![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
122 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
QC cell count steps |
combined. 2. Find the square root of the sum and multiply by 2. If this product is higher than the diff, continue, if not, make new slides. 1. Find sum, ave, and diff of sides A and B combined.2. Find the square root of the sum and multiply by 2. If this product is higher than the diff, continue, if not, make new slides.3.Sum × 10 × dilution ÷ # squares used to find the sum (remember 1 5×5 square counts as 1, not 25).4. Round answer as mm^3. # squares used to find the sum (remember 1 5×5 square counts as 1, not 25). 3.Sum × 10 × dilution ÷ # squares used to find the sum (remember 1 5×5 square counts as 1, not 25).4. Round answer as mm^3. 4. Round answer as mm^3. |
|
|
Pyuria Definition1 What does it bring about1 Clin sig3
|
Wbcs in the urine. Brings about pus. Infection/inflammation anywhere in the tract, pancreatitis. |
|
|
What does protein pos, RBC pos and wbc pos? Disease1 Syndrome1 What and how are 2 other diseases caused? |
Proteinuria. A nephrotic syndrome. Most of the protein lost is albumin because the podocytes are damaged. This leads to hypoalbuminemia, which causes edema. |
|
|
Explain difference between nephrotic syndrome and nephritic syndrome. |
Nephrotic only loses proteins, mostly albumin. Nephritic also loses protein and rbcs because the condition is more advanced. |
|
|
What happens when you leave a hypotonic, SG<1.008 out for 2 hours? |
Wbcs break down up to 50% |
|
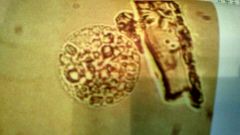
What is it? Definition1 Clin sig5 |
Oval fat body. Renal tubular cell containing fat. Chronic glomerulonephritis, D. Milletus, lipid nephrosis, eclampsia, and fat embolism. |
|
|
What would you do to help you distinguish between rbcs and yeast? |
Apply 1 drop of acetic acid to the slide. The rbcs will lyce. |
|
|
Casts Clin sig4 |
Renal failure, anuria, acidic blood or high solutes. |
|
|
What is body fluid made out of? Composing parts3 Percentages. |
Water, electrolytes and other chemicals. Intracellular 55% Extracellular 45% |
|
|
How is body fluid regulated? |
Hydrostatic/Osmotic pressure. |
|
|
Transudate Definition1 Sometimes it causes1 |
Fluid that passes through a membrane which filters out all the cells and much of the protein, yielding a watery solution. Sometimes this fluid accumulates and causes edema. |
|
|
Exudate Definition1 What's the purpose1 |
Fluid rich in protein and cellular elements that oozes out of the blood vessels due to inflammation. The idea is to restore the permeability of the blood vessels. |
|
|
What color are CSF, synovial fluid and serous fluid normally respectively? |
The 1st 2 are colorless and clear while the 2nd is slightly yellow and clear. |
|
|
For body fluids, match the turbidity with the color. Clear Hazy Cloudy Milky Oily Purulent-Wbc presence Pellicle |
Colorless Pink or red Serous Sanguinous Xanthochromic-Hgb degradton Yellow/green-sepsis Excess protein |
|
|
What's the advantage of cytocentrefugation? |
A cytologist can identify the cells more easily by staining them. |
|

What is it1 Clin sig1 Notes1 |
Starch Cornstarch Lycopodium |
|
|
Ketones Normal range1 Clin sig5 Confirm test1 |
Diabetic ketoacidosis, stones (with crystals on scope), fasting, vomiting and exercise. Acetest |
|
|
PH Normal range1 Clin sig6 I-Sub1
|
4.0-8.0 Acidic-diabetes, fever, emphysema. Alkaline-Chronic renal failure, tubular acidosis, UTI. "Run-over" |
|
|
Urobilinogen Normal range1 Clin sig4 Confirm test1 |
Norm or 0.2 Liver disease, GI block, anemia, hemolysis. Watson/Ehrlich's reagent |
|
|
Blood Normal range1 Clin sig6 I-Sub2 Confirm test1 |
Neg Hematuria, myoglobinuria, hemoglobinuria, UTI, anemia, stones, injury High bacteria, menstral blood Microscope |
|
|
Calcium Sulphate |
Looks exactly like calcium phosphate, one is acidic, the other isn't. |
|
|
All alkaline crystals5 |
Triple phosphate, amorphous phosphate, calcium phosphate, calcium carbonate, ammonium biurates. |
|

