![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
124 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

|
Lymphocyte
|
|
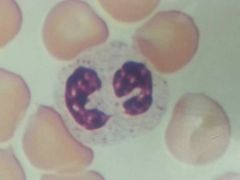
|
Neutrophil
|
|
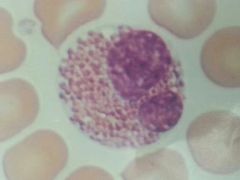
|
Eosinophil
|
|
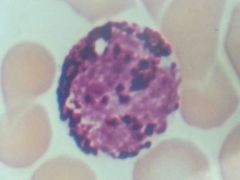
|
Basophil
|
|

|
Monocyte
|
|
|
Formed elements make up what percentage of whole blood?
|
45%
|
|
|
Plasma makes up what percentage of whole blood?
|
55%
|
|
|
What are the five leukocytes?
|
1. Neutrophil
2. Lymphocytes 3. Monocytes 4. Eosinophil 5. Basophil |
|
|
Normal hematocrit value for adults?
|
Female: 37 - 48%
Male: 45 - 52% |
|
|
Hemoglobin values for normal adults?
|
Female: 12 - 16g/100Ml
Male: 13 - 18g/100Ml |
|
|
Normal range of platelets for adults?
|
130,000 - 360,000 platelets/ul
|
|
|
Which antigen is on type A blood
|
A antigen
|
|
|
Which antigen is on type B blood?
|
B antigen
|
|
|
Which antigen is on type AB blood?
|
A & B antigens
(universal recipient) |
|
|
Which antigen is on type O blood?
|
No antigen
(universal donor) |
|
|
Which antibodies are on type A blood?
|
Anti B antibodies
|
|
|
Which antibodies are on type B blood?
|
Anti A antibodies
|
|
|
Which antibodies are on type AB blood?
|
No antibodies
(universal recipient) |
|
|
Which antibodies are on type O blood?
|
Anti A & B antibodies
(universal donor) |
|
|
What are the normal total blood count ranges?
|
RBC count for females: 4.0 - 5.5 million cells/ul
RBC count for males: 4.5 - 6.0 million cells/ul WBC count for females and males: 4,300 - 10,800 cells/ul |
|
|
Heparin
|
Anticoagulant
|
|
|
Hemoglobin
|
Oxygen carrying protein
|
|
|
Deficiency of hemoglobin
|
Iron-Deficiency anemia
|
|
|
Measures the amount of hemoglobin.
|
Hemoglobinometer
|
|
|
Vitamin & mineral crucial to clotting process?
|
Vitamin K & Calcium
|
|
|
Stoppage of blood?
|
Hemostasis
|
|
|
Protein produced for clotting?
|
Fibrin
|
|
|
Clumping of red blood cells?
|
Agglutination
|
|
|
Deficiency of red blood cells?
|
Anemia
|
|
|
Elevated RBC count.
|
Erythrocytosis/Polycythemia
|
|
|
Deficiency of leukocytes?
|
Leukopenia
|
|
|
Device that counts the number of WBCs & RBCs?
|
Hemocytometer
|
|
|
Lubb
|
1st sound, closing of the cuspid valves.
|
|
|
Dupp
|
2nd sound, closing of the semilunar valves
|
|
|
Gurgling sound made by the back flow of blood is?
|
Heart murmur
|
|
|
Blood pressure
|
Force exerted by blood on the walls of blood vessels.
(occurs because of ventricals contractions) |
|
|
Cuff used to measure blood pressure?
|
Sphygmomanometer
|
|
|
120/80 what does the 120 represent?
|
Systolic pressure
|
|
|
The ventricle is ____________ during systolic pressure.
|
contracting
|
|
|
120/80 what does the 80 represent?
|
Diastolic pressure
|
|
|
The ventricle is ____________ during diastolic pressure.
|
relaxing
|
|
|
What is Korotkoff's sounds?
|
Sound of blood flowing turbulently through a partially constricted vessel.
|
|
|
Systolic pressure minus diastolic pressure is?
|
Pulse pressure
|
|
|
Hypertension
|
High blood pressure
|
|
|
Artery of the cervical region?
|
Carotid artery
|
|
|
Artery of the antibrachial region?
|
Radial artery
|
|
|
Artery behind the knee?
|
Popliteal artery
|
|
|
What is pulse?
|
Wave of pressure that can be palpated in the major arteries.
|
|
|
What is pulse rate?
|
Beats per minute
|
|
|
A high heart rate is called?
|
Tachycardia
|
|
|
A low heart rate is called?
|
Bradycardia
|
|
|
What is automaticity/autorhymicity?
|
Spontaneous generation of action potentials in the absence of neural or hormonal stimulation.
|
|
|
Name the cardiac conduction system (nodal system) in order.
|
1. sinoatrial (sa) node
2. atrioventricular (av) node 3. atrioventricular (av) bundle (bundle of HIS) 4. (left & right) atrioventricular (av) branches 5. purkinje fibers |
|
|
What is an electrocardiogram (ECG)?
|
Recording (paper)
|
|
|
What is an electrocardiograph?
|
Instrument used to take an ECG
|
|
|
The P-wave represents?
|
Atrial depolarization
|
|
|
The QRS complex represents?
|
Ventricle depolarization (hidden atrial repolarization)
|
|
|
What is hidden in the QRS complex?
|
Atrial repolarization
|
|
|
The T-wave represents what?
|
Ventricular repolarization
|
|

