![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
80 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the following boundaries of the anterior cervical triangle?
Superior: Anterior: Posterior: |
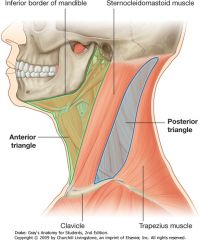
Superior: mandible
Anterior: midline Posterior: SCM |
|
|
What are the subordinate triangles of the anterior cervical triangle?
|
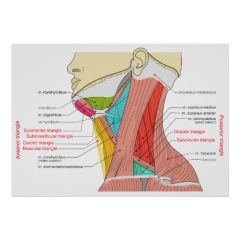
Submandibular (digastric) triangle
Submental (suprahyoid) triangle Carotid traingle Muscular triangle |
|
|
Anterior Cervical Triangle
What are the following borders of the submandibular triangle? Superior: Anterior: Posterior: |
Superior: mandible
Anterior: anterior belly of digastric Posterior: posterior belly of digastric |
|
|
Anterior Cervical Triangle
What are the following borders of the submental triangle? Superior: Inferior: Lateral: |
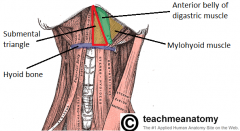
Superior: symphysis of mandible
Inferior: hyoid bone Lateral: anterior belly of digastric |
|
|
Anterior Cervical Triangle
What are the following borders of the carotid triangle? Superior: Anterior: Posterior: |
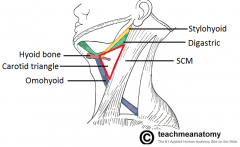
Superior: posterior belly of digastric
Anterior: superior belly of omohyoid Posterior: SCM |
|
|
Anterior Cervical Triangle
What are the following borders of the muscular triangle? Superior: Anterior: Posterior: |
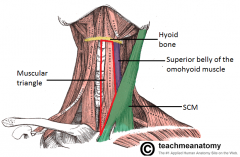
Superior: superior belly of omohyoid & hyoid bone
Anterior: midline Posterior: SCM |
|
|
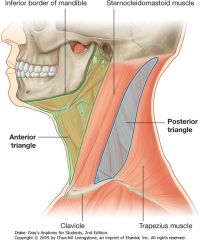
What are the following boundaries of the posterior cervical triangle?
Anterior: Posterior: Inferior: |
Anterior: SCM
Posterior: trapezius Inferior: calvicle |
|
|
What are the subordinate triangles of the posterior cervical triangle?
|
Occipital triangle
Subclavian triangle |
|
|
Posterior Cervical Triangle
What are the following borders of the occipital triangle? Anterior: Posterior: Inferior: |
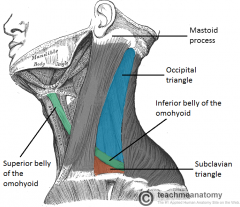
Anterior: SCM
Posterior: trapezius Inferior: inferior belly of omohyoid m |
|
|
Posterior Cervical Triangle
What are the following borders of the subclavian triangle? Superior: Inferior: Anterior: |
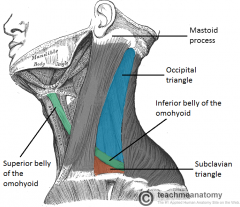
Superior: inferior belly of omohyoid
Inferior: clavicle Anterior: SCM |
|
|
What are the four main fascial layers of the neck?
|
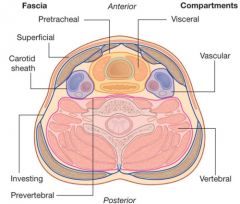
Superficial cervical fascia
Superficial layer of deep cervical fascia (investing fascia) Middle layer of deep cervical fascia (visceral fascia) Deep layer of deep cervical fascia (prevertebral fascia) |
|
|
What does the superficial cervical fascia envelop?
|
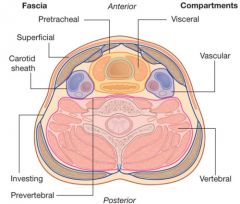
Platysma & muscles of fascial expressions
|
|
|
What are the following boundaries of the superficial cervical fascia?
