![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
72 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
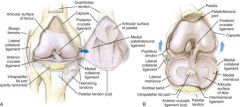
What is the largest sesamoid bone in the body?
|
Patella
|
|
|
At what area of the patella may you see a failed fusion leading to bipartite patella and is sometimes confused for a fracture?
|
Superolateral
|
|
|
What is the difference of the shapes in the medial and lateral tibia?
|
Medial: Oval and Concave (ball on tee with femur)
Lateral: Circular and Convex (barrell of a gun) |
|
|
What structure lies on the lateral side of the proximal tibia and is the site for attachment of the IT band?
|
Gerdy's Tubercle
|
|
|
What attaches at the styloid of the fibula?
|
LCL and Biceps femoris
|
|
|
How far down the tibia does the knee joint capsule extend?
|
15mm distal to the subchondral surface of the tibial plateau
|
|
|
Injury to what location of the menisci can be repaired?
|
Peripheral thirds of the menisci are vascular and can be repaired; the inner two thirds are nourished by synovial fluid
|
|
Which meniscus tears more often and why?
|
The medial meniscus tears three times more often because the lateral is more mobile
|
|
|
What nerve is @ risk with medial meniscal repairs?
|
Saphenous
|
|
|
What is the most common meniscal tear with acute acl injury?
|
Lateral meniscus
|
|
|
What nerve is @ risk with lateral meniscal repairs?
|
Peroneal
|
|
|
Which bundles of the ACL and PCL are tight in flexion?
|
Both are the anterior bundles.
ACL: Anteromedial PCL: Anterolateral (FALT: Flexion AnteroLateral Tight) Also, PAL: Pcl AnteroLateral |
|
|
The PCL lies between what 2 ligaments?
|
The ligament of Humphreys and the ligament of Wrisberg.
Ligament of humphreys is the anterior meniscofemoral ligament and Wrisberg is the posterior meniscofemoral ligament |
|
|
What structures make up the posterolateral corner?
|
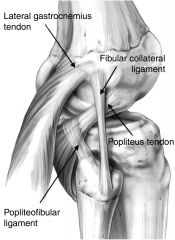
There are 6 structures:
1. LCL* 2. Popliteus tendon* 3. Popliteofibular ligament* 4. Arcuate ligament 5. Posterolateral capsule 6. Lateral head of the gastroc |
|
|
Isolated PCL injuries cause the greatest instability with what motion?
|
Knee flexion
|
|
|
Combined injuries of the PCL and posterolateral corner result in increasing instability what what degrees of flexion?
|
30-90 degrees
|
|
|
Isolated posterolateral corner injuries result in increasing instability most notable at what degree of flexion?
What motion makes it more stable? |
30 degrees.
Stability increases with increasing flexion to 90 degrees |
|
|
What 2 hamstring tendons are used with ACL autograft?
|
Gracilis and Semitendinosus
|
|
|
What is the origin, insertion, and function of the following ligament of the knee?
Retinacular |
Origin: Vastus medialis and vastus lateralis
Insertion: Tibial condyles Function: Forms anterior capsule |
|
|
What is the origin, insertion, and function of the following ligament of the knee?
Posterior Fibers |
Origin: Femoral condyles
Insertion: Tibial condyles Function: Forms posterior capsule |
|
|
What is the origin, insertion, and function of the following ligament of the knee?
Oblique popliteal |
Origin: Semimembranosus tendon
Insertion: Lateral femoral condyle/posterior capsule Function: Strengthens capsule |
|
|
What is the origin, insertion, and function of the following ligament of the knee?
Deep MCL |
Origin: Medial epicondyle
Insertion: Medial meniscus Function: Holds medial meniscus to femur |
|
|
What is the origin, insertion, and function of the following ligament of the knee?
Superficial MCL |
Origin: Medial epicondyle
Insertion: Medial condyle of tibia Function: Resists valgus force -The more important of the 2 MCL bundles |
|
|
What is the origin, insertion, and function of the following ligament of the knee?
Arcuate |
Origin: Lateral femoral condyle, over popliteus
Insertion: Posterior tibia/fibular head Function: Posterior support |
|
|
What is the origin, insertion, and function of the following ligament of the knee?