What is it1 Clin sig5 |
Calcium oxalate Diabetes, liver/renal disease, ethylene glycol poisoning, stones, |
|

What is it1 Clin sig2 Notes1 |
Tyrosine Severe liver disease, tyrosinosis Careful. Looks just like sulphamide drug. |
|

What is it1 Clin sig1 Notes1 |
Mucus threads Tract inflammation Tends to hold onto wbcs |
|
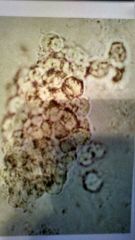
What is it1 Clin sig2 |
Wbc cast Acute pylophritis or renal infection/inflammation |
|
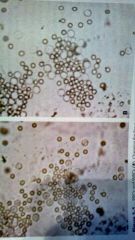
What is it1 Clin sig3 Notes1 |
Rbcs Injury, hematuria infection/inflammation A comparison must be made with proteins. |
|
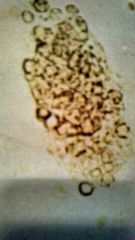
What is it1 Clin sig3 |
RBC cast Pathologic renal hematuria, glomerulonephritis or a half dozen other things. |
|
|
Nitrite Normal range1 Clin sig2 Notes1 |
Neg Asymptomatic bacturiuria, UTI If RBC pos, wbc pos and nitrite pos, definitely UTI |
|
|
Protein Normal range1 Clin sig2 I-Sub1 Confirm test3 |
Neg-Trace Glomulonephritis, pylophritis Rbcs can falsely elevate. SSA, white foam, casts on the microscope |
|

What is it1 Clin sig2 |
Cystine Congenital cystanosis Congenital cystanuria |
|
What is it1 Clin sig1 |
Sulfonamide crystals Sulfonamide drugs |
|

What is it1 How is it made1 Clin sig3 Notes2 |
Cholesterol From degraded renal tube cells Tissue breakdown, nephritis, lymph damage Urine may be white, Looks more like New Mexico than in the picture. |
|

What is it? Clin sig2 |
Bilirubin crystals Liver damage, jaundice |
|
|
Anuria |
<600 ml urine output in 2-3 days |
|
|
Polyuria 2 Different causes |
An abnormal increase in urine volume. Brought on by both diabetes milletus/insipidus. |
|
|
Oliguria |
An abnormal decrease in urine volume, brought on by shock or acute nephritis. |
|
|
No picture because there are too many shapes. What is it1 Clin sig1 Notes1 |
Bacteria UTI If you see wbcs, definitely UTI. |
|
What is it1 Clin sig1 Notes1 |
Yeast UTI UTI especially with diabetes. |
|
|
Glucose Normal range1 Clin sig1 Confirm test1 |
Neg Glycosuria Clinitest on reducing substances |
|

What is it1 Clin sig1 |
Coarse and fine casts Significant renal failure. |
|

What is it1 Notes1 |
Hippuric acid Always have pointed ends. |
|
|
Bilirubin Normal range1 Clin sig2 Confirm test1 |
Neg Liver damage, jaundice Ictotest |
|

What is it1 Clin sigs1 |
Trichomonas vaginalis STD |
|
What is it1 Clin sig3 Notes1 |
Wbc Acute Pylonephritis, infection/inflammation, UTI They glitter when they inflate. |
|
|
Factors that influence the making of casts5 What are they made out of 1 |
Renal failure Anuria/urinary stasis Acidic urine High solute concentration Pos protein is indicative Tam-hosfall microprotein |
|
What is it1 Clin sig3 |
Headline cast It could be in normal urine, because of exercise or disease or dehydration |
|
|
What are epithelial cell casts indicative of2 |
Some kind of tubular problem because that's where the cells come from, also nephrotoxins. |
|

