![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
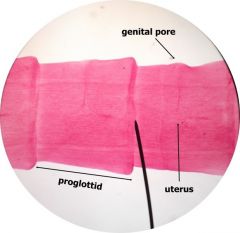
Taenia sp beef or pork worm Proglottids Label: proglottids Genital pore Reproductive organs |
|
|
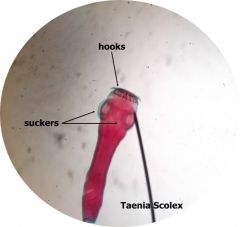
Taenia sp beef or pork worm Scolex label: scolex suckers hooks |
|
|
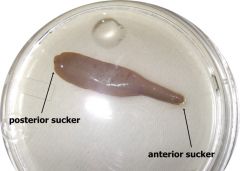
Haemopsis sp leech label: anterior suckerposterior sucker |
|
|
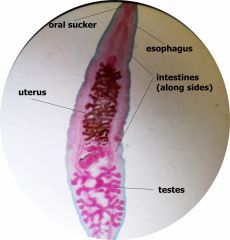
Clonorchis sinesis Liver fluke Label: oral suckers ventral suckers esophagus intestines reproductive organs |
|
|
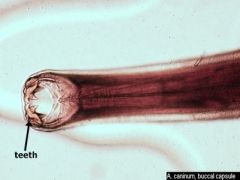
Ancylostoma caninum hookworm Label: teeth, male or female (males have posterior bursa, females don't) |
|
|
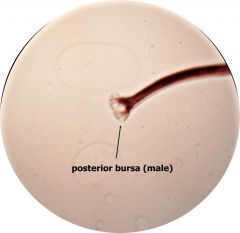
Ancylostoma caninum hookworm Label: maleor female posterior bursa |
|
|
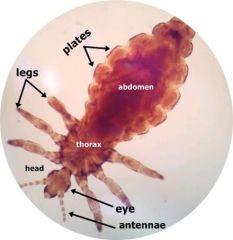
Pediculus humanus corporis or capitus Human head or body louse Label:AntannaeEyesHeadThoraxAbdomenlegs |
|
|
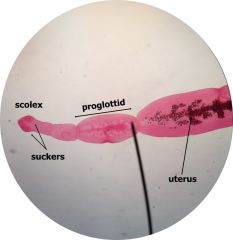
Echinoccous granulosus Dog worm Label:ScolexSuckersproglottids |
|

|
Ascaris lumbricoides Intestinal roundworm Label:Male or female |
|

|
Enterobius vermicularis Pin worm Label: Esophagus, Esophageal bulb |
|
|
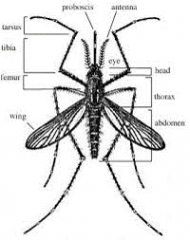
Aedes aegypti Mosquito Label: Antennae, Head, Thorax, Legs Abdomen, proboscis |
|
|
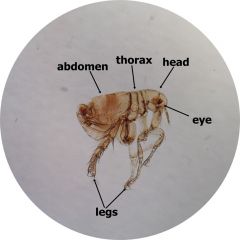
Xenopsylla sp Flea Label: Eyes, Head, Thorax, Abdomen, legs |
|

|
Ixodes species Deer tick Label: head abdomen legs |
|
|
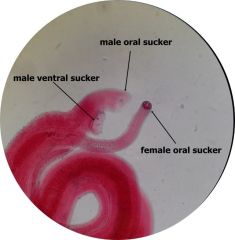
Schistosoma mansoni Blood fluke Label: Male, Female, Oral suckers, Ventral suckers |
|
|
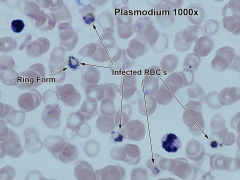
plasmodium Malaria Label: Leukocyte, Parasite, erythrocyte |
|
|
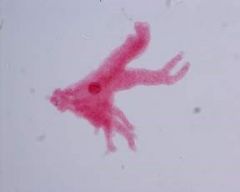
Amoeba proteus Free living microbe Label: Nucleus, pseudopod |
|
|
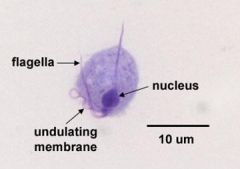
Trichomonas vaginalis urogenital parasite label: nucleus, flagella, undulating membrane |
|

