![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
88 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
In reference to biarticular muscles, what must the ends do to stretch? |
Both ends must lengthen |
|
|
In reference to biarticular muscles, what must the ends do to strengthen? |
1 end must lengthen the other must shorten |
|
|
In the talocural joint what are the dorsiflexors? (4) |
Tibialis anterior (Tom) Extensor Digitorum Longus (Dick) Extensor Hallicus Longus (Harry) Peroneus Tertus |
|
|
In the talocural joint what are the plantarflexors? (8) |
Gastroc Soleus Tibialis Posterior Flexor Digitorum Longus Flexor Hallicus Longus Plantaris Peroneus Longus Peroneus Brevis |
|
|
Where is the axis of rotation for the talocural joint? |
M-L through the malleoli |
|
|
What are the evertors of the talocural joint? (3) |
Peroneus Longus Peroneus Brevis Peroneus Tertus |
|
|
What are the invertors of the talocural joint? (8) |
Tibialis anterior (Tom) Extensor Hallicus Longus (Harry) Gastroc Soleus Plantaris Tibialis Posterior Flexor Digitorum Longus Flexor Hallicus Longus |
|
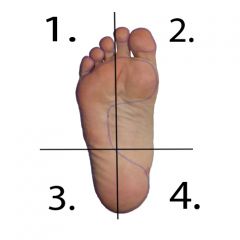
What movement and muscles are responsible in quadrant 1? (2) |
Dorsiflexion and Eversion -Tibialis Anterior (Tom) -Extensor Hallicus Longus (Harry) |
|
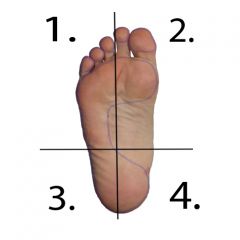
What movement and muscles are responsible in quadrant 2? (1) |
Dorsiflexion and Inversion -Peroneus Tertus |
|
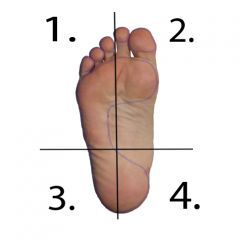
What movement and muscles are responsible in quadrant 3? (6) |
Plantarflexion and Eversion -Gastroc -Soleus -Tibialis Posterior -Plantaris -Flexor Hallicus Longus -Flexor Digitorum Longus |
|
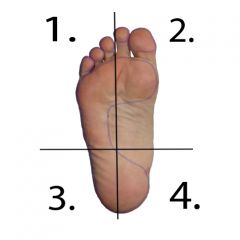
What movement and muscles are responsible in quadrant 4? (2) |
Plantarflexion and Inversion -Peroneus Longus -Peroneus Brevis |
|
|
Where is the axis of rotation for the knee? |
M-L through the femoral epicondyle |
|
|
What are the extensors of the knee? (4) |
Quardriceps -Vastus Medialis -Vastus Intermedius -Vastus Lateralis -Rectus Femoris |
|
|
What are the flexors of the knee? (8) |
Hamstrings: -Biceps femoris (Long Head and Short Head) -Semitendinosus -Semimembranosus -Gracilis -Satorius -Popliteus -Plantaris -Gastroc |
|
|
What are the external rotators of the knee? |
Bicep Femoris (Long Head and Short Head) |
|
|
What are the internal rotators of the knee? (5) |
Semitendinosus Semimembranosus Popliteus Gracilis Sartorius |
|
|
Where is the axis of rotation for the hip? |
M-L through the femoral head |
|
|
What are the flexors of the hip? (5) |
Rectus Femoris Iliacus Psoas Major Sartorius TFL (Tensor Fascia Latae) |
|
|
What are the extensors of the hip? (5) |
Gluteus Max Biceps Femoris (Long Head) Semitendinosus Semimembranosus Adductor Magnus |
|
|
What are the aBductors of the hip? (2) |
TFL (Tensor Fascia Latae) Gluteus Medius |
|
|
What are the aDductors of the hip? (5) |
Pectineus Sartorius Adductor Brevis Adductor Longus Adductor Magnus
|
|
|
What are the external rotators of the hip? (5) |
Glutueus Maximus Piriformis Sartorius 6 small external rotators (we do not need to know the 6) |
|
|
True or False, the gastroc is a biarticular muscle? |
True |
|
|
In order to stretch the gastroc what must the proximal joint do? |
Extend |
