![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
182 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
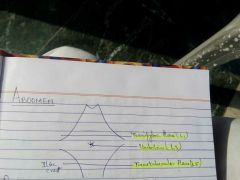
level of transpyloric plane, umbilicus and transtubercular plane |
|
|
|
Umbilicus nerve supply? lymphatic? |

|
|
|
abdominal wall layers |

|
|
|
superficial fascia layers |

|
|
|
fascia scarpa in pelvis is k/a |
fascia colles |
|
|
deep fascia of penis is k/a |
bucks fascia |
|
|
deep inguinal ring opening is in which layer |
Fascia transversalis |
|
|
superficial inguinal ring opening in |
External oblique muscle |
|
|
Median plane b/w 2 RA muscles k/a? paramedian plane b/w RA and EO |

|
|
|
Fold of douglas/Arcuate line ? |
lowest fibre of internal oblique muscle |
|
|
External oblique muscle fibre direction? lowest fibres of EO muscle folded inside to form |

|
|
|
internal oblique muscle fibres direction ? |

|
|
|
IO muscle pierced by |

|
|
|
Conjoint tendon |

|
|
|
conjoint tendon also k/a |

|
|
|
Inguinal canal? extension? length? |

|
|
|
Ant. roof post. floor of Inguinal canal formed by |

|
|
|
Structures present in Inguinal canal |

|
|
|
Pathway of spermatic cord and ilioinguinal nerve |

|
|
|
Direct vs Indirect inguinal hernia |

|
|
|
Causes of Direct inguinal hernia in children |

|
|
|
Hesselbach triangle / Inguinal triangle |

|
|
|
Structure present in spermatic cord |

|
|
|
Layers of spermatic cord |

|
|
|
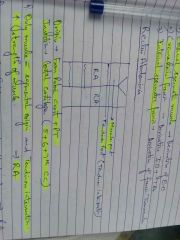
Origin and insertion of Rectus Abdominis? feature of RA |
|
|
|
Chief muscles helping in bending the trunk |

|
|
|
Rectus sheath structures ? |

|
|
|
Muscles of abdomen and their nerve supply |

|
|
|
Pyramidalis supplied by ? Cremasteric supplied by ? |

|
|
|
Retro peritoneal organs are ? |

|
|
|
Peritoneal cavity divides into two parts ? |

|
|
|
omentum ? |

|
|
|
extensions (pouch) of greater sac |

|
|
|
Anterior and Posterior wall of pouch of Douglas |

|
|
|
Collection of pus in pouch of douglas seen in which conditions |

|
|
|
Anterior and posterior wall of hepato renal pouch |

|
|
|
collection of pus in hepato renal pouch seen in |

|
|
|
Pouch = |
MC site of collection of pus |
|
|
MC site of collection of pus in abdomen |
Supine position - morrison pouch erect position - pouch of douglas |
|
|
MC site of collection of pus in pelvis |
supine - pouch of Douglas erect - pouch of Douglas |
|
|
Greater sac and lesser sac communicate through |

|
|
|
autonomic nervous system supply through hypothalmic nuclei? |

|
|
|
Parasympathetic fibres of facial nerve regulates? |

|
|
|
Vagus nerve regulate |

|
|
|
parasympathetic supply to urinary bladder, uterus, rectum causes |

|
|
|
Nerve that carry pain sensation in pelvic organ |

|
|
|
Sympathetic supply to head and neck? nerve supply to dilator pupillae |

|
|
|
Causes of miosis |

|
|
|
Sympathetic supply to lung and heart |

|
|
|
Pain in AMI from which branches? why in arms amd jaws? Pain in Inferior wall MI ? |

|
|
|
Thoracic splanchnic nerve root? greater splanchnic nerve root? leesr and least splanchnic nerve roots? |

|
|
|
Thoracic splanchnic nerve pass through |
Pass through crus of diaphragm |
|
|
nerve root supply(pain transmission) to stomach, GB, Small intestine, caecum, appendix, transverse colon, ascending colon, descending colon, sigmoid colon, rectum |

