![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
103 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Where does energy come from |
Your food |
|
|
What is the energy in food measured in |
Jewels or kilojoules |
|
|
How much is 1 kilojoule |
1,000 joules |
|
|
Underweight people |
Often suffer from health problems such as poor immune system lack energy to do things and are often tired Likely to suffer from a lack of vitamins or minerals |
|
|
Overweight people have an increased risk of |
Heart disease Stroke Diabetes Some cancers |
|
|
Where is body mass stored |
As fat under the skin |
|
|
Obese |
If a person becomes extremely overweight |
|
|
Deficiency |
Not have enough of a certain vitamin or mineral |
|
|
What does alcohol contain |
A drug called ethanol |
|
|
What does ethanol affect |
Your nervous system |
|
|
What type of chemical is ethanol |
A depressant because it slows down your body's reaction |
|
|
Depressant |
Slows down your body's reactions |
|
|
How much does the government recommend adult women should drink |
Maximum of two units of alcohol per day |
|
|
How much alcohol does the government recommend a male should drink |
A maximum of three units per day |
|
|
How much is one unit of alcohol |
10 ml of pure alcohol |
|
|
What can drinking large amounts of alcohol over a long time cause |
Stomach ulcers Heart disease Brain and liver damage |
|
|
What happens to the livers of heavy drinkers from breaking down large amounts of ethanol |
They become scarred The lever works less efficiently taking longer to break down alcohol and other chemicals |
|
|
Cirrhosis of the liver |
When the liver becomes scared and works less efficiently taking longer to break down alcohol and other chemicals this can result in death |
|
|
What risks does drinking alcohol have on pregnant women |
Miscarriage Stillbirth Premature birth Low birth weight babies |
|
|
Fetal alcohol syndrome |
affects the way a baby's brain develops it can result in children with learning difficulties facial problems and poor immune systems |
|
|
Producers |
Organisms such as plants and algae that make their own food |
|
|
How does algae differ from plants |
Can be unicellular or multicellular organisms Live underwater while most plants live on land Do not have leaves stems or roots |
|
|
Consumers |
Organisms such as animals that have to eat other organisms to survive |
|
|
What is photosynthesis |
A chemical reaction in which plants take in carbon dioxide and water and changes them into glucose that provides the plant with food. oxygen is a waste product of the reaction plants need to use light from the sun in the chemical reaction |
|
|
Word equation for photosynthesis |
Light Carbon dioxide+water ➡ ️ glucose+oxygen (Reactants). (Products) |
|
|
How does water get into a plant |
What are diffusers into a root hair cell it then transported around the plant in xylem tubes as water evaporates from the leaves more water is grown up through the plant |
|
|
How do gases get into and out of a plant |
On the other side of the leaf there are tiny holes that allow gases to diffuse into the leaf |
|
|
How are leaves adapted for photosynthesis |
They contain careful which absorbs sunlight there are then which allows gases to defuse in and out of the leaf easily They have large surface areas to absorb as much light as possible They have veins that contains island tubes which transport water and phloem tubes which transport glucose |
|
|
Phloem tubes |
Transports glucose around the plant |
|
|
Why is the top of the leaf waxy |
It reduces the amount of water evaporating out of the leaf |
|
|
Stomata |
Holes found at the bottom of the leaf that allows gases to diffuse in and out of the leaf |
|
|
What opens and closes the stomata |
Guard cells |
|
|
Palisades layer |
Contain sounds backed with chloroplast this is where most of the photosynthesis occurs |
|
|
Spongy layer |
They're in a leaf that contains air spaces allowing carbon dioxide to diffuse through the leaf Oxygen diffuses out of the leaf |
|
|
What minerals do plants need |
Nitrates Phosphates Potassium Magnesium |
|
|
Nitrates |
Contains nitrogen and plants needed for healthy growth |
|
|
Phosphates |
Contains phosphorus and plants needed for healthy roots |
|
|
Potassium |
Plants needed for healthy leaves and flowers |
|
|
Magnesium |
Makes chlorophyll in plants |
|
|
Nitrate deficiency in plants |
France will have poor growth and older leaves are yellowed |
|
|
Magnesium deficiency in plants |
John's leaves will turn yellow |
|
|
Phosphorus deficiency in plants |
Plants will have poor root growth and younger leaves look purple |
|
|
Potassium deficiency influence |
Has yellow leaves with dead patches |
|
|
Chemosynthesis |
Reaction performed by bacteria using energy transferred from chemical reactions to produce glucose |
|
|
Product of chemosynthesis |
Glucose |
|
|
Source of energy in chemosynthes |
Chemicals |
|
|
Reactant in chemosynthesis |
Carbon dioxide |
|
|
Bacteria that perform chemosynthesis |
Chemosynthetic |
|
|
Symbiotic or mutualistic relationship |
type of biological relationship between organisms where Each organism benefits the other |