Superior: Inferior: |
Superior: zygomatic process
Inferior: clavicle |
|
|
What are the roles of the superficial cervical fascia?
|
1) Main plane of resistance to deep neck spread of cellulitis
2) Allows mobility of skin over deep neck structures 3) Easily separated when raising neck flaps from deep cervical fascia in subplatysmal potential space (adipose, sensory nerves, blood vessels) |
|
|
What does the superficial layer of deep cervical fascia envelop?
|
AKA Investing layer
- Trapezius, SCM, strap muscles - Submandibular and parotid glands *** - Muscles of mastication: masseter, pterygoids, and temporalis |
|
|
What are the following boundaries of the superficial layer of deep cervical fascia?
Superior: Inferior: Anterior: Posterior: |
AKA Investing layer
Superior: Mandible and zygoma Inferior: clavicle, acromion, spine of scapula Anterior: hyoid bone Posterior: mastoid process, superior nuchal line of cervical vertebrae |
|
|
Which fascial layer forms the stylomandibular ligament posteriorly?
|
superficial layer of deep cervical fascia
|
|
|
What does the middle layer of deep cervical fascia envelop?
|
AKA visceral fascia
Muscular division: strap muscles (sternohyoid, sternothyroid, thyrohyoid, and omohyoid) Visceral division: pharynx, larynx, trachea, esophagus, thyroid, parathyroid, buccinators, constrictor muscles of pharynx |
|
|
What are the following boundaries of the middle layer of the deep cervical fascia?
Superior: Inferior: |
Superior: base of skull
Inferior: mediastinum |
|
|
Which cervical fascial layer forms the buccopharyngeal fascia?
|
The middle layer of deep cervical fascia
|
|
|
Which cervical fascial layer forms the pretracheal fascia?
|
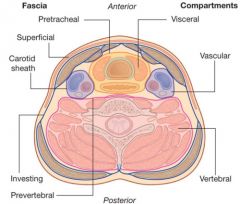
The middle layer of deep cervical fascia
|
|
|
What does the deep layer of deep cervical fascia envelop?
|
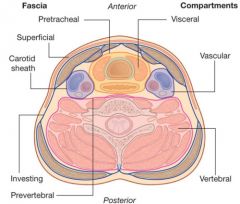
AKA Prevertebral fascia
paraspinous muscles and cervical vertebrae |
|
|
What are the following boundaries of the middle layer of the deep cervical fascia?
Superior: Inferior: |
Superior: base of skull
Inferior: chest |
|
|
What are the two layers of the deep layer of deep cervical fascia?
|
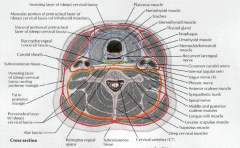
Prevertebral layer - attaches to the transverese process laterally and covers the vertebral bodies, paraspinous, and scalene muscles. It extends from the base of skull to the coccyx.
Alar layer - lies between the prevertebral layer and the visceral layer of the middle fascia and covers the cervical sympathetic trunk. Extends from the base of skull to the mediastium. |
|
|
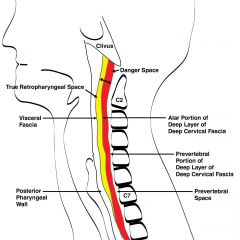
What are the anterior and posterior borders of the cervical danger space?
|
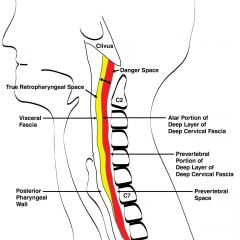
Anterior: alar fascia/layer
Posterior: prevertebral layer |
|
|
Name the layers and spaces going posteriorly, starting with the buccopharyngea/fascial layer
|
Buccopharyngea/fascial layer (of middle layer of deep cervical fascia) --> retropharyngeal space --> alar fascia (of deep layer of deep cervical fascia) --> danger space --> preverterbal layer (of deep layer of deep cervical fascia)
|
|
|
The prevertebral layer extends how far inferiorly?
|
from the base of the skull to the coccyx
|
|
|
The alar layer/fascia extends how far inferiorly?
|
extends from the base of skull to the mediastinum
|
|
|
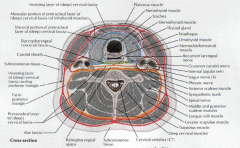
What are the following boundaries of carotid sheath?
