![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
56 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is classical learning |
Learning of reflexes |
|
|
Assignment |
Everything I do, should be linked to theory. They will be looking at theoretical evidence when marking. |
|
|
Classical conditioning |
Origins of field: Experiments on reflexes conducted Russian physiologist. Conditioning/learned Respondent learning. Reflect conditioning Classical conditioning is learning of reflexes. Replace conditioning with learning, skinner didn’t like the word learning. |
|
|
Neutral stimulus Extinction |
Repeated exposure If you repeatedly expose patients to their fear, they will realise, if they keep facing a situation,nothing bad will happen. Next time they go into situation they will feel less fear. |
|
|
Behaviour |
Everything we do is a behaviour. Right now your heart is beating, is your heart doing something. There what your heart is doing is a behaviour. Behaviour will include thoughts, physiological symptoms, feelings and observable behaviours. |
|
|
Positive reinforcement |
Something good happens is positive reinforcement
This is tough, your doing well will give patient a sense of achievement. Makes patient feel a sense of hope even when not doing well. |
|
|
Frontal lobe |
I will say to myself, I’m not brave enough |
|
|
Exposure |
When we do exposure the needs to be prolonged enough so that our fear reduces. |
|
|
Classical conditioning learning Respondent learning. Re place respondent to reflex learning Classical conditioning is the learning of reflexes |
Classical conditioning is the learning of reflexes. |
|
|
Can we learn reflexes |
Yes |
|
|
Antecedent is situation. Behaviour is strategy Consequence is situation Operant schedule |
The bell has become a learned stimulus. |
|
|
Operant principles |
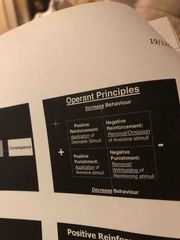
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Positive reinforcement |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Operant model |
Learning of behaviours |
|
|
What are strategies |
Operant behaviours |
|
|
Negative reinforcement |
If something bad is taken away it is called negative reinforcement What is seems as rewarding to one patient can be seen as punishing to another. |
|
|
What is rumination |
Rumination is a strategy as it is something you are doing which is under your control |
|
|
Negative automatic thoughts |
Are reflexes, we don’t challenge reflexes, we normalise them in behavioural activation. Normalise negative automatic thoughts, target rumination. |
|
|
Repeat: extinction Prolonged-habituation Graded -engaged Focused -learning |
Repeat: extinction Prolonged-habituation Graded -engaged Focused -learning |
|
|
Vacations Learning |
When you learn from other people |
|
|
Operant schedules |
Antecedent:situation at street corner with friends. Behaviour/strategy telling dirty jokes Situation/consequence laughing and paying attention Consequence/situation laughing and paying him attention Operant schedule/ positive reinforcement |
|
|
Negative reinforcement is the removal of a stimulus which increases the likelihood of a behaviour recurring in the presence of a given trigger.
|
Antecedent: electric shot rat Behaviour: pressing of bad Situation/consequence: Removal of electric shock This is negative reinforcement |
|
|
Info |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Extinction |
If you keep repeating something, you learn nothing happens and there is no danger. |
|
|
Neutral stimulus |
The spider was initially a neutral stimulus for the baby. However when the baby screamed it was learned stimulus.
The bell for the dog 🐕 was initially a neutral stimulus for the dog but later it was a learned stimulus. |
|
|
Avoidance modification: |
-Help clients understand discomfort experienced following a situational trigger is followed by an action to extinguish the aversive experience. Avoidance services as an adaptation function in short term. However in the longer term avoidance maintains depression and prevents addressing actual triggers. -there is important to identify alternative coping strategies that break avoidance patterns. Allow modification of situational triggers. |
|
|
Exposure |
The aim of exposure is to correct misinterpretations. |
|
|
Operant schedule |
Learning of strategies Coping mechanism |
|
|
Purpose of assessment is |
-Diagnosis -Case formulation -Treatment Planning -Treatment monitoring & Evaluation |
|
|
Diagnosis |
Accurate diagnoses are essential for evidence based psychological Practice. |
|
|
Models to use |
-Social phobia and agoraphobia David Clarke. GAD DUGAS Beck cognitive therapy OCD Kozak or Stekette |
|
|
CBT |
Nice recommended for depression and anxiety. In 2008 only a few clients were able to access it. Nhs 5 year forward plan. Helping people to stay employed, social inclusion and employment. Provision accreditation first year, full accreditation 2nd year. |
|
|
PTSD |
Guidance states you can’t do trauma work with someone who has been self harming in last 3 months.
