![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
140 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Granular IF
|
Type 3 rxn.
|
|
|
Linear, smooth IF
|
Anti-GBM Ab
|
|
|
Minimal change disease LM & IF
|
normal glomeruli
lipid droplet in proximal tubular epithelium no deposit |
|
|
Nephrotic syndrome in children 2-6 yrs.
|
minimal change disease
|
|
|
Test for minimal change disease
|
steroids
|
|
|
Minimal change disease EM
|
effacement of epithelial (podocytes) foot processes
|
|
|
Minimal change disease C/F & lab
|
proteinuria of albumin 4+
slightly cloudy urine yellow urine oval fat body Lab: high serum cholesterol normal complement levels |
|
|
Nephrotic syndrome in adults
& etiology |
membranous nephropathy
Etiology: idiopathic or genetic Drug (penicillamine), renal transplantation, Heymann nephritis SLE, DM, amyloidosis Adenocarcinoma of lung and colon |
|
|
Morphology of MGN
|
LM: H& E Stain--> diffuse thickening of capillary wall
Silver stain--> spikes IF: granular deposits of IgG and C3 EM: Sub epithelial deposit along BM |
|
|
Urinalysis and Lab of MGN
|
urine:
protein 4+ WBC/hpf = <2/hpf Lab: low complements |
|
|
MGN C/F
|
HTN
hematuria may progress to renal failure |
|
|
Types of Acute glomerulonephritis
|
acute post streptococcal glomerulonephritis
non-streptococcal causes |
|
|
Acute nephritic syndrome in a child
|
Acute post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis
ASO titer: high Age: 2-4 years |
|
|
Acute post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis
Etiology--> Path--> Hypersensitivity rxn--> |
beta hemolytic group A strep infection of THROAT & SKIN
complement mediated tissue damage w/ the help of PMN Type 3 (circulating IC) |
|
|
Non-streptococcal glomerulonephritis
Causes--> D/D--> Test--> |
pneumococcal pneumonia
Hep B, C SLE, PAN Malaria Acute post-strep ASO titre |
|
|
Morpho Acute post-strep glomerulonephritis
|
LM: hypercellular, large glomeruli contain neutrophils
Tubules: RBC cast IF: granular deposit of IgG, IgM, C3 in all glomerulous EM: subepithelial humps |
|
|
Urinalysis, C/F
Acute post-strep glomerulonephritis |
Urine: smoky b/c of acid hemetin (due to hematuria), dysmorphic RBC (b/c RBC squeezing through glomerulus)
Serum complement low (C3 & C5). Complements used up by IC ARF = acute nephritic syndrome C/F: abrupt onset, malaise, slight fever, nausea |
|
|
Past hx. of post strep glomerulonephritis?
|
pharyngitis, dermatitis, impetigo (honey-crusted lesions)
|
|
|
Complication of post strep glomerulonephritis
|
may progress to crescentric GN
may progress to chronic GN |
|
|
rapidly occurring acute nephritic syndrome?
LM--> C/F--> |
CrGN
all types show glomerular crescent hematuria and in 2-3 days ARF + uremia |
|
|
Composition of crescent in CrGN
|
epithelial cells (podocytes)
fibrin monocytes |
|
|
Type 1 CrGN
C/F D/D |
1. AKA Anti-GBM DISEASE
2. AKA: Good pasture syndrome. - Presence of Anti GBM antibody in serum: this react with alveolar capillary → pulmonary alveolar hemorrhage. - Present as hematuria and hemoptysis 3. IF: Linear and smooth deposit of IgG, and C3 on GBM. C/F--> decrease C3 D/D--> wegener (+c-anca) |
|
|
Ab to which antigens in CrGN
|
lung and GBM
|
|
|
Which type of hypersensitivity rxn is type 1 CrGN?