Lateral Collateral |
Origin: Lateral epicondyle
Insertion: Lateral fibular head Function: Resists varus force |
|
|
What is the origin, insertion, and function of the following ligament of the knee?
Anterior Cruciate |
Origin: Anterior intercondylar tibia
Insertion: Posteromedial lateral femoral condyle Function: Limits hyperextension/sliding |
|
|
What is the origin, insertion, and function of the following ligament of the knee?
Posterior Cruciate |
Origin: Posterior sulcus of tibia
Insertion: Anteromedial femoral condyle Function: Prevents hyperflexion/sliding |
|
|
What is the origin, insertion, and function of the following ligament of the knee?
Coronary |
Origin: Meniscus
Insertion: Tibial periphery Function: Meniscal attachment |
|
|
What is the origin, insertion, and function of the following ligament of the knee?
Wrisberg |
Origin: Posterolateral meniscus
Insertion: Medial femoral condyle (behind posterior cruciate ligament) Function: Stabilizes lateral meniscus |
|
|
What is the origin, insertion, and function of the following ligament of the knee?
Humphrey |
Origin: Posterolateral meniscus
Insertion: Medial femoral condyle (in front) Function: Stabilizes lateral meniscus |
|
|
What is the origin, insertion, and function of the following ligament of the knee?
Transverse meniscal |
Origin: Anterolateral meniscus
Insertion: Anteromedial meniscus Function: Stabilizes menisci |
|
|
What are the 2 compartments in the knee that develop OA with an isolated-PCL deficient knee and why do these areas develop OA?
|
Patellofemoral: Because the knee becomes quad-dependent for stability
Medial: Because this compartment becomes functionally meniscectomized because the medial meniscus is not nearly as mobile as the lateral meniscus |
|
|
What are the muscles of the anterior compartment of the leg?
|
Tibialis anterior
Extensor Hallucis Longus Extensor Digitorum Longus Peroneus Tertius |
|
|
What are the muscles of the lateral compartment of the leg?
|
Peroneus Longus
Peroneus Brevis |
|
|
What are the muscles of the superficial posterior compartment of the leg?
|
Gastrocnemius
Soleus Plantaris |
|
|
What are the muscles of the deep posterior compartment of the leg?
|
Popliteus
Flexor Hallucis Longus Flexor Digitorum Longus Tibialis Posterior |
|
|
What is the origin, insertion, action, innervation, and compartment for the following muscle of the leg?
Tibialis Anterior |

Origin: Lateral tibia
Insertion: Medial cuneiform, first metatarsal Action: Dorsiflexing, inverting foot Innervation: Deep peroneal (L4) nerve Compartment: Anterior |
|
|
What is the origin, insertion, action, innervation, and compartment for the following muscle of the leg?
Extensor Hallucis Longus |
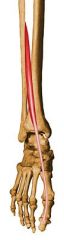
Origin: Mid-fibula
Insertion: Great toe, distal phalanx Action: Dorsiflexing ankle, extending toe Innervation: Deep peroneal (L5) nerve Compartment: Anterior |
|
|
What is the origin, insertion, action, innervation, and compartment for the following muscle of the leg?
Extensor digitorum longus |

Origin: Lateral condyle of fibula, upper 2/3 - 3/4 of medial fibular shaft surface, upper part of interosseous membrane, fascia cruris, and anterior intermuscular septum
Insertion: Splits into 4 tendon slips after inferior extensor retinaculum, each of which insert on dorsum of middle and distal phalanges as part of extensor expansion complex Action: Extend toes 2 - 5 and dorsiflexes ankle Innervation: Deep peroneal nerve (L4, L5, S1) Arterial Supply: Anterior tibial artery Compartment: Anterior |
|
|
What is the origin, insertion, action, innervation, and compartment for the following muscle of the leg?