|
|
|
features of GB pain |

|
|
|
Blood supply of abdomen and pelvis |

|
|
|
External iliac artery branches and course |

|
|
|
Internal iliac artery branches |

|
|
|
Vesical artery branches |

|
|
|
Abdominal aorta division and its branches |

|
|
|
Paired and unpaired branches of abdominal aorta |

|
|
|
Organs developing from foregut |

|
|
|
Which part of pancreas develop from foregut and which from midgut? |

|
|
|
blood supply of pancreas? |

|
|
|
Lt. gastric artery, common hepatic artery, splenic artery supply and their branches |

|
|
|
Inferio pancreatico duodenal artery is branch of |

|
|
|
Duodenal ulcer most common in which wall complications in anterior vs posterior wall |

|
|
|
Structures developing from midgut ? and arteries supplying it |

|
|
|
Branches of superior mesenteric artery |

|
|
|
Inferior mesenteric artery supply branches ? |

|
|
|
Part of colon with least blood supply |

|
|
|
Portal vein formed by ? and at the level of? |

|
|
|
Inferior mesentric vein drains into |

|
|
|
Length of large intestine ? Tinea coli ? what are they responsible for ? |

|
|
|
Appendices epiploicae |

|
|
|
Tunica adventitia |

|
|
|
Intra peritoneal organs and their peritoneum |

|
|
|
Structure developing in ventral mesogastrium vs in dorsal mesogastrium |

|
|
|
peritoneum in ventral mesogastrium and dorsal mesogastrium |

|
|
|
Peritoneum in midgut and hindgut |

|
|
|
Policeman of gut |
greater omentum |
|
|
Structures related to greater and lesser omentum |

|
|
|
Mesentry ? length? width? |

|
|
|
arteries related to Esophagus in upper 1/3rd , middle 1/3rd , lower 1/3rd |

|
|
|
Constrictions in esophagus |

|
|
|
stomach arterial supply ? |

|
|
|
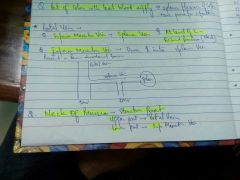
Structures present in the upper and lower part of neck of pancreas |
|
|
|
Portal vein receives blood from |

|
|
|
Tributaries of portal vein |

|
|
|
Branches of portal vein vs systemic vein |

|
|
|
Layers of gut |

|
|
|
Layers of mucosa |

|
|
|
Epitheilum of gut? exceptions ? |

|
|
|
simple columnar epithelium with villi present in ? without villi ? simple columnar epithelium with goblet cell nd without goblet cells ? |

|
|
|
Glands of stomach |

Peptic / cheif cell (present at base of gland) secretes pepsinogen Mucus neck cell - mucus |
|
|
Small intestinal glands ? gland present only in duodenum? function of these glands |

|
|
|
Base of intestinal glands contain special type of cells |

|
|
|
glands in large intestine |

|
|
|
Lamina propria |

|
|
|
Function of muscularis mucosa |

|
|
|
Rugae ? function |

|
|
|
mucosal fold of small intestine k/a features ? |

|
|
|
structures in gut that Increases absorption |

|
|
|
mucosal folds in large intestine |

|
|
|
Temporary mucosal folds im gut are |

|
|
|
Submucosa contain ? nerve plexus in sub-mucosa k/a Does mucosa contain blood vessels? |

|
|
|
Muscle layer (outer vs inner ) ? nerve plexus in muscle layer |

|
|
|
Muscle layer in esophagus |

|
|
|
Special feature of stomach muscular layer |

|
|
|
Stomach bed ? spleen, pancreas, right kidney and right adrenal separated from stomach by |

|
|
|
Peritoneum in duodenum |

|
|
|
Ulcer of duodenum? |

|
|
|
D2 of duodenum is separated by ? |

|
|
|
Upper and lower part of D2 supplied by |

|
|
|
Causes of obstruction of D2 in neonate diagnosis by ? |

|
|
|
Causes of neonatal vomiting (within hours, on 2nd day, on 21st day |

|
|
|
Causes of D3 obstruction |

|
|
|
D4 of duodenum is supported by? clinical importance of it? where it is attached? |

|
|
|
Jejunum vs Ileum (length, wall thickness, vascularity) |

|
|
|
Meckel diverticulum (length = ? , true or false diverticulum? epithelium is of which type? derivative of ?) |