|
|
Word equation for aerobic respiration |
Glucose+oxygen ➡️ carbon dioxide+water (+energy) |
|
|
What carries oxygen through your body |
Red blood cells |
|
|
What does red blood cells contain |
Haemoglobin |
|
|
Haemoglobin |
The substance that makes blood cells red |
|
|
Anaerobic respiration |
Type of respiration that does not use oxygen your body is as nice type of respiration to transfer energy from glucose when there's not enough oxygen for aerobic respiration to take place |
|
|
Food chain |
Diagram that shows watching organisms eat it shows the transfer of energy between organisms |
|
|
Features in a food chain |
1. first organism is a producer and energy transferred from the sun to the organism and is changed into glucose by photosynthesis 2. The second organism is a herbivore 3. Third organism is a carnivore 4.arrows show the transfer of energy stored in food from one organism to the next |
|
|
Food web |
Set of linked food chains |
|
|
How to test for hydrogen in a gas |
Collect the gas by holding an empty test tube above the reaction test tube Light a splint Hold this blend in the test soup but now contains the gas Listen if the splint goes out with a squeaky pop the gas is hydrogen |
|
|
Reactivity series ranging from reactive to unreactive |
Potassium Sodium Lithium Calcium Magnesium Aluminum Zinc Iron Lead Copper Silver Gold |
|
|
Different types of rock |
Sedimentary Igneous Metamorphic |
|
|
Porous |
Material had small gaps that may contain substances in their liquid or gas states water can suck into a porous material |
|
|
Different types of weathering |
Chemical weathering Biological weathering Physical weathering |
|
|
Chemical weathering |
Happens when rain falls on rocks acid in the rain reacts with substances in the rock |
|
|
Biological weathering |
Happens when plants and animals break up rocks |
|
|
Physical weathering |
Happens because of temperature changes |
|
|
Erosion |
The breaking of rock into sediments |
|
|
Transport |
Precious move sediment far from the original rock |
|
|
Deposition |
Sediment stop moving and settle in one place |
|
|
Example of igneous rock |
Basalt |
|
|
How is igneous rock formed |
When liquid rock cools and freezes |
|
|
What does igneous rock consist of |
Crystals |
|
|
What is igneous rock useful for |
Pavements and underneath the railway tracks |
|
|
Magma |
Underground liquid rock |
|
|
What forms from magma |
Granite |
|
|
Lava |
Liquid rock on the surface |
|
|
What rock comes from lava |
Basalt |
|
|
How does metamorphic rocks form |
When heat high pressure will both change existing rock |
|
|
How does marble form |
When limestone below the Earth's surface heats up the limestone does not mouth but it's particles are rearranged |
|
|
How is slate made |
When high pressure underground squashes much then there's squeezes out water and make layers of new crystals |
|
|
Example of sedimentary rock |
Mudstone |
|
|
What are metamorphic rocks made up of |
Crystals They are not porous |
|
|
How does the rock cycle recycle materials |
water pours into a crack. the water freezes and the ice pushes against the side of the crack sediment breaks free a steam flows over the sediments it transports them to a lake sediment settles in the lake bed over many years sediment joins together this makes sedimentary rock layers of rock build up the lower layers heat up particles in these layers move forming crystals metamorphic rock forms the other metamorphic rock magnet pushes upwards the magma heat the rock the rock mountain becomes part of the magma magma moves upwards it forces its way to the surface and erupts a volcano the liquid rock cools and freezes igneous rock forms |
|
|
Up lift |
Happens when huge photos forces inside the Earth push rock upwards |
|
|
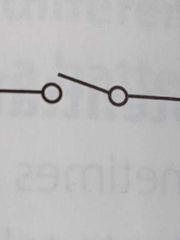
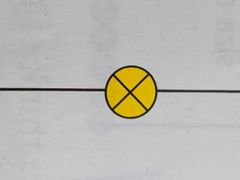
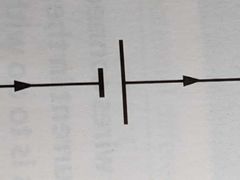
Parts of a circuit |
Switch Battery Bulb |
|
|
Switch |
|
|
Bulb |
|
|
Battery |
|
|
Types of energy stores |
Chemical Thermal Kinetic Gravitational potential Elastic |
|
|
Elastic store |
energy to do with Changing shape stretching or squashing |
|
|
Gravitational potential store |
Energy to do with position in a gravitational field |
|
|
Kinetic store |
Energy to do with moving objects |
|
|
Thermal Store |
Finish you to do with hot objects |
|
|
Chemical store |
Energy to do with food feuls and batteries |
|
|
Moment |
The turning effect of a force |
|
|
What does the moment depend on |
The first being applied and how far it is from the pivot |
|
|
Pivot |
The point about which a lever or seesaw balances |
|
|
How to calculate moment |
Moment =force x perpendicular distance from the pivot |
|
|
Why do you measure force in |
Newton's |
|
|
What measurement do you calculate the moment in |
Newton meters |
|
|
Law of moments |
When an object is in equilibrium the sum of the clockwise moment is equal to the sum of the anti-clockwise moments |
|
|
which side should the clockwise moment be |
On the right |
|
|
Which side is the anti-clockwise moment |
Left |
|
|
Word equation for anaerobic respiration |
Glucose ➡️ lactic acid (+energy) |