Peroneus Tertius |
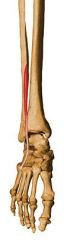
Origin: Fibula and extensor digitorum longus tendon
Insertion: Dorsal surface of base of fifth metatarsal Action: Everting, dorsiflexing, abducting foot Innervation: Deep peroneal (S1) nerve Compartment: Anterior |
|
|
What is the origin, insertion, action, innervation, and compartment for the following muscle of the leg?
Peroneus Longus |

Origin: Head of fibula, upper 1/2 - 2/3 of lateral fibular shaft surface; also anterior and posterior intermuscular septa of leg
Insertion: Plantar posterolateral aspect of medial cuneiform and lateral side of 1st metatarsal base Action: Everts foot and plantar flexes ankle; also helps to support the transverse arch of the foot Innervation: Superficial peroneal nerve (L5, S1, S2); may also receive additional innervation from common or deep peroneal nerves (L5, S1, S2) Arterial Supply: Anterior tibial and peroneal arteries Compartment: Lateral |
|
|
What is the origin, insertion, action, innervation, and compartment for the following muscle of the leg?
Peroneus Brevis |

Origin: Inferior 2/3 of lateral fibular surface; also anterior and posterior intermuscular septa of leg
Insertion: Lateral surface of styloid process of 5th metatarsal base Action: Everts foot and plantar flexes ankle Innervation: Superficial peroneal nerve (L5, S1, S2) (L5, S1, S2) Arterial Supply: Muscular branches of peroneal artery Compartment: Lateral |
|
|
What is the origin, insertion, action, innervation, and compartment for the following muscle of the leg?
Gastrocnemius |

Origin: Posterior medial and lateral femoral condyles
Insertion: The two heads unite into a broad aponeurosis which eventually unites with the deep tendon of the soleus to form the Achilles tendon, inserting on the middle 1/3 of the posterior calcaneal surface Action: Plantar flexing foot Innervation: Tibial (S1) nerve Compartment: Superficial Posterior |
|
|
What is the origin, insertion, action, innervation, and compartment for the following muscle of the leg?
Soleus |

Origin: Fibula/tibia
Insertion: Eventually unites with the gastrocnemius aponeurosis to form the Achilles tendon, inserting on the middle 1/3 of the posterior calcaneal surface Action: Plantar flexing foot Innervation: Tibial (S1) nerve Compartment: Superficial Posterior |
|
|
What is the origin, insertion, action, innervation, and compartment for the following muscle of the leg?
Plantaris |

Origin: Inferior aspect of lateral supracondylar line of distal femur
Insertion: Middle 1/3 of the posterior calcaneal surface, just medial to Achilles tendon Action: Plantar flexor of ankle; also flexes knee Innervation: Tibial nerve (L5, S1, S2) (L5, S1, S2) Arterial Supply: Sural arteries Compartment: Superficial Posterior |
|
|
What is the origin, insertion, action, innervation, and compartment for the following muscle of the leg?
Popliteus |
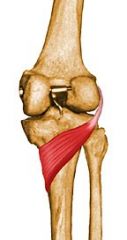
Origin: Anterior part of the popliteal groove on lateral surface of lateral femoral condyle
Insertion: Tendon runs posterior to the LCL and inserts at posterior surface of tibia in a fan-like fashion, just superior to the popliteal line Action: Rotates knee medially and flexes the leg on the thigh Innervation: Tibial nerve (L4, L5, S1) Arterial Supply: Medial inferior genicular branch of popliteal artery and muscular branch of posterior tibial artery Compartment: Deep Posterior |
|
|
What is the origin, insertion, action, innervation, and compartment for the following muscle of the leg?
Flexor hallucis longus |
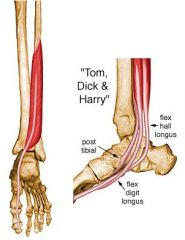
ORIGIN
Inferior 2/3 of posterior surface of fibula, lower part of interosseous membrane. INSERTION Plantar surface of base of distal phalanx of great toe. ACTION Flexes great toe, helps to supinate ankle, and is a very weak plantar flexor of ankle INNERVATION Tibial nerve (S2, S3) (S2, S3) ARTERIAL SUPPLY Muscular branch of peroneal and posterior tibial artery Compartment: Deep Posterior |
|
|
What is the origin, insertion, action, innervation, and compartment for the following muscle of the leg?