What is it1 Clin sig4 |
Waxy cast Severe chronic renal failure, pylonephritis, hypertension, amylodosis (high protein) |
|
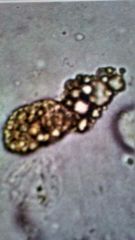
What is it1 Clin sig2 |
Renal tube degradation Lipoid nephrosischronic |
|
|
Which crystals are caused by inheritance4 |
Cystine, leucine, tyrosine, cholesterol. |
|
|
Acute glomerulonephritis What would you see on the scope3 |
Protein, blood, casts |
|
|
Monilliasis |
Yeast infection |
|
|
How is bilirubin formed1 |
Breakdown of rbcs |
|
|
Why is the a divit in the rbcs? |
That's where the hgb sits to carry the O2. |
|
|
Does e.coli give a pos nitrite? |
Yes |
|
|
Diapedesis |
Getting wbcs out of circulation and into the tissues to fight stuff. |
|
|
What can create clearance tests and gfr be used to detect? |
An eGFR which can be used to detect chronic kidney disease. |
|
|
Suprapubic Why is it used2 |
Single urine sample, cytology studies. |
|
|
24 hour urine Why is it used2 |
Crea, protein |
|
|
Clean catch Why is it used2 |
Culture, regular UA |
|
|
Catheter Why is it used2 |
Avoid VD, trouble voiding |
|
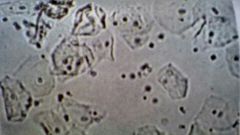
What is it1 Clin sig1 |
Squamous Vaginal contamination |
|
|
Business CAP1 QA1 QC1 |
Sends unknown samples of your tests to test you on them Uses a variety of methods to insure compitance Sets procedures and protocols. |
|
|
Refractive index |
The velocity of light in a sample vs. The velocity in the air |
|
|
Osmolarity vs SG |
Osmolarity measures the number whereas SG measures the weight |
|
|
What does ADH do1 What do low amounts of it cause1 |
Regulates the absorption of water in the distal. When the body needs water, ADH is secreted. Low amounts can lead to D.Incepidus |
|
|
D.Insipidus |
Inability to concentrate urine. |
|
|
What is urochrome1 Where does it come from1 |
Gives urine its color. The more there is, the darker the urine. It comes from the breakdown of bilirubin, which it self comes from the breakdown of rbcs. |
|
|
Random UA Why is it done3 |
Regular UA, post-pranial, urobilinogen |
|
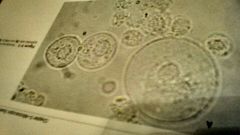
What is a,b,c1 Clin sig of a1 |
Trans,renal,wbc UTI because it comes from the bladder |
|

What is it1 |
Amorphous urates |
|

What is it1 Clin sig1 |
Radiographic dye crystals X-ray |
|
|
What causes chyle |
Lymph destruction |
|
|
What is the most common cause of UTI? |
E.coli from your normal flora. |
|
|
How can you tell if a teen has orthostatic/positional protein? |
The morning void is neg and the random is pos |
|
|
What is high bacteria, lyced rbcs and low casts indicative of? |
Alkaline urine |
|
|
Thrombopoitein |
A hormone made by the liver and kidneys to make platelets |
|
|
What is proteinuria1 What causes it3 |
High protein in the urine. Various glom disorders, fever, exercise |
|
|
Where does urobilinogen come from? |
Bilirubin and albumin become conjugated in the liver. They then enter the small intestine and are converted to urobilinogen by the good bacteria. urobilinogen by the good bacteria. |
|
|
Abnormal urine color. Match color to cause Clear White Yellow orange Yellow green Pinkred Redpurple Redbrown Brownblack Bluegreen |
D.Insipidus Chyle, pyuria Bilirubin, urobilin Bilirubin, biliverdin Porphyrins Methemoglobin Hgb,myoglobin Porphyrins Methemoglobin Homogensic acid, melanin Biliverdin, idicans |
|
|
Specific gravity Normal range1 Confirm test1 |
1.005-1.025 Refractometer |
|
|
Hematuria |
Intact rbcs in the blood. Blotchy on the pad. |
|
|
Myoglobiuria Clin sig1 |
The heme protein the RBC. Heart/muscle damage |
|
|
Hemoglobinuria Clin sig1 |
Free hgb floating around. Blue to black on the pad. IV hemolysis |
|
|
What is anuria1 What causes it1 |
Almost a complete stoppage of urine flow. Brought on by medulla over-saturated. |
|
|
What is hypostenuria1 What causes it1 |
Constant low SG A concentration problem |
|
|
Leukocyte esterase Normal range1 Clin sig5 I-Sub2 Confirm test1 |
Neg UTI, infection/inflammation, glom neph, pancreatitis, cystitis Microscope |
|
|
What is glycosuria 1 What causes it3 Notes1 |
High glucose in the urine High blood-glucose, GFR, tube reabsorption Clinitest on all patients >2 years old |
|
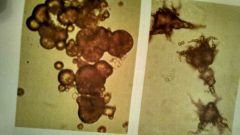
What is it1 |
Ammonium biurates |
|

What is it1 Clin sig4 |
Triple phosphate Chronic pylitis, chronic cystitis, enlarged prostate, anuria. |
|