Superior: Inferior: |
Superior: base of skull
Inferior: thorax |
|
|
Which layers of the cervical fascia make up the carotid sheath?
|
ALL THREE layers of the deep cervical fascia (superficial, middle and deep)
|
|
|
What is "The Lincoln Highway of the Neck?"
|
The carotid sheath, due to potential avenue for rapid spread of infection
|
|
|
What are the following borders of the parapharyngeal space?
Superior: Inferior: Anterior: Posterior: Medial: Lateral: |
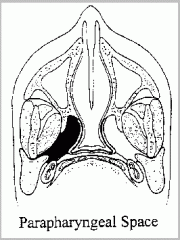
Superior: base of skull (middle cranial fossa)
Inferior: hyoid bone Anterior: pterygomandibular raphe Posterior: prevertebral fascia Medial: pharyngobasilar fascia (superiorly), superior constrictor Lateral: deep lobe of parotid gland, mandible, and medial pterygoid |
|
|
What are the two main compartments of the parapharyngeal space?
|
Prestyloid and Poststyloid compartments separated by the styloid process
|
|
|
What are the contents of the prestyloid and poststyloid compartments of the parapharyngeal space?
|
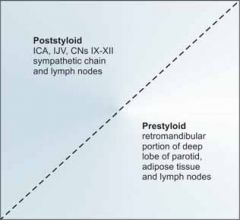
Prestyloid compartment
- Fat - Lymph nodes - Internal maxillary artery - Inferior alveolar, lingual, and auriculotemporal nerves - Medial and lateral pterygoid muscles - Deep lobe parotid tissue Poststyloid compartment - Carotid artery - IJ vein - Sympathetic chain - Cranial nerves 9, 10, 11, 12 |
|
|
What are the following boundaries of the pterygopalatine (pterygomaxillary) fossa?
Superior: Anterior: Posterior: Medial: Lateral: |
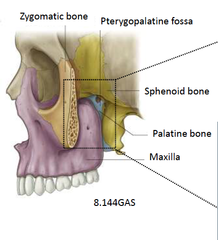
Superior: sphenoid body, palatine bone (orbital process)
Anterior: posterior wall of maxillary antrum Posterior: pterygoid process, greater wing of sphenoid Medial: palatine bone, nasal mucoperiosteum Lateral: temporalis muscle via pterygomaxillary fissure |
|
|
What are contents of the pterygopalatine (pterygomaxillary) fossa?
|
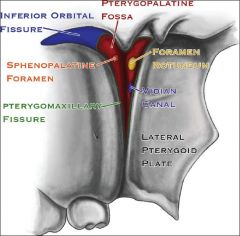
Maxillary nerve (V2)
Sphenopalatine ganglion Internal maxillary artery |
|
|
What are the following boundaries of the masticator space?
Lateral: Medial: |
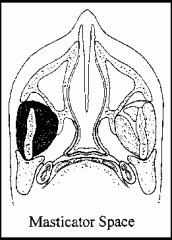
Lateral: fascia over masseter muscle (superficial layer of deep cervical fascia)
Medial: fascia medial to pterygoid muscles (superficial layer of deep cervical fascia) |
|
|
What are the contents of the masticator space?
|
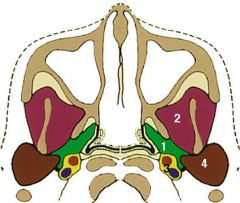
(Number 2 in the picture; parotid space is number 4, and parapharyngeal space is 1)
Masseter muscle Lateral and medial pterygoid muscles Ramus and posterior body of mandible Temporalis muscle tendon Inferior alveolar nerve (V3) Internal maxillary artery |
|
|
What are the following boundaries of the temporal fossa?