|
Type 2
|
|
|
Type 2 CrGN
|
Etiology: mainly SLE
IF: Granular deposit Clinical : progress to renal failure. Serum: ANA present Type 3 hypersensitivity |
|
|
C/F of SLE
|
butterfly rash over bridge of nose
photosensitivity anemia anti-smith Ab, dsDNA Ab |
|
|
Type 3 CrGN
|
Aka: Pauci-immune (no immune reaction)
Disease association: Wagner Granulomatosis, polyarteritis Nodosa Serum: Normal complements Positive ANCA (c or p) LM: glomerular crescent IF and EM: no deposit |
|
|
C/F PAN
|
malaise, HTN, fever, purpura in skin (ulcer)
|
|
|
C/F Type 3 CrGN
|
acute onset of hematuria, hemoptysis,
RPGN--> ARF, uremia |
|
|
Prognosis of crescentric glomerulonephritis
|
depends upon the number of crescent in kidney: so biopsy is indicated
|
|
|
Causes of IgA elevation
|
longstanding-->
lung infection GI disease (celiac sprue) |
|
|
IgA elevation leads to deposits in...
|
kidney
blood vessels --> HSP dermis--> dermetitis herpetiformis |
|
|
recurrent hematuria in children and young adults
|
Berger's (IgA nephropathy)
|
|
|
Berger's
|
Syndrome: recurrent hematuria
This hematuria occur 1-2 days after upper respiratory tract infection. May progress to Chronic renal Failure(25%-50%). IgA deposit in skin- dermatitis herpetiformis. Asso: Gluten enteropathy. LM: focal proliferation of mesangial cells IF: IgA is deposited mainly in mesangium. |
|
|
Henoch-Schonlein Purpura
|
It is associated with
1.Skin purpuric Rash 2.Abdominal Pain 3.Arthritis 4.And Kidney change Q: What is the similarity? A: Both are caused by IgA deposition in Mesangium and skin deposit of IgA. |
|
|
nephrotic syndrome in adults
|
MPGN type 1
|
|
|
MPGN Type 1
|
Etiology: Hepatitis B and C, HIV, SLE, chronic liver diseases, chronic Bacterial Infection.
LM: H&E: hyper cellular glumeruli ( but no PMNs) and thick GBM. Silver stain : Tram track IF: Granular deposit. Serum: low complements ( particularly C3) |
|
|
Tram-tracking
|
double basement membranes b/c of basement membrane splitting
MPGN 1 |
|
|
Syndrome: Hematuria/ chronic renal failure-->
|
MPGN 2
|
|
|
MPGN 2
|
40% progress to end stage renal failure
IF: Dense deposit in GBM . Aka dense deposit diseases. Serum: C3NeF (C3 Nephritic Factor) autoantibody is Present. |
|
|
Where are the dense deposits in MPGN 2?
|
C3 deposits in capillary walls and mesangium
--> bad prognosis. Why? deposition on mesangium is inescapable b/c of lack of blood supply Granular |
|
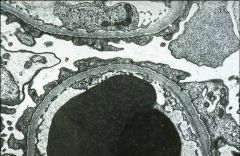
|
podocyte effacement
minimal change disease |
|
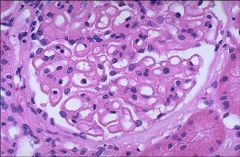
|
MGN
|
|
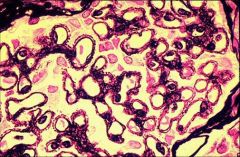
|
MGN
|
|

|
hypercellular glomeruli
acute post-strep glomerulonephritis |
|

|
subepithelial humps
acute post-strep glomerulonephritis |
|
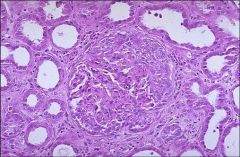
|
CrGN
|
|
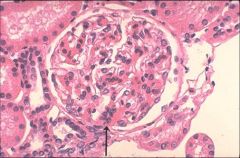
|
Focal proliferation of mesangial cells
Berger's |
|
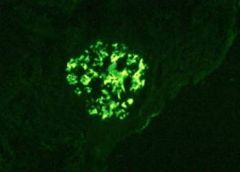
|
IgA deposit in mesangium
Berger's |
|
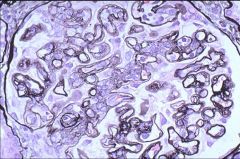
|
tram-tracking
MPGN 1 |
|
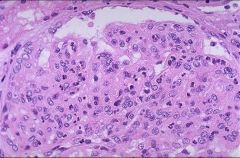
|
Proliferative
|
|
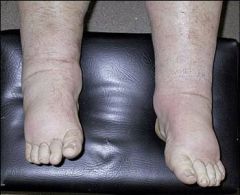
