![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Pepsin |
a proteolytic enzyme (protein digesting) secreted in an inactive form pepsinogen |
|
|
Pepsinogen |
secreted by gastric glands In gastric lumen, activated by hydrochloric acid and active pepsin is formed |
|
|
Peptic digestion of proteins results in formation of (3) |
Proteoses Peptones Polypeptides |
|
|
proteoses, peptones, polypeptides are eventually digested into amino acids in the small intestine under the influence of (3) |
trypsin chymotrypsin carboxypeptidase |
|
|
what pH level is pepsin most effective |
pH 2.0 |
|
|
many of the carbohydrates we eat are in form of starch known as |
polysaccharides |
|
|
to absorb into the bloodstream the polysaccharides must be broken down to? |
monosaccharides |
|
|
salivary amylase or ptyalin is secreted in the mouth to break the polysaccharides into the ? |
disaccharide maltose |
|
|
salivary amylase is inactivated by the acid conditions in the stomach after 15-30 minutes, this results in |
the digestion of starch (polysaccharide) by salivary amylase is minimal |
|
|
what does pancreatic lipase digest (2) |
triglycerides to monoglycerides free fatty acids |
|
|
the optimum pH for activity of pancreatic lipase depends on the types of fatty acids contained in the triglyceride molecule and ranges from what pH levels? |
pH 7 - 9.0 |
|
|
because the pancreas also secretes large amounts of sodium bicarbonate into the small intestine, the luminal fluid is usually acidic? alkaline?, alowing form optimal lipase activity |
alkaline |
|
|
Define emulsification |
the dispersion (separation) of large aggregates of fat (lipids) into smaller droplets *only way for lipase to be most effective to attack lipids |
|
|
primary function of bile salts |
emulsification |
|
|
purpose of tubes being incubated at 37.0 C |
to mimic human body temperature |
|
|
purpose of Benedicts solution |
test for presence of monosaccharides and disaccharides |
|
|
purpose of Lugol's Iodine |
tests for presence of starch |
|

|
Taste bud |
|

|
Salivary gland Pointer on salivary duct |
|

|
Stomach Know Tunica mucosa, submucosa, muscularis, serosa, rugae, simple columnar epithelium of mucosa, gastric pits down to submucosa: mucous cells, parietal and chief cells |
|

|
Small intestine Know 4 layers, villi, intestinal glands (Crypts of Lieberkuhn) in tunica Mucosa, duodenal glands (Brunners) glands in submucosa |
|
|
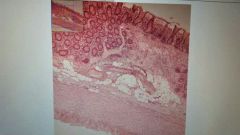
Colon / large intestine Know goblet cells, lymphoid nodules |
|

|
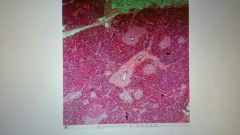
Liver Know central vein, hepatocytes, sinusoids |
|
|
Pancreas Islets of Langerhans, scattered among acini |
|
|
What is ptyalin |
Salivary amylase |