What is it1 |
Sodium urate |
|

What is it1 Clin sig2 |
Calcium phosphate Normal or stones |
|
|
What happens to rbcs in a: Hypotonic solution1 Hypertonic solution1 |
Low SG lyce and lose their hgb. High SG creanate/shrivle |
|
|
What happens to wbcs in hypotonic solutions? |
Inflate and glitter. |
|
|
What is sturnheimer-malbin? |
A stain composed of crystal-violet and safranin. Used for urine samples. |
|
|
What is the best specimen for a routine UA? |
First morning void. |
|
|
Quantitative urine tests are performed on which specimens? |
Timed specimens |
|
|
Does D.Milletus interfere with the production of ADH? |
No |
|
|
What does a pos glucose and pos ketones mean1 How does this happen1 |
Diabetes The body can't use the glucose, so it has to use fat. When the fat is broken up, it makes ketones. |
|
What is it1 |
Amorphous urates |
|
|
Glomerulonephritis1 What do you see in urine3 Origin1 Syndromes2 |
General term for sterile inflammatory things affecting the glom. Blood, protein, casts Immune in origin Nephrotic and nephritic syndromes. |
|
|
Nephrosis1 You see in the urine1 Clin sig2 Notes1 |
Degeneration of the kidney via damage to the basement membrane, causing the podocytes charges to change. Protein Tubular damage, edema. No inflammation |
|
What is it1 Clin sig2 Notes1 |
Leucine Maple syrup urine disease, cirrhosis. Usually seen with tyrosine |
|

What is it1 Clin sig3 |
Uric acid Gout, chronic nephritis or normal urine |
|

What is it1 |
Calcium carbonate |
|
What is it1 Clin sig1 |
Trichomonas vaginalis STD |
|
|
What is the counter-current mechanism? |
Causes water to be reabsorbed at the descending limb and solutes without water to be reabsorbed at the ascending limb. |
|
|
Renin cascade steps |
Made by juxmed cells, reacts with angiotensinogen to make angiotensen I. Reacts with ACE in the lungs to make angiotensen II. It affects dilation/constriction by stimulating Na reabsorption by releasing aldosterone in the adrenal and ADH in the pituitary. |
|
|
What is a threshold substance1 What is it for glucose1 |
Substances that are almost completely reabsorbed. Glucose is 160-180 |
|
|
What is GFR1 What can it be used to detect1 |
The amount of plasma filtered through the gloms in a given time Kidney disease. |
|
|
Cystitis |
Inflammation of the bladder |
|
|
Nephritis1 |
Inflammation of the kidneys with or without infection. |
|
|
Pylonephritis Acute1 What will you see1 Chronic1 What will you see7 |
Wbcs in the urine with pus, caused by... Acute-Bacteria backing up in the system. Wbc casts Chronic-Lots worse Tubular damage, renal failure, granular casts, waxy casts, protein, hematuria, low SG |
|
|
Glomeruler disorders1 Immune1 Non-immune3 |
Any disease affecting the filtration membrane. They can be immune in origin, brought on by immune complexes, increasing IgA. They could also be brought on by membrane thickening, charge interference, toxins, amyloid disposition |
|
|
Acute poststreptococcal glom neph (AGN) What causes it1 About it1 You'll see5 |
Group A strep laryngitis They have a protein M cell wall Hematuria, proteinuria, oliguria, RBC casts, hyaline casts |
|
|
Rapid progressive glom neph3 You'll see2 |
Systemic immune disorder. Macrophages damage capillary walls. Fibrin causes permanent damage to small vessels. High protein, low GFR |
|
|
Goodpastuer syndrome What does it affect2 What does it lead to2 You'll see3 |
Autoimmune disease affecting the glom and alviolar membranes. Chronic glom neph, and RF Hemoptsis, hematuria, proteinuria, RBC casts |
|
|
Wenger's syndrome1 It has1 You'll see4 |
Inflammation of the small vessels of the lungs and kidneys Granulomas-localized inflammation (I think) Hematuria, proteinuria, RBC casts, high BUN/CREA |
|
|
Henoch-Schonlein purpura3 You'll see3 |
Children after resp. Infection, raised red particles in the skin, bloody sputum. Hematuria, proteinuria, RBC casts. |
|
|
Membranous glom neph1 Diseases it leads to3 You'll see2 |
IgG complexes affect basement membrane. Systemic lupus, hep B, thrombosis Hematuria, proteinuria. |
|
|
Membranousproliferative glom neph Type I2 Type II2 You'll see on both2 |
Thickening of cap. Walls, leads to nephrotic syndrome Thickening of glom. Membrane, leads to chronic glom. Neph. Hematuria, proteinuria. |

