![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
a) The microsomal ethanol oxidizing system (MEOS)?
1) is a mixed function oxidase, 2) is associated with the endoplasmic reticulum, 3) requires NADPH, 4) requires O2, 5) all of the above, 6) none of the above. |
5) all of the above,
|
|
|
g ) Which carbohydrate is a “so-called” reducing sugar?
1) sucrose, 2) trehalose, 3) lactose, 4) maltose, 5) both 1) and 2) above, 6) both 3) and 4) above. |
6) both 3) and 4) above.
|
|
|
h) Lactose is hydrolyzed by the catalytic active of lactase to generate?
1) glucose only, 2) glucose and galactose, 3) glucose and fructose, 4) fructose only, 5) fructose and mannose, 6) none of the above. |
2) glucose and galactose,
|
|
|
i) Which of the following energy sources provides about 7 kcal/g?
1) proteins, 2) fats, 3) carbohydrates, 4) alcohol, 5) both 1) and 2) above, 6) none of the above. |
4) alcohol = 7
fats = 9 carbs =4 |
|
|
k) Which of the following may serve as a precursor for the synthesis of new glucose?
1) acetoacetic acid, 2) ethanol, 3) palmitic acid (16:0), 4) acetyl-S-CoA, 5) all of the above, 6) none of the above. |
6) none of the above.
|
|
|
m) A Hill plot may give us information about the following:
1) h, the number of binding sites on a protein, 2) Kh, the binding constant for a ligand binding to a protein, 3) whether a plot is hyperbolic or sigmoidal, 4) all of the above, 5) none of the above. |
4) all of the above,
|
|
|
n) An enzyme exhibiting negative homotropic cooperativity?
1) should give an h value less than 1, 2) should exhibit neither hyperbolic or sigmoidal kinetics, 3) may be consistent with the Koshland model, 4) is inconsistent with the MWC model, 5) all of the above, 6) none of the above. |
5) all of the above,
|
|
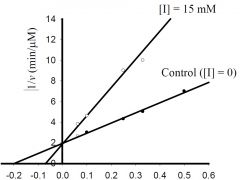
b) What is the approximate KM for the control?
1) 5 mM, 2) -0.5 mM, 3) 0.5 μmol/min, 4) -0.2 mM, 5) 2 μmol/min 6) none of the above. |
1) 5 mM,
|
|
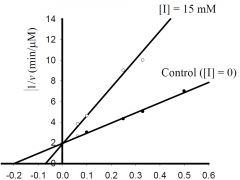
c) What is the approximate Vmax for the control?
1) 5 μM/min, 2) 5 mM, 3) 0.5 μM/min, 4) 100 μM/min, 5) 20 mM, 6) none of the above. |
3) 0.5 μM/min,
|
|
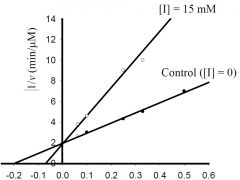
d) What type inhibitor is I?
1) competitive, 2) uncompetitive, 3) pure-noncompetitive, 4) mixed, 5) all of the above, 6) none of the above. |
1) competitive,
|
|
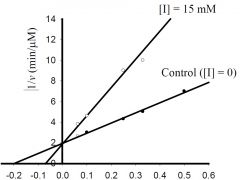
e) What is the approximate value for KI or KI’?
1) 0.2 mM, 2) 2 min-1, 3) 3 mM, 4) 5 μM/min, 5) 20 mM, 6) none of the above. |
6) none of the above.
|
|
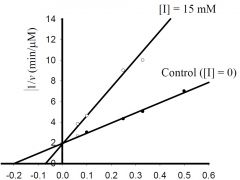
f) If [ET] = 0.025 μM, kcat is about?
1) 2 mM, 2) 2 min-1, 3) 0.2 μM/min, 4) 20 min-1, 5) 5 μM/min, 6) none of the above. |
4) 20 min-1,
|
|
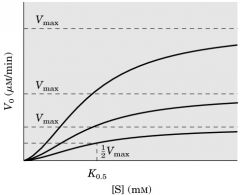
j) The observed curves are indicative of:
1) a Michaelis-Menten type enzyme, 2) a K-series enzyme, 3) a V-series enzyme, 4) all of the above, 5) none of the above. |
3) a V-series enzyme,
|
|
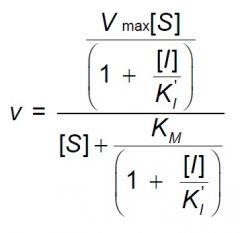
l) The equation below is characteristic of what type inhibitor?
1) competitive, 2) uncompetitive, 3) non-competitive, 4) mixed, 5) all of the above, 6) none of the above. |
2) uncompetitive
|
|
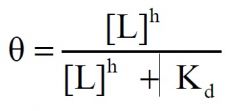
r) Consider the equation:
If h = 2, this equation predicts what type of ligand binding curve? 1) hyperbolic, 2) sigmoidal, 3) neither hyperbolic or sigmoidal, 4) linear, 5) none of the above. |
2) sigmoidal
|
|
|
o) According to the MWC model, an allosteric (heterotropic) inhibitor should have what effect on the relative value of L?
1) increase L, 2) decrease L, 3) have no effect on L, 4) all of the above, 5) none of the above. |
1) increase L,
|
|
|
__________p) Which of the following compounds may be converted to new glucose in mammals?
1) palmitic acid (16:0 fatty acid), 2) malic acid, 3) acetate unit of acetyl-S-CoA, 4) none of the above, 5) all of the above. |
4) none of the above,
|
|
|
q) In a Scatchard plot the following parameters are plotted on the y-axis?
1) [Bound], 2) [Free], 3) [Free]/[Bound], 4) [Bound]/[Free]), 5) none of the above. |
3) [Free]/[Bound],
|
|
|
s) Which of the following compounds can act as a substrate for the enzyme, hexose kinase?
1) glucose, 2) fructose, 3) mannose, 4) all of the above, 5) none of the above. |
4) all of the above,
|
|
|
t) If h is 2, the cooperativity index is?
1) 1, 2) 3, 3) 4, 4) 9, 5) 81, 6) none of the above. |
4) 9,
|
|
|
--- Animal Cells ---
GLYCOGEN to LACTIC ACID Pathway Intermediates? |
GLYCOGEN > glucose-1-P > glucose-6-P > steps in glycolysis > pyruvate > LACTIC ACID
|
|
|
--- Animal Cells ---
GALACTOSE to synthesis of new GLYCOGEN Pathway Intermediates? |
GALACTOSE > UDP-galactose > UDP-glucose > GLYCOGEN
|
|
|
--- Animal Cells ---
ETHANOL to GLUCOSE Pathway Intermediates? |
ethanol cannot serve as a precursor of new glucose in animals
|