Flexor Digitorum Longus |
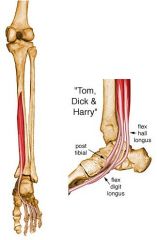
Origin: Posterior surface of tibia distal to popliteal line
Insertion: Splits into four slips after passing through medial intermuscular septum of plantar surface of foot; these slips then insert on plantar surface of bases of 2nd - 5th distal phalanges Action: Flexes toes 2 - 5; also helps in plantar flexion of ankle Innervation: Tibial nerve (S2, S3) (S2, S3) Arterial Supply: Muscular branch of posterior tibial artery Compartment: Deep Posterior |
|
|
What is the origin, insertion, action, innervation, and compartment for the following muscle of the leg?
Tibialis Posterior |

Origin: Posterior aspect of interosseous membrane, superior 2/3 of medial posterior surface of fibula, superior aspect of posterior surface of tibia, and from intermuscular septum between muscles of posterior compartment and deep transverse septum
Insertion: Splits into two slips after passing inferior to plantar calcaneonavicular ligament; superficial slip inserts on the tuberosity of the navicular bone and sometimes medial cuneiform; deeper slip divides again into slips inserting on plantar surfaces of metatarsals 2 - 4 and second cuneiform Action: Principal invertor of foot; also adducts foot, plantar flexes ankle, and helps to supinate the foot Innervation: Tibial nerve (L4, L5) Arterial Supply: Muscular branches of sural, peroneal and posterior tibial arteries Compartment: Deep Posterior |
|
|
What nerve supplies the anterior compartment of the leg?
|
Deep Peroneal
|
|
|
What nerve supplies the lateral compartment of the leg?
|
Superficial peroneal
|
|
|
What nerve supplies the posterior compartment of the leg?
|
Tibial
|
|
|
What muscles border the popliteal fossa, and which muscle makes up the floor?
|
The popliteal fossa is bordered by the gastrocnemius muscles, the semimembranosus, and the biceps; the plantaris muscle makes up the floor of the fossa.
|
|
|
What neurovascular structures are released when the anterior compartment of the leg is released?
|
Deep Peroneal Nerve
Anterior Tibial Artery |
|
|
What neurovascular structures are released when the lateral compartment of the leg is released?
|
Superficial peroneal nerve
|
|
|
What neurovascular structures are released when the superficial posterior compartment of the leg is released?
|
Sural nerve
|
|
|
What neurovascular structures are released when the deep posterior compartment of the leg is released?
|
Posterior Tibial Artery and Vein
Tibial Nerve Peroneal Artery and Vein |
|
|
The course of the Tibial Nerve:
Continues in the thigh _________ (deep/superficial) to the long head of the biceps femoris and enters the popliteal fossa. Crosses _________ (over/under) the popliteus muscle and splits the two heads of the _______________, passing deep to the ___________ on its course to the posterior aspect of the medial malleolus Terminates as the ____________________ Muscular branches supply the posterior leg along its course (superficial and deep posterior compartment |
The course of the Tibial Nerve:
Continues in the thigh DEEP to the long head of the biceps femoris and enters the popliteal fossa. Crosses OVER the popliteus muscle and splits the two heads of the GASTROCNEMIUS, passing deep to the SOLEUS on its course to the posterior aspect of the medial malleolus Terminates as the MEDIAL AND LATERAL PLANTAR NERVES Muscular branches supply the posterior leg along its course (superficial and deep posterior compartment |
|
|
Course of the common peroneal nerve:
The _______ (smaller/larger) terminal division of the sciatic nerve, this nerve runs laterally along the popliteal fossa in the interval between ________________. It winds around the neck of the fibula and runs deep to the ___________, where it divides into the superficial and deep branches. It can be injured with traction and by lateral meniscal repair. |
The SMALLER terminal division of the sciatic nerve, this nerve runs laterally along the popliteal fossa in the interval between THE MEDIAL BORDER OF THE BICEPS AND THE LATERAL HEAD OF THE GASTROC.