Name what this is.
|
Electrocardiogram
|
|
|
An elevated level of WBCs is called what?
|
Leukocytosis
|
|

What is the arrow pointing at?
|
T-wave
|
|

What is this device called?
|
Hemocytometer
|
|

Name this device.
|
Microhematocrit reader
|
|

Name this.
|
Heparinized capillary tube
|
|

Name the highlighted area.
|
QRS complex
|
|

What is the arrow pointing at?
|
P-wave
|
|
|
Pulmonary circuit
|
Right side - de-oxygenated
|
|
|
Systemic circuit
|
Left side - oxygenated
|
|
|
The outer most membrane of the heart?
|
Parietal pericardium
|
|
|
What is the space between the parietal pericardium & the visceral pericardium?
|
Pericardial cavity
|
|
|
What is the membrane that tightly covers the heart?
|
Visceral pericardium
|
|
|
Name the membrane lining the heart chambers.
|
Endocardium
|
|

Name this region of the heart.
|
Apex
|
|

Name the structure at the end of the probe.
|
Papillary muscle
|
|

Name this structure.
|
Myocardium
|
|

Name this structure. The structure is in the wall of the atria & auricles. The above photo is of an atria.
|
Pectinate muscle
|
|
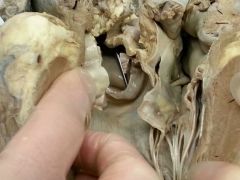
Identify the structure the probe is pointing to.
|
Semilunar valve
|
|

What is the probe pointing at?
|
Chordae tendineae
|
|
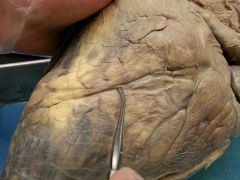
Name this depression.
|
Anterior interventricular groove/sulcus
|
|
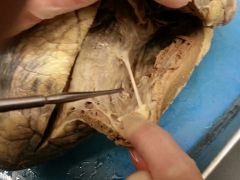
What is the probe pointing at?
|
Moderator band
|
|

Name this specific type of lab equipment.
|
Lancet
|
|
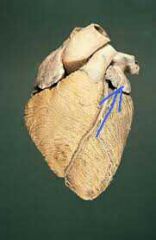
Name this.
|
Left auricle
|
|

Name this tissue.
|
Adipose tissue
|
|

Name this region.
|
Base
|
|

Name these vessels.
|
b. coronary arteries
c. coronary (cardiac) veins |
|

Name this.
|
Ligamentum arteriosum
|
|
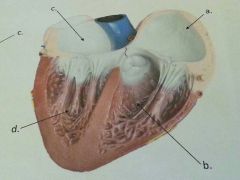
Name a, b, c, & d.
|
a. right atrium
b. right ventricle c. left atrium d. left ventricle |
|
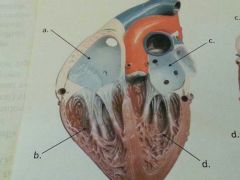
Name a, b, c, & d.
|
a. right atrium
b. right ventricle c. left atrium d. left ventricle |
|

