![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
22 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
nephritic syndrome symptoms |
Oliguria, proteinuria, haematuria, oedema & hypertension |
|
|
Nephrotic syndrome features |
Proteinuria ( >3 gm/DL), hypoalbiminuria,( 1-3 gm/DL, reversed ratio) hyperlipidemia, lipiduria, hypercoagubility |
|
|
Oedema in nephritic vs nephrotic |
Nephritic due to sodium & water retention; nephrotic is due to increase on colloid osmotic pressure along with sod & water retention |
|
|
Acute post streptococcal GN morphplogy |
Gross: enlarged, flea bitten appearance of cortex due to petechial haemmoraghes. Microscopy: glomerulus is hypercellular due to proliferation of mesangial, endothelial cells and polymorph's & monocytes; interstitium has oedema. Tubules & vessels NS. electron microscopy shows electron dense HUMPS on the epithelial side of GBM. Immune florescence shows irregular deposits mainly IGG and IGM |
|
|
Diabetic nephropathy defn |
Syndrome of renal symptoms in DM- nephrosclerosis, diabetic pyelopnephritis, vascular symptoms, tubular (AM lesions) |
|
|
Diabetic nephrosclerois EP |
Hyperglycemia causes renal hypertension, renal hyper perfusion, protein deposition, sclerosis |
|
|
Morphology of Diabetic nephrosclerosis |
Grossly: DIFFUSE & NODULAR. Diffuse: gross fibrin deposition. Places- GBM lining, mesangium, fibrin CAP- peripheral membrane of Bowman's capsule, hyaline drop- lining of capillary of glomerus |
|
|
Microscopy of glomerular sclerosis |
Eosinophilc, acellular , fibrin deposits |
|
|
Other lesions in D. nephropathy describe |
Tubular- armani ebstein lesions due to glycogen deposits. Vascular atheroma, diabetic pyelonephritis |
|
|
WILMS tumor defn |
Embroyonic tumor of primitive epithelial & mesenchymal tissue of the kidney. most common and tumor in young children be 1-6 yrs |
|
|
Wilma tumor etiopathogenesis |
Defect in chromosome 11p13; monozygotic twins; seen with other congenital anomalies; malignancies like osteosarcoma, neuro, retinoblastoma |
|
|
Wilma tumor gross |
Large, spheroidal, replaces most of the kidney. Usually unilateral. C.S shows soft, fishflesh like Grey white or creamy yellow tumor with foci of necrosis & hemorrhage. Grossly identifiable tubular & cartilaginous elements. |
|
|
Willms Tumor microscopy |
Lots of an a plastic, sarxomatoid Timor cells. Abortive tubules, poorly formed glomerular structures, mesenchymal elements like cartilage, bone, fat & fibrous tissue |
|

Label |
Anaplastic sarcomatoid Timor cells, poorly formed glomerulus, abortive tubules |
|
|
Adenocarcinoma of kidney |
Malignant tumor. pathogenesis: tobacco- 20-30% of RNC, genetic factors: con hippel lindau VHL disease, hereditary clear cell RCC, papillary RCC, chromophobe RCC/ cystic diseases of kidney: nephroma, adult polycystic disease. Other risk factors: obesity, asbestos exposure |
|
|
Morphology of renal adenomcarcinoma |

Poles of kidney, solitary & unilateral, large, golden yellow, circumscribed. N & h. Cystic change Microscopy- refer chart |
|

Types and histology |
Clear cell type- solid, trabacular. Papillary- cuboidal with round nuclei. Granular- acidophilic cytoplasm, chromophobe- halo... |
|
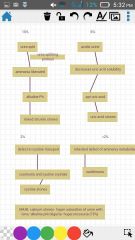
Urinary calculi pathohenesis |

Types of stones diagram |
|
|
Lupus nephritis |
Renal manifestations of systemic lupus. Incidence 40-70%. Two cardinal manifestations are proteinuria & hematuria. Red cell casts, fatty casts & leukocytes Types: 1) minimal lesions, 2) mesangial 3) focal segmental 4) diffuse profilerative 5) membranous 6) sclerosing |
|
|
Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis |
Acute reduction in renal function resulting in renal failure in 2-3 wks. Formation of crescents is characteristic. This is outside glomerular capillaries. formed from epithelial cells lining BC. stimulus is presence of fibrin in capsular space. |
|
|
Morphology of RPGN |
kidneys are enlarged & pale with smooth outer surface . c.s shows pale cortex & congested medulla. glomeruli- cresesents which are collections of pale staining polygonal cells tend to be elongated. They compress glomeruli Tubules- hyaline deposits Intestitium- oedema & fibrosis Vessels- no change Electron microscopy: good pastture linear deposits, post infectious show electron dense sunendothelial deposits If: linear pattern- GP Granular- posy infectious RPGN Scanty -pauci immune |
|

Learn |
Learn it!!! Repeat |