It winds around the neck of the fibula and runs deep to the PERONEUS LONGUS, where it divides into the superficial and deep branches. It can be injured with traction and by lateral meniscal repair. |
|
|
Course of the superficial peroneal nerve:
Runs along the border between the ______________ and ____________ compartments in the leg, supplying muscular branches to the ____________ and ____________ (lateral compartment) Terminates in two cutaneous branches (medial dorsal and intermediate dorsal cutaneous nerves) supplying the dorsal foot Supplies dorsal medial sensation to the great toe |
Runs along the border between the LATERAL and ANTERIOR compartments in the leg, supplying muscular branches to the PERONEUS LONGUS and BREVIS (lateral compartment)
Terminates in two cutaneous branches (medial dorsal and intermediate dorsal cutaneous nerves) supplying the dorsal foot Supplies dorsal medial sensation to the great toe |
|
|
Course of the Deep peroneal nerve
Sometimes known as the anterior tibial nerve, this nerve runs along the anterior surface of the _______________, supplying the musculature of the anterior compartment: __________, __________, ________, ________ |
Sometimes known as the anterior tibial nerve, this nerve runs along the anterior surface of the INTEROSSEOUS MEMBRANE, supplying the musculature of the anterior compartment: TIBIALIS ANTERIOR , EHL ,EXTENSOR DIGITORUM LONGUS, and PERONEUS TERTIUS
Sensation to the first web space is provided by the deep peroneal nerve. |
|
|
What nerve of the leg supplies sensation to the first webspace of the foot?
|
Deep peroneal nerve
|
|
|
The saphenous nerve is a continuation of what nerve? Where does it supply innervation?
|
The saphenous nerve (L3 to L4) is the continuation of the femoral nerve of the thigh. It supplies sensation to the medial aspect of the leg and foot
|
|
|
What 2 nerves unite to form the sural nerve?
|
The medial sural cutaneous (branch from tibial nerve) and lateral sural cutaneous (branch from common peroneal)
|
|
|
The popliteal artery enters the popliteal fossa between the ____________ and ____________ and descends underneath the _____________, terminating between the ____________________________ and dividing into the anterior and posterior tibial arteries.
|
The popliteal artery enters the popliteal fossa between the BICEPS and SEMIMEMBRANOSUS and descends underneath the TIBIAL NERVE, terminating between the MEDIAL AND LATERAL HEADS OF THE GASTROC and dividing into the anterior and posterior tibial arteries.
|
|
|
What is the blood supply to the menisci?
|
Medial and lateral geniculate arteries
|
|
|
What is the blood supply to the cruciates?
|
Middle genicular artery
|
|
|
What artery passes between the popliteal tendon and LCL in the posterolateral corner of the knee?
|
Inferior geniculate artery
|
|
|
What is the first branch of the popliteal artery?
|
Anterior Tibial
|
|
|
The Anterior Tibial Artery:
Passes between the two heads of the __________ and the ________________ to lie on the anterior surface of that membrane between the _______________ |
Passes between the two heads of the TIBIALIS POSTERIOR and the INTEROSSEOUS MEMBRANE to lie on the anterior surface of that membrane between the TIB ANT and EHL
|
|
|
What does the anterior tibial artery terminate as?
|
The dorsalis pedis artery
|
|
|
The posterior tibial artery continues in the _____________ compartment of the leg, coursing obliquely to pass behind the medial malleolus
Terminates by dividing into the ___________________________ Main branch: _______________ given off ________ cm distal to the popliteal fossa and continues in the ____________________ compartment lateral to its parent artery between the _____________________________ □ Terminates in the calcaneal branches |
The posterior tibial artery continues in the deep posterior compartment of the leg, coursing obliquely to pass behind the medial malleolus
Terminates by dividing into the MEDIAL AND LATERAL PLANTAR ARTERIES Main branch: THE PERONEAL ARTERY given off 2.5 cm distal to the popliteal fossa and continues in the DEEP POSTERIOR compartment lateral to its parent artery between the TIBIALIS POSTERIOR AND FHL Terminates in the calcaneal branches |