What is e pointing to?
|
Interatrial septum
|
|

What is the arrow pointing at?
|
Fossa ovalis
|
|

What is b?
|
Fossa ovalis
|
|

What is d?
|
Pectinate muscle
|
|
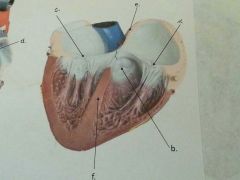
What is f?
|
Interventricular septum
|
|

Name this.
|
Trabeculae carnae
|
|

What is a?
|
Chordae tendineae
|
|

What is b?
|
Papillary muscle
|
|
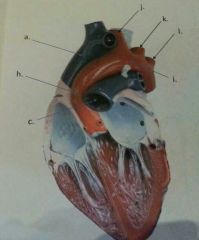
What vessel is "a" pointing to?
|
Superior vena cava
|
|
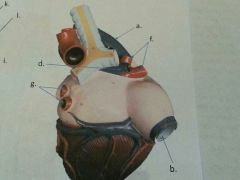
What is b?
|
Inferior vena cava
|
|

Name this. It is located in the right atrium.
|
Opening to the coronary sinus
|
|

Name c.
|
Bicuspid valve
|
|
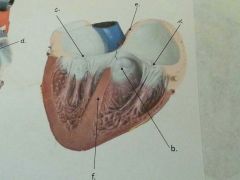
Name b.
|
Pulmonary semilunar valve
|
|

Name c.
|
Pulmonary trunk
|
|
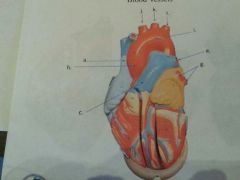
Name c.
|
Pulmonary trunk
|
|

What is d?
|
Right pulmonary artery
|
|
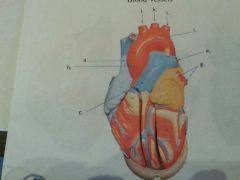
What is e?
|
Left pulmonary artery
|
|

What is f?
|
Right pulmonary veins
|
|

What is g?
|
Left pulmonary veins
|
|
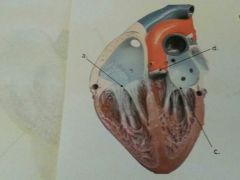
What is c?
|
Biscuspid (mitral) valve
|
|

What is c?
|
Bicuspid (mitral) valve
|
|

What is d?
|
Aortic semilunar valve
|
|
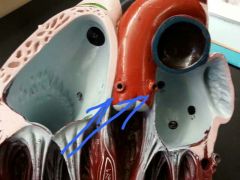
Name the openings.
|
Openings to the coronary arteries
|
|
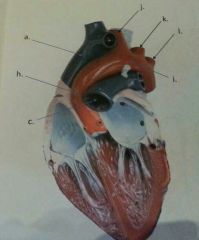
What is h?
|
Ascending aorta
|
|

What is i?
|
Aortic arch
|
|

Name j.
|
Brachiocephalic artery
|
|

Name k.
|
Left common carotid artery
|
|

Name L.
|
Left subclavian artery
|
|

What is a?
|
Sinoatrial (SA) node
|
|

What is b?
|
Atrioventricular (AV) node
|
|

Name c.
|
Atrioventricular (AV) bundle (bundle of HIS)
|
|

Name e & d.
|
Left & right atrioventricular (AV) bundle branches
|
|

Name this part of the conduction system.
|
Purkinje fibers
|
|
|
Name the three formed elements of whole blood.
|
1. erythrocytes
2. leukocytes 3. platelets |
|
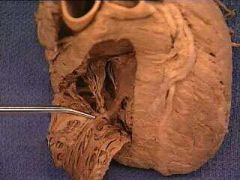
Name this.
|
Trabeculae carnae
|