|
anasarca
nephrotic syndrome |
|

|
granular
circulating immune complex |
|
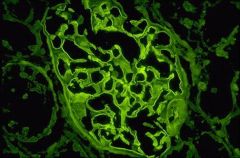
|
linear, smooth
anti-GBM |
|
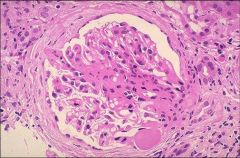
|
FSGS
|
|
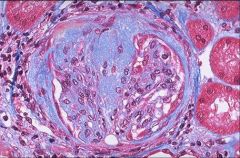
|
Trichrome stain demonstrating blue, collagen deposits
FSGN |
|
|
Non-selective proteinuria of nephrotic range
|
FSGS
|
|
|
nephrotic syndrome in child and adult
|
FSGN
|
|
|
proteins in non-selective proteinuria
|
albumin
fibrinogen globulin |
|
|
Morpho
FSGN |
H&E: sclerosis of some glomeruli, w/ partial involvement
Trichrome: blue |
|
|
Urinalysis of FSGS
|
frothy b/c of albumin
thick b/c of fibrinogen |
|
|
D/x of FSGS
|
biopsy
|
|
|
FSGS
clinical |
Clinical:
A. Poor response to corticosteroid B. Hematuria, Hypertension C. Progression to chronic renal failure D. 50% develop End stage Renal failure within 10 years. |
|
|
D/D of FSGS from minimal change disease
|
poor response to steroids
|
|
|
Secondary glomerulonephritis
|
Diabetes Mellitus
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Amyloidosis Goodpasture Syndrome Wagner granulomatosis Henoch-Schönlein Purpura Bacterial Endocarditis |
|
|
Complications of nephrotic syndrome
|
1. MI
2. repeated infection 3. DVT |
|
|
An adult comes in with nephrotic syndrome, what is the order of possible causes you will suspect?
|
1. MGN
2. DM 3. SLE 4. Amyloid |
|
|
Test for
DM? SLE? amyloidosis? |
DM--> PAS positive, deposit composition
SLE --> anti-smith Ab, dsDNA Ab amyloidosis--> congo red |
|
|
D/x for lupus nephritis?
|
decrease in C1q
|
|
|
Which diseases have a normal looking glomerulus?
|
minimal change disease & (FSGS?) Type 3 CrGN?
|
|
|
LM of SLE
|
wire loop
|
|
|
IF of lupus nephritis
|
C1q deposits
Circulating IC nephritis (Type 3) granular |
|
|
All Type 3 hypersensitivity rxns (nephrotic) have anasarca, proteinuria, and lipiduria, but if oliguria is present also what will you suspect?
|
CrGN
|
|
|
1. CrGN= RPGN
2. Focal proliferative GN = ANS 3. Wire loop= NS 4. Mesangial lupus GN = NS 5. Normal glomerulus = NS |
Lupus nephritis
|
|
|
Etiology of scleroderma and kidney
|
interlobular arteries of the kidney show intimal thickening (deposits on and w/in intima).
|
|
|
C/F of scleroderma and the kidney
nephritic or nephrotic? |
shiny taught skin, increased dermal collagen, HTN, proteinuria +2 (non-nephrotic)
|
|
|
What is difference between CREST and Scleroderma?
|
CREST--> focal
Scleroderma--> diffuse, HTN, increased collagen |
|
|
Composition of deposits inside glomerulus of diabetic kidney?
Nephrotic or nephritic? |
increased glucose & subendothelial collagen
nephrotic |
|
|
A diabetic kidney is at risk of....
|
infection
MI thrombosis (DVT |
|
|
What vascular change does a diabetic kidney undergo?
|
hyaline arteriosclerosis
|
|
|
Which test will not be useful in diagnosing a diabetic kidney?
|
IF
|
|
|
Amyloidosis of Kidney
Gross? |
waxy pale surface
Pale b/c of lack of blood vessels |
|
|
LM of amyloidosis of kidney
|
pink hyaline like deposit in mesangium
|
|
|
What are the diagnosing features of primary amyloidosis of the kidney?
