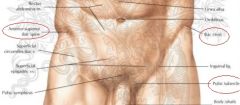
|
|
|
Pic of surface anatomy (pelvic girdle - posterior) |
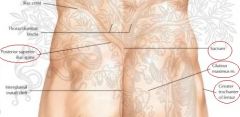
|
|
|
What is the origin, insertion and action of the Psoas Major? |
Origin: T12 and lumbar vertebrae (lateral side) Insertion: lesser trochanter of femur Action: flexes thigh and trunk, lateral flexion of vertebral column |
|
|
What is the origin, insertion and action of the Iliacus? |
Origin: iliac fossa and crest, lateral sacrum Insertion: lesser trochanter of femur and shaft of femur Action: flexes thigh and trunk, lateral flexion of vertebral column (same as psoas major) |
|
|
What is the origin, insertion and action of the Gluteus Maximus? |
Origin: dorsal ilium, sacrum, coccyx Insertion: gluteal tuberosity of the femur Action: extends the thigh, lateral rotation and abduction of thigh |
|
|
What is the origin, insertion and action of the Gluteus Medius? |
Origin: lateral surface of the ilium on anterior gluteal line Insertion: greater trochanter of femur Action: abducts and medially rotates the thigh |
|
|
What is the origin, insertion and action of the Tensor fasciae latae? |
Origin: anterior iliac crest and ASIS Insertion: iliotibial tract Action: flexes and abducts the thigh, medial rotation of thigh |
|
|
What is the origin, insertion and action of the Sartorius? |
Origin: ASIS Insertion: medial aspect of the proximal tibia Action: flexes, abducts and laterally rotates thigh, flexes the leg *indian style muscle |
|
|
What is the origin, insertion and action of the Vastus medialis? |
Origin: linea aspera and intertrochanteric line Insertion: tibial tuberosity via patellar ligament Action: extension of leg |
|
|
What is the origin, insertion and action of the Rectus femoris? |
Origin: ASIS and superior margin of the acetabulum Insertion: tibial tuberosity via the patellar ligament Action: extension of the leg and flexes the thigh |
|
|
What is the origin, insertion and action of the Gracilis? |
Origin: inferior ramus and body of pubis and ischial ramus Insertion: medial surface of the tibia inferior to medial condyle Action:adducts, flexes, medially rotates thigh, flexes leg |
|
|
What is the origin, insertion and action of the Adductor magnus? |
Origin: ischial and pubic rami and ischial tuberosity Insertion: linea aspera and adductor tubercle of the femur Action:adducts, medially rotates, and flexes the thigh extends the leg |
|
|
What is the origin, insertion and action of the Semitendinosus? |
Origin: ischial tuberosity Insertion: medial aspect of the tibia Action:extension of the thigh and flexion of the leg |
|
|
What is the origin, insertion and action of the Biceps femoris? |
Origin: ischial tuberosity and linea aspera of the femur Insertion: head of the fibula and lateral condyle of the tibia Action:extends the thigh and flexes the leg |
|
|
What is the origin, insertion and action of the Tibialis anterior? |
Origin: lateral condyle of the tibia, tibial shaft and interosseous membrane Insertion: base of the 1st metatarsal Action:dorsiflexes and inverts the foot |
|
|
What is the origin, insertion and action of the Gastrocnemius? |
Origin: medial and lateral condyles of the femur Insertion: calcaneous via calcaneal tendon Action: plantar flexion of the foot and weak flexion of the leg |
|
|
What is a First class lever (Class I)? |
- fulcrum in the middle E-F-L *can be either mechanical advantage or disadvantage ex) triceps extending forearms (disadvantage, but speedy) |
|
|
What is a 2nd class lever (Class II)? |
- load in the middle F-L-E ex) wheelbarrow or toes; high strength, low speed, low range of motion |
|
|
What is a 3rd class lever (Class III)? |
- effort in the middle F-E-L ex) biceps *most common in skeletal muscles (always operates as a mechanical disadvantage; used because it is speedy and has high range of motion) |
|
|
What is mechanical advantage? |
load closer to fulcrum than effort - less effort required |
|
|
What is a mechanical disadvantage? |
load farther from the fulcrum than the effort - more effort required |
|
|
Skeletal muscle histology |
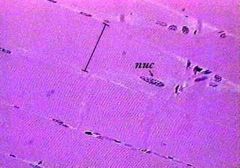
note the multiple nuclei along the periphery, and the striations |
|
|
Smooth muscle histology (100x) |
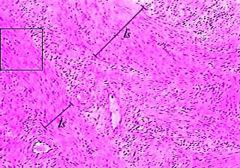
- no striations |
|
|
Smooth muscle histology (400x) |
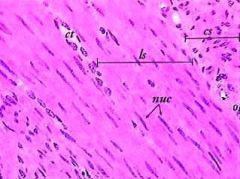
- the exam will show a cross section of the gut, showing a wide tubular smooth muscle later surrounding the gut lumen |
|
|
Smooth muscle (gut) |
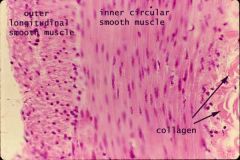
2 layers of smooth muscle: wide band (easy to see; cause constrict) and longitudinal smooth muscle (shorten and dilate) - nuclei of circular smooth muscle |
|
|
Cardiac muscle |
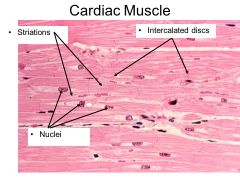
- the disks should appear darker and thicker than the striations |