Superior: Inferior: Lateral: Medial: |
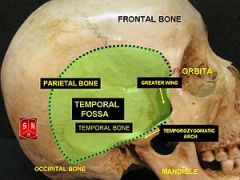
Superior: temporal lines on lateral surface of skull (attachment of temporalis muscle)
Inferior: zygomatic arch Lateral: temporalis fascia Medial: skull including pterion |
|
|
What are the following boundaries of the infratemporal fossa?
Medial: Lateral: Anterior: Superior: |
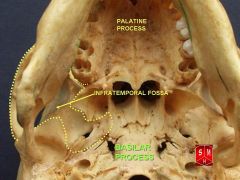
Medial: lateral pterygoid plate with tensor and levator palatini muscles, superior constrictor
Lateral: mandibular ramus, coronoid process Anterior: infratemporal surface of maxilla Superior: infratemporal crest bone (sphenoid and temporal bones) medially, space deep to zygomatic arch laterally |
|
|
What are the contents of the infratemporal fossa?
|
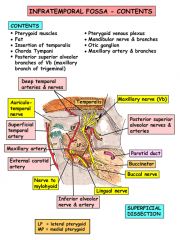
Medial and lateral pterygoid muscles
Insertion of temporalis on coronoid process Internal maxillary artery and branches Pterygoid venous plexus V3 with otic ganglion and chorda tympani Posterior superior branch of V3 |
|
|
What are the following boundaries of the parotid space?
Medial: Lateral: |
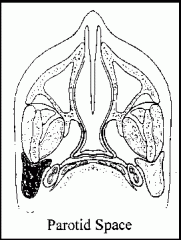
Medial: parapharyngeal space
Lateral: parotid fascia (superficial layer of deep cervical fascia) |
|
|
What are the contents of the parotid space?
|
Parotid gland
Facial nerve External carotid artery and branches Posterior facial vein |
|
|
What are the following boundaries of the peritonsillar space?
Medial: Lateral: |
Medial: palatine tonsil
Lateral: superior constrictor muscle |
|
|
What are the contents of the pertonsillar space?
|
Loose connective tissue
Tonsillar branches of lingual, facial and ascending pharyngeal vessels |
|
|
What are the following boundaries of the submandibular (submaxillary) space?
Superior: Inferior: Anterior: Posterior: Medial: Lateral: |
Superior: floor of mouth mucosa
Inferior: digastric muscle Anterior: mylohyoid and anterior belly of digastric Posterior: posterior belly of digastric and stylomandibular ligament Medial: hyoglossus and mylohyoid Lateral: skin, platysma, and mandible |
|
|
Which muscle divides the submandibular space into two compartments? What are these two compartments?
|
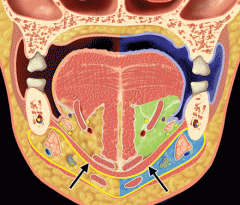
The mylohyoid muscle (arrows) acts like a sling to divides the submandibular space into a sublingual (green; infections anterior to 2nd molar) and submaxillary (light blue; infections of 2nd and 3rd molars) compartments
|
|
|
What are the contents of the sublingual space/compartment?
|
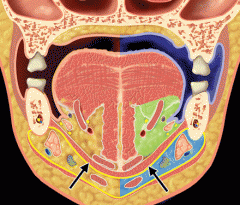
Sublingual space/compartment (Supramylohyoid)
- sublingual gland - Wharton's duct - Lingual nerve *** |
|
|
What are the contents of the submaxillary space/compartment?
|
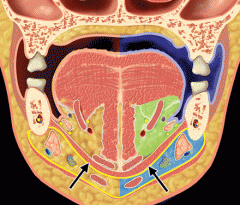
Submaxillary (inframylohyoid) space/compartment:
- Submandibular gland - Lymph nodes - Hypoglossal nerve *** - Facial vein & artery - Marginal branch of facial nerve |
|
|
What are the following boundaries of the carotid space?
Anterior: Posterior: Medial: Lateral: |
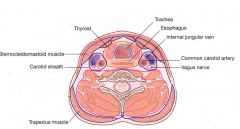
Anterior: SCM
Posterior: prevertebral space (deep layer of DCF) Medial: visceral space (middle layer of DCF) Lateral: SCM |
|
|
What are the contents of the carotid sheath?
|
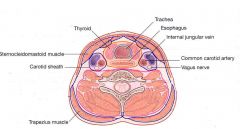
Common carotid artery
Internal jugular vein (IJV) Vagus nerve Ansa cervicalis |
|
|
What are the following boundaries of the visceral space?