|
Primary: (multiple myeloma)
M spike Bence-Jones protein in urine (amyloid light chain) |
|
|
Where do you expect to find amyloid in the kidney?
|
acellular paraprotein deposits in the extracellular space causing atrophy
|
|
|
What is the secondary (reactive- in rheumatoid arthritis) type of amyloid?
|
AA
|
|
|
C/F of secondary type of amyloid of the kidney?
|
symmetrical joint pain in the morning, morning stiffness.
|
|
|
Hereditary recurrent hematuria in children?
|
Alport syndrome
|
|
|
Which organs are involved in Alport syndrome and what is the resulting effect?
|
ears--> nerve deafness
eye--> cataract, lens dislocation, corneal dystrophy |
|
|
Sign of Alport syndrome?
|
family history of chronic renal failure
|
|
|
Inheritance of Alport syndrome?
|
X-linked autosomal recessive or dominant
|
|
|
What do we find in the tubules?
|
deposition of foamy cells (macrophages) containing mucopolysaccharide (MPS)
Seen on LM Simulates a storage disease |
|
|
What is the pathogenesis of Alport syndrome?
|
defective gene (alpha5) produces abnormal collagen type IV
|
|
|
Differential for alport syndrome and is there a genetic history with this differential disease?
|
thin membrane disease
No genetic hx. like Alport does. |
|
|
What is found in the glomeruli of Alport syndrome under a light microscope?
|
irregular thickening b/c of collagen
|
|
|
Where do we find recurrent hematuria?
|
IgA nephropathy (Berger's disease)- kidney only
Henoch-Schonlein Purpura- systemic ( joint, abdomen, GIT, skin) Alport syndrome (+ family hx. of hematuria) |
|
|
Where do we find RPGN?
|
CrGN
|
|
|
What are the associates of CrGN?
|
1. Good pasture syndrome--> lungs
2. Wegner granulomatosis--> lungs 3. PAN--> kidney, skin 4. SLE--> multi organ (crescent, wire-looped, normal?) |
|
|
C/F chronic glomerulos nephritis?
|
increasing BUN and creatinine, uremia, HTN, CRF, specific gravity= 1010, occasional polyuria unless in terminal stage
|
|
|
How long does it usually take to achieve CGN?
|
10 years
|
|
|
Which nephrotic syndromes are most likely to convert from acute Gn to chronic GN in 10years?
|
MGN & FSGS
|
|
|
Rx. for CGN?
|
30%-50% of all patients need hemodialysis and renal transplant
|
|
|
Gross of CGN?
|
cortical atrophy
|
|
|
LM of CGN?
Does this allow us to find the source of the problem? |
non-specific findings (biopsy not useful)
Scarring of Glomeruli, bowmen’s space Hyalinization of glomeruli. Interstitial fibrosis. Tubular atrophy Thickening of the small and medium sized arteries. NO! |
|
|
GFR of ESKD?
|
less than 5% of the normal
Use GFR to tell when the kidney reaches the end stage |
|
|
What is the appearance of the glomeruli in CGN?
|
all sclerosed
|
|
|
Test for proteinuria?
|
24 hour urine collection
dipstick |
|
|
What is the cause of nephritic syndrome in an adult?
|
infections:
1. Hepatitis 2. malaria 3. SLE |
|
|
What is the cause of nephritic syndrome in a child?
|
post-strep
|
|
|
What is the name of type 2 hypersensitivity reaction?
|
in-situ IC nephritis
|
|
|
What is the cause of hyperlipiduria and lipiduria?
|
decreased albumin in blood triggers lipoprotein synthesis
|
|
|
How does lipiduria present?
|
oval fat body in urine
|
|
|
What does hyperlipiduria do in the kidney?
|
steatosis of tubular epithelial cells causing increased permeability of GBM to lipoproteins
|
|
|
C/F of acute nephritic syndrome
|
anuria or oliguria
proteinuria 2+ 3+ hematuria azotemia HTN |
|
|
Onset of nephritic syndrome
|
weeks
|
|
|
Diseases where circulating immune complex nephritis (Type 3- B-cell activation) is seen?
|
1. SLE
2. Strep 3. Hep B 4. Treponema pallidum (syphillis) 5. Malaria IF--> granular deposits |
|
|
Antibody reacting to in-situ antigen in glomeruli (Type 2)?