|
|
In order to stretch the gastroc what must the distal joint do? |
Dorsiflex |
|
|
In order to strengthen the gastroc what must the proximal joint do? |
Extend |
|
|
In order to strengthen the gastroc what must the distal joint do? |
Plantarflexion |
|
|
When strengthening the gastroc which joint is the moving joint, the proximal or distal? |
Distal |
|
|
True or False, the hamstring is a biarticular muscle? |
True |
|
|
In order to stretch the hamstring what must the proximal joint do? |
Flexion |
|
|
In order to stretch the hamstring what must the distal joint do? |
Extension |
|
|
In order to strengthen the hamstring what must the proximal joint do? |
Flexion |
|
|
In order to strengthen the hamstring what must the distal joint do? |
Flexion |
|
|
When strengthening the hamstring what joint is the moving joint? |
Distal Joint |
|
|
What is it called when both ends of an articular muscle shorten? |
Active insufficiency |
|
|
In order to stretch the rectus femoris what must the proximal joint do? |
Extension |
|
|
True or false, the quadriceps is a biarticular muscle? |
False |
|
|
True or false, the only part of the quadriceps that is a biartiuclar muscle is the rectus femoris? |
True |
|
|
When both ends of an articular muscle lengthen it is called what? |
Passive insufficiency |
|
|
What the flexors for the trunk? (3) |
Rectus Abdominis External Obliques Internal Obliques |
|
|
What are the extensors for the trunk? (5) |
Erector Spinae Spinalis Iliocostalis Longissimus Multifidus |
|
|
What muscles are used in lateral bending of the trunk? (5) |
External Oblique Internal Oblique Quadratus Lomburom Longissimus Iliocostalis |
|
|
What word means to rotate to the same side? |
Ipsilateral |
|
|
What word means to rotate to opposite sides? |
Contralateral |
|
|
What are the Ipsilateral muscles of the trunk? (2) |
Internal Oblique Rector Spinae |
|
|
What are the contralateral muscles of the trunk? (2) |
External Oblique Multiffidus |
|
|
What does the transverse abdominis do? |
Muscular girdle that helps to stiffen the spine but has no role in moving |
|
|
What muscles are used in scapulo-thoracic protraction? (2) |
Serratus Anterior Pec Minor |
|
|
What muscles are used in scapulo-thoracic retraction (2) |
Midddle Traps Rhomboids |
|
|
What muscles are used in scapulo-thoracic upward rotation? (3) |
Upper Trap Lower Trap Serratus Anterior |
|
|
What muscles are used in scapulo-thoracic downward rotation? (3) |
Levator Scapulae Rhomboid Pec Minor |
|
|
What muscles are used in scapulo-thoracic elevation? (3) |
Upper Traps Levator Scapulae Rhomboid |
|
|
What muscles are used in scapulo-thoracic depression? (2) |
Lower Trap Pec Minor |
|
|
What muscles are responsible for glenohumeral flexion? (4) |
Anterior Delt Biceps Brachii (Long Head) Pec Major (Clavicle Portion) Corico Brachialis |
|
|
What muscles are responsible for glenohumeral extension? (4) |
Triceps (Long Head) Posterior Delt Lats Teres Major |
|
|
What muscles are responsible for GH aBduction? (40 |
Mid Delt Anterior Delt Posterior Delt Supraspinatus |
|
|
What muscles are responsible for GH aDduction? (3) |
Pec Major Lats Teres Major |
|
|
What muscles are responsible for GH internal rotation? (4) |
Lats Subscapularis Pec Major Teres Major |
|
|