Superior: Inferior: Anterior: Posterior: Lateral: |
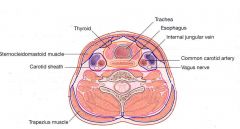
Visceral space (middle layer of DCF)
Superior: hyoid bone Inferior: mediastinum (T4 level/arch of aorta) Anterior: superficial layer of DCF Posterior: retropharyngeal space; prevertebral fascia Lateral: parapharyngeal space; carotid fascia |
|
|
What are the contents of the visceral space?
|
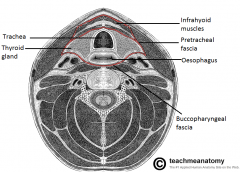
Pharynx
Larynx Esophagus Trachea Thyroid gland |
|
|
What are the following boundaries of the retropharyngeal (retrovisceral) space?
Superior: Inferior: Anterior: Posterior: Medial: Lateral: |
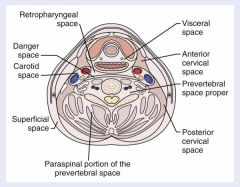
Superior: base of skull
Inferior: superior mediastinum; tracheal bifurcation (T4); middle layer of DCF fuses with alar layer of deep layer of DCF Anterior: pharynx and esophagus (middle layer of DCF - buccopharyngeal fascia) Posterior: alar fascia Medial: midline raphe of superior constrictor muscle (results in unilateral abscess in this space) Lateral: carotid sheath |
|
|
What are the contents of the retropharyngeal space?
|
retropharyngeal lymph nodes (pediatric infections of sinuses or nasopharynx)
connective tissue |
|
|
What are the following boundaries of the danger space?
Superior: Inferior: Anterior: Posterior: |
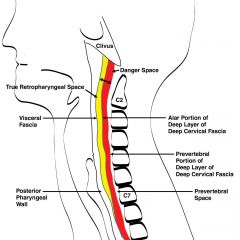
Superior: base of skull
Inferior: diaphragm Anterior: alar fascia of deep layer of DCF Posterior: prevertebral fascia of deep layer of DCF |
|
|
What are the contents of the danger space?
|
loose areolar tissue (danger space named due to potential for rapid spread of infection through this space)
|
|
|
What are the following boundaries of the prevertebral space?
Superior: Inferior: Anterior: Posterior: Lateral: |
Superior: base of skull
Inferior: coccyx Anterior: prevertebral fascia (results in midline abscess in this space) Posterior: vertebral bodies Lateral: transverse process of vertebrae |
|
|
What are the contents of the prevertebral space?
|
Dense alreolar tissue
Muscle - paraspinous, prevertebral, or scalene Vertebral artery and vein Brachial plexus and phrenic nerve |
|
|
What is the most common cause of deep neck space infections in adults? How about in kids?
|
adults - dental infections
pediatric - acute pharyngitis of Waldeyer's ring |
|
|
Describe the pathway of spread of the following infections to the deep neck.
Acute tonsillitis |
Acute tonsillitis --> peritonsillar abscess --> parapharyngeal space --> retropharyngeal space (will lead to the carotid sheath) OR submandibular space (will lead to the visceral space)
|
|
|
Describe the pathway of spread of the following infections to the deep neck.
Rhinosinusitis/upper pharyngitis |
Rhinosinusitis/upper pharyngitis --> retropharyngeal lymph node --> retropharyngeal space --> parapharyngeal space or carotid sheath
|
|
|
Describe the pathway of spread of the following infections to the deep neck.
Upper jaw dental infection |
Upper jaw dental infection --> masticator space --> ptergymaxillary space --> parapharyngeal space OR infratemporal space
|
|
|
Describe the pathway of spread of the following infections to the deep neck.
Lower jaw dental infection |
1st molar infections --> sublingual space --> submandibular space
2nd and 3rd molar infections --> submandibular space --> parapharyngeal or visceral spaces |
|
|
Describe the pathway of spread of the following infections to the deep neck.