|
Anti-GBM Ab
Ex. Good pasture syndrome (CrGn type 1) IF--> linear, smooth deposits |
|
|
Primary glomerular diseases
|
Minimal change disease
Membranous glomerulonephritis Acute glomerulonephritis Crescentic glomerulonephritis Berger's disease (IgA nephropathy) Membrenoproloferative GN Alport syndrome |
|
|
What stain is useful for minimal change disease?
|
Oil O-red stain, b/c of fat in tubular epithelium hence the name lipoid nephrosis
|
|
|
Mucin deposits from which complication is one of the causes of MGN?
|
adenocarcinoma of lung and colon
|
|
|
Acute nephritic syndrome is hand in hand with....
|
ARF b/c of the decrease in GFR caused by the proliferation/ hypercellularity
|
|
|
What is responsible for the proliferation in acute glomerulonephritis?
|
neutrophils
|
|
|
How would you distinguish post-strep GN from non-strep GN?
|
ASO titer
|
|
|
D/D for post-strep GN?
|
pyelonephritis, but WBC casts will signify pyelonephritis
|
|
|
Humpy-dumpy lesions- large IC
|
Acute post-strep GN
|
|
|
c-anca (+)
|
Wegner's
Type 3 CrGN |
|
|
p-anca (+)
|
PAN
Type 3 CrGN |
|
|
Where would IgA deposit in the skin (dermatitis herpetiformis)?
|
papillary dermis
|
|
|
Treatment for IgA nephropathy or elevation?
|
stop primary source of infection
|
|
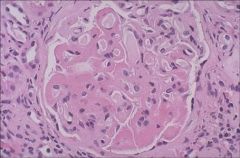
|
SLE (lupus nephritis)
LM: wire loop |
|
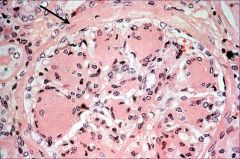
|
Diabetic Kidney
LM: nodular hyaline deposit PAS positive Kimmelstiel-Wilson disease or Nodular glomerulosclerosis |
|
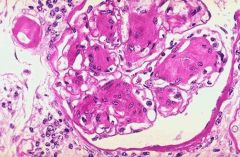
|
DM kidney
hyaline arteriosclerosis |
|
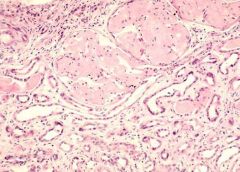
|
Amyloidosis of kidney
LM: pink hyaline like deposit in mesangium |
|
|
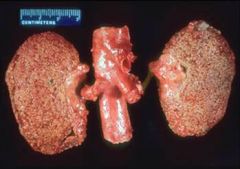
CGN
"contracted kidney" coarse granular surface |
|
|
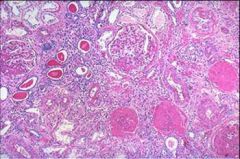
CGN
hyalinized glomeruli |
|
|
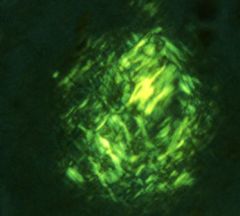
IF
amyloidosis |
|
|
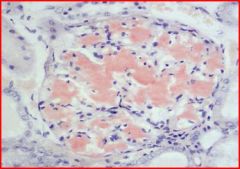
amyloidosis
LM: congo red stain- brick red |
|
|
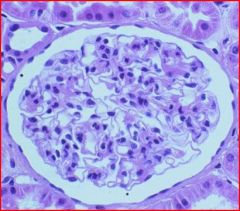
LM
normal glomerulus |
|
|
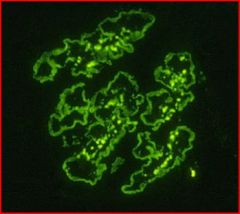
MPGN type 2
Dense deposit These bright deposits are of C3 in capillary walls and in the mesangium. |
|
|
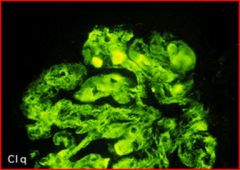
SLE
lupus nephritis IF: C1q deposits everywhere granular, Type 3 rxn. |