|
Diatoms plankton |
|
|
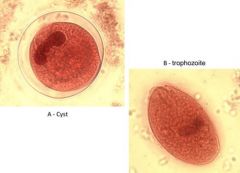
Balantidium coli Intestinal parasite Label: trophozoite, cytostone (mouth of trophozoite), Cilia, Macronucleus, Cyst (clear wall), |
|
|
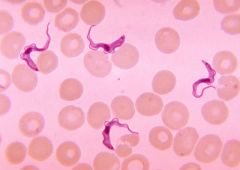
Trypanosoma Extracellular blood parasite Label: Nucleus, Kinetoplast (dots like eyes)Flagella with undulating membrane |
|
|
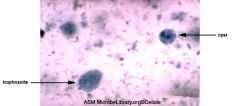
Entamoeba histolytica Amoebic dysentery Label:Cyst (2-4 nucleus), Trophozite, nuclei |
|
|
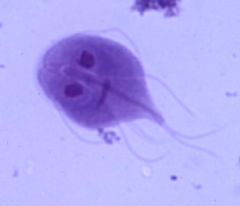
Giardia lamblia Intestinal parasite Label: Axoneme, Flagella, nucleus |
|
|
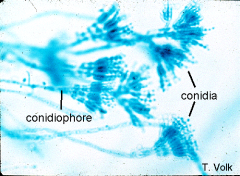
Penicillium Source of penicillin Label: Conidia, Hyphae, conidiphores |
|
|
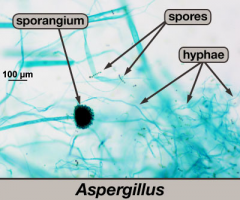
Aspergillus aspergiliosis infection label: conidia, hyphae, conidiphores |
|
|
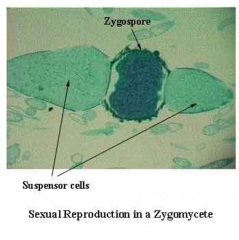
Rhizopus Black bread mold Label:Zygosporangium: zygote & hyphae |
|
|
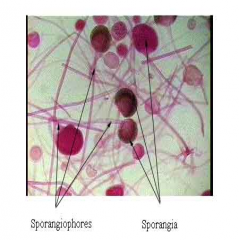
Rhizopus Black bread mold Label:Sporangiospores: hyphae, sporangiospores, sporangium |
|
|
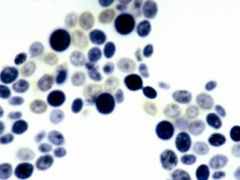
Saccharomyces cerevisiae Yeast Label:Yeast cellBlastospore bud |
|
|
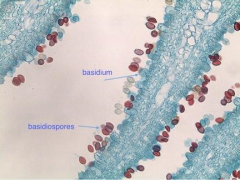
Coprinus mushroom label: basidiospores basidium |
|
|
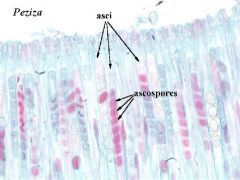
Peziza Cup fungi Label:Ascusascospores |
|
|
Sterilizer: Sanitizer: Disinfectant: Antiseptic: |
Antiseptic: an agent that kills or inhibits growth of microbes but is safe to use on human tissue Disinfectant: an agent used to disinfect inanimate objects or surfaces; it is generally too toxic to use on human tissues Sanitizer: a chemical agent that reduces but may not eliminate, microbial numbers to a safe level Sterilizer: the destruction of all life forms |
|
|
Germicidal UV: Thymine dimers: UVGI: Zone of inhibition: |
Zone of inhibition: circular zones in which no bacterial growth occurs, diameters indicate how susceptible the test organism is UVGI: sterilization method that uses ultraviolet light radiation at a sufficiently short wavelength to break down microorganisms Thymine dimers: A pair of abnormally chemically bonded adjacent thymine bases in DNA, resulting from damage by ultra-violet irradiation. The cellular processes that repair this lesion often make errors that create mutations. Two bases become one base. So when the DNA gets replicated, it causes a frame shift mutation meaning that every protein expressed after the thymine dimer occurs is incorrect in every 3 base pair codon. Germicidal UV: the short range UV that is one of the various ranges that UV can be separated into |
|
|
Compare and contrast antiseptics to disinfectants
|
Both antiseptics and disinfectants eliminate disease-causing organisms. The difference is in how each substance is used. Antiseptics are applied to living skin or tissue to prevent infection. Disinfectants are applied to surfaces, equipment or other inanimate objects |
|
|
Be familiar with the basic purpose, procedure, and results of the filter paper disc
|
Purpose: to determine the effectiveness of antiseptics Procedure: a disc of filter paper is dipped into an antiseptic or disinfectant and then placed on an agar plate that has been inoculated with a bacterial culture. The plate is then incubated to allow bacterial growth. Results: if the chemical is inhibitory, the zone of inhibition will surround the disc. |
|
|
Be familiar with the basic purpose, procedure, and results of Be familiar with the basic purpose, procedure, and results of UV light
|
Purpose: sterilization method that uses UV light radiation at a sufficiently short wavelength to break down microorganism Procedure: make a bacterial lawn, place the plate in the UV light box and remove lid. Cover ½ the plate with an index card to have a control side. Results: the thymine dimers bind to each other when the DNA is replicated, an incorrect base pair is incorporated into the newly synthesized strand therefore destroying the bacterial cell, rendering it harmless, or prohibiting growth and reproduction. |
|
|
Be familiar with the basic purpose, procedure, and results of Be familiar with the basic purpose, procedure, and results of the Kirby-bauer
|
Purpose: To assess the susceptibility of a particular pathogen bacterium to a selected panel of antibiotics uniformlyProcedure: an agar plate is uniformly inoculated with a carefully adjusted lawn of the pure test organism. Paper disks, with antibiotics on them, are placed on the agar surface. Results: zones of inhibition show how susceptible the organism is. A gram negative bacteria (Pseudomonas) should be more resistant to chemicals than the gram positive bacteria (Staph) because the gram negative bacteria have a stronger cell wall because they have that outer membrane made of lipids. |
|
|
What factors are necessary in order for UV light to be germicidal
|
Time of exposure Presence of materials that will block the radiation from reaching cells |
|
|
Explain how germicidal UV leads to thymine dimers
|
At the germicidal UV (short range) wavelength, UV will break the molecular bonds within a microorganis's DNA, producing thymine dimer
|