|
|
|
Zenker diverticulum? true or false? and why? present where? in b/w which muscle? MC symptom |

|
|
|
goblet cells present in ? tinea coli ? appedices epiploicae ? |

|
|
|
Nerves related to caecum |

|
|
|
Appendix length ? MC position ? arterial supply ? nerve supply ? |

T 10 - T 11 |
|
|
Mc Burney's point |

|
|
|
Length of large and small intestine ? max lumen in large intestine? least lumen in largre intestine ? |

|
|
|
Carcinoma colon common in ? prognosis? |

|
|
|
Ascending colon tumor ? prognosis |

|
|
|
Features of rectum ? is it different from large intestine? |

|
|
|
Arterial supply of rectum |

|
|
|
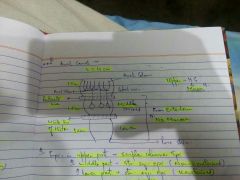
Anal canal total length ? upper, middle and lower parts length? whats differentiation between all three ? epithelium in each part? upper and middle part separated by ? middle and lower part separated by |
|
|
|
Venous drainage of kidney |

|
|
|
Which renal vein is larger ? |

|
|
|
Left renal vein receives blood from |

|
|
|
which kidney selected for transplantation ? why |

|
|
|
structures in cortex and medulla of kidney |

|
|
|
Collecting duct join to form a large duct k/a |

Duct of Bellini.....open into minor calyx |
|
|
Weight of adrenal gland |
5 g |
|
|
Cortex and medulla of adrenal gland derived from |

|
|
|
Arterial supply of adrenal gland |

|
|
|
Venous drainage of Adrenal gland |

|
|
|
Ureter is present on which muscle |

Psoas major muscle |
|
|
Nerve posterior to ureter |

|
|
|
Ureter identification and its importance |

|
|
|
3 constrictions of ureter ? narrowest out of these is |

|
|
|
Ureter related to 3 bony points ? |

|
|
|
Arterial supply of ureter |

|
|
|
Ligament that supports apex of UB |
|
|
|
Parts of UB |
Base Neck Neck of UB present only in empty bladder |
|
|
Is peritoneum present b/w UB and Vas deferens |

|
|
|
Structures related to base of UB |

|
|
|
UB derived from ? part of UB in which mucosal folds are absent |

|
|
|
Parasympathetic and sympathetic nerve supply to UB |

|
|
|
Male genital system pathway |

|
|
|
Function of Testis and Epididymis |

|
|
|
Function of Vas deferens, Ejacuatory duct, Seminal vesicles, prostate and urethra |

|
|
|
Final maturation of sperm take place in ? |

|
|
|
Vas deferens length ? blood supply ? it hooks around which artery ? |

|
|
|
Cells in testis and their function ? |

|
|
|
Functional unit of Testis ? sperm pathway |

|
|
|
Layers of testis |

|
|
|
Hydrocele ? communicating hydrocele ? |

|
|
|
Arterial supply of Testis |

|
|
|
Venous drainage of Testis |

|
|
|
Varicocele is due to ? clinically described as ? common on which side |

|
|
|
MC correctable cause of male infertility |
Varicocele |
|
|
varicocele can be due to which carcinoma |

|
|
|
Lymphatic drainage of Testis |

|
|
|
Descent of testis |

|
|
|
Weight of prostate ? and lobes in prostate |

|
|
|
Urethra and ejaculatory duct relation with prostate |

|
|
|
BPH involve which lobe of prostate |

|
|
|
Carcinoma prostate involve which lobe ? clinical features ? arterial supply |

|
|
|
MC site of metastasis of Ca prostate ? and why |

|
|
|
Composition of Prostate |

|
|
|
Length of male and female urethra ? parts of male urethra |

|
|
|
Widest urethra ? narrowest urethra ? narrowest part of urethra ? |

|
|
|
Epithelium of Urethra in males ? |

|
|
|
Epithelium of urethra in female |

|
|
|
Structure opening in prostatic urethra |

|
|
|
Male uterus |

|
|
|
Structures opening in membranous urethra ? structures related to membranous urethra ? |

|
|
|
Structures opening in penile urethra |

|