Esophagoscopy/intubation/trauma |
Esophagoscopy/intubation/trauma --> parapharyngeal space or retropharyngeal space --> danger space and/or mediastinum
|
|
|
A neck phlegmon/abscess is identified on a CT. What percentage of cases will yield no pus return on neck exploration?
|
25%
|
|
|
What is the main source of mortality from deep neck infections?
|
loss of airway
|
|
|
Airway is most at risk with infections of which cervical spaces?
|
submandibular space
parapharyngeal space retropharyngeal space |
|
|
What are the indications for acute "quinsy" tonsillectomy?
|
1) Recurrent peritonsillar abscess
2) Massive tonsils causing acute airway obstruction 3) Patient already under general anesthesia due to comfort issues or poor exposure. |
|
|
Describe the three common transcervical incision and drainage approaches
|
Choice depends on involved spaces:
1) Modified blair incision (parotid) - parotid space - temporal or infratemporal fossa - submandibular or parapharyngeal space (with extension of neck incision 2) Horizontal lateral neck incision upper neck (2cm below mandible body) - masticator space (lower border of mandible and staying along lateral surface) - submandibular space (between posterior belly of diagastric and mandible body) - sublingual space (lateral to anterior digastric body with blunt spreads through mylohyoid muscle) - parapharyngeal space/pterygomaxillary space 3) Horizontal lateral neck incision mid-neck (level 3 at cricoid cartilage) - Retropharyngeal/danger/prevertebral spaces - dissection medial to carotid sheath (retracted laterally) and lateral to strap muscles (retracted medially) - deep cervical fascia and paraspinous muscles identified - blunt dissection superior (skull base) to inferior (mediastinum) |
|
|
What is the most common etiology of ludwig's angina?
|
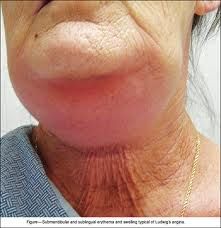
dental origin
|
|
|
Ludwig's angina spreads rapidly though the ___________.
|
fascial planes (not lymphatics
|
|
|
What is the typical description of the feel of the neck in a pt with Ludwig's angina?
|
a woody, indurated neck
|
|
|
What is the mortality rate of cavernous sinus thrombosis?
|
30-40%
|
|
|
What is Lemierre syndrome?
|
Thrombophlebitis of the internal jugular vein
- a possible complication of deep neck infections - usually caused by the bacterium Fusobacterium necrophorum (anaerobic gram-negative bacillus) - bacterium spreads to the IJ from tonsillar veins where endotoxin causes platelet aggregation. - associated with pharyngitis, spiking "picket fence" fevers" |
|
|
What is the Tobey-Ayertest?
|
Compression of the thrombosed IJ (in Lemierre syndrome) during spinal tap does not increase CSF pressure as opposed to the contralateral side.
|
|
|
Carotid artery pseudoaneurysm or rupture is associated with infection of which cervical spaces?
|
retropharyngeal and parapharyngeal space
- mortality rate 20-40% - internal carotid artery is the cause 49% of time. |
|
|
What are signs of carotid artery pseudoaneurysm or rupture in a patient with deep neck infection?
|
Pulsatile neck mass
Horner syndrome Palsies of CN 9-12 Expanding hematoma Neck ecchymosis Sentinel bright red bleed from nose or mouth Hemorrhagic shock |
|
|
Mediastinitis is associated with infections of which cervical spaces?
|
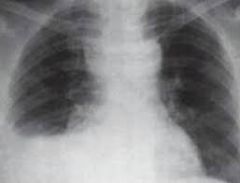
retropharyngeal space (most common; superior mediastinum)
danger space (posterior mediastinum to diaphragm) - tx of mediastinitis is best with a combined transcervical and transthoracic incision and drainage |
|
|
What is the most common cause of necrotizing fasciitis of the neck?
|
dental infections (mixed aerobic and anaerobic flora)
- mortality is 20-30% - neck CT shows tissue gas in 50% of cases |