What muscles are responsible for GH external rotation? (2) |
Infraspinatus Teres Minor
|
|
|
What muscles are responsible for GH horizontal aBduction? (1) |
Post Delt |
|
|
What muscles are responsible for GH horizontal aDduction? (1) |
Pec Major |
|
|
What are the 4 "P's" of the shoulder? |
Protector Pivoters Positioners Propellors |
|
|
What are the protectors of the shoulder? (5) |
Supraspinatus Infraspinatus Teres Minor Subscapularis (S.I.T.S.) Biceps Brachii (Long Head) |
|
|
What are the pivoters and what do they do? |
They position the scapula on the thorax All the scapulothoracic muscles |
|
|
What are the positioners and what do they do? |
Position the arm in relation to the trunk Delt muscles |
|
|
What are the propellors and what do they do? (3) |
Transfer energy from the trunk to arm as well as generate energy Pec Major Lats Teres Major |
|
|
What muscles are responsible for flexion at the elbow? (3) |
Biceps Brachii (Long Head and Short Head) Brachioradialis Brachialis |
|
|
What muscles are responsible for extension at the elbow? (3) |
Triceps (Long Head, Medial Head, and Lateral Head) Aonconeus |
|
|
Where do the muscles in the forearm attach to? |
The radius |
|
|
What muscles are responsible for supination? (3) |
Brachioradialis Supinator Biceps Brachii |
|
|
What muscles are responsible for pronation? (3) |
Brachioradialis Pronator Teres Pronator Quadratum |
|
|
When does position of the wrist matter? |
When the muscles attaches to the radius |
|
|
When doesn't position of the wrist matter? |
When the muscles attach to the ulna |
|
|
What muscle attaches to the ulna? |
Triceps |
|
|
What muscles attach to the radius? (3) |
Biceps Brachioradialis Brachialis |
|
|
What muscles are responsible for extension of the wrist? (4) |
Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus Extensor Carpi Radialis Brevis Extensor Carpi Ulnaris Extensor Digitorum |
|
|
What muscles are responsible for flexion of the wrist? (5) |
Flexor Carpi Ulnaris Flexor Carpi Radialis Flexor Digitorum Superficialis Flexor Digitorum Profundus Palmaris Longus |
|
|
What muscles are responsible for ulnar deviation? (2) |
Flexor Carpi Ulnaris Extensor Carpari Ulnaris |
|
|
What muscles are responsible for radial deviation? (3) |
Flexor Carpi Radialis Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus Extensor Carpi Radialis Brevis |
|
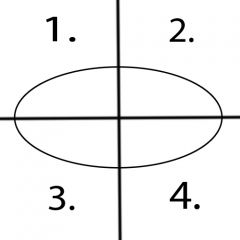
What motions occur in quadrant 1? |
Flexion and Ulnar Deviation |
|
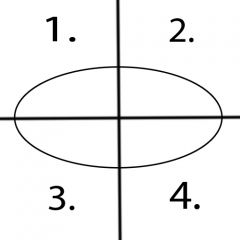
What motions occur in quadrant 2? |
Flexion and Radial Deviation |
|
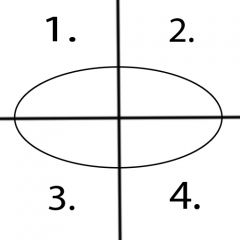
What motions occur in quadrant 3? |
Extension and Ulnar Deviation |
|
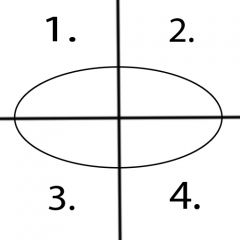
What motions occur in quadrant 4? |
Extension and Radial Deviation |
|
|
What muscle controls felxion and ulnar deviation? (1) |
Flexor Carpi Ulnaris |
|
|
What muscle controls flexion and radial deviation? (1) |
Flexor Carpi Radialis |
|
|
What muscle controls extension and ulnar deviaiton? (1) |
Extensor Carpi Ulnaris |
|
|
What muscles controls extension and radial deviation? (2) |
Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus Extensor Carpi Radialis Brevis |
|
|
Where do wrist extensors attach to? |
Lateral condyle of the ulna |