Discuss clients who are supervising in supervision. Familiarise yourself with iapt manual |
|
|
Disorders you will be treating are |
OCD Depression PTSD specific Disorder Social phobia GAD Panic Disorder |
|
|
Threshold for Caseness in IAPT/ cut off |
-PHQ 9 = 10 -GAD 7 = 8 -Phobia Scales = 4 -Agoraphobia mobility Inventory (MI) =2.3 -Health Anxiety Inventory (Short week) (SHAI) = 18 -Obsessive Compulsive Inventory (OCI) =40 -Impact of Events Scale (IES-R =33 -Social Phobia Inventory (SPIN) = 19 -WASAS =10 |
|
|
Patient |
Make sure they have a note book or a electronic device to write down key learning points for them from the session. Learning points will be the points which you put in relapse prevention plan. Replaces prevention starts when treatment begins. Keep therapy simple. |
|
|
Diagnosis and formulation go hand in hand. All evidence based cbt is based on diagnosis. |
Diagnosis and formulation go hand in hand. All evidence based cbt is based on diagnosis. Need to use DSM 5 when doin a diagnosis. codes for icd10 and DSM are the same.
ADSM scale should be administered every session with PHQ9 and GAD 7. Become familiar with DSM5 criteria. |
|
|
PTSD questions |
When you recall the incident do you feel anxious? Do you find your more irritable PTSD think about cognition Additional Disorder Specific Measures (ADSMS) |
|
|
Which of these problems would you day is having the main impact? IE safety, functioning, distress.
|
Which is the main problem in terms of safety, functioning, and distress. |
|
|
Operant behaviour |
Learning of strategies |
|
|
Strategies can be reinforced if something good is happening or something bad is taken away |
X |
|
|
Strategies can be reinforced if something good is happening or something bad is taken away |
X |
|
|
Psychological problems and problem behaviours will involved negative reinforcement. Positive means did it involve the application of something. |
Psychological problems and problem behaviours will involved negative reinforcement. Positive means did it involve the application of something. Something bad is happening is positive punishment. Positive punishment is avoidance. Negative punishment go to shake someone and they don’t shake hand. They held something good so this is why it is negative punishment.
|
|
|
Positive punishement |
You go to shake someone’s hand and they don’t put thief hand out. It is the holding of something good. |
|
|
Habituation is? decrease in |
A decrease in response to a stimulus during its presentation. Think about the example you go to the see and dip your toes as the water is freezing cold. |
|
|
Habituation/ Desensitisation |
The principle about when we get in the sea. So we go the sea side and we go into the sea and after a while what happens to the feeling of the sea. Initially you go into the sea and it feels freezing cold, and your like huh huh it’s cold. But Once you Finally get to the point, where you do, what you need to do and that is fully emerse yourself. I do this really rubbish thing, which is the bit by bit approach and you know it’s not the best way but you just do it and after a while you think this is just stupid. When you get up to your waste and the waves are coming in duda dah and your like huh huh.
The point is when you dunk yourself , what happens after a while, does the sea stay as cold no.It gets warmer.
So Does that mean with our bodies we have heated up the entire Atlantic Ocean? And The Answer is no, we have habituated. But the principle being that when we are faced with a stimuli after a while we get used to it. Exposure therapy works in the same way. When we confront a feared stimulus, if we don’t avoid after a while we get used to it. Just in the same way we get used to the cold sea. The sea starts to feel warmer, you will start to feel warmer as we do this process. |
|
|
Habituation |
We get Extinction within in practice and we get it across practice. The extinction bit is the most important. Why do we even care about habituation. The key answer is that Habituation gives the patient an incentive to keep on practicing. There is fairly good evidence showing that those patients that don’t habituate within practice can still get a good treatment outcome. The problem is that if they don’t get habituation, they often don’t want to keep practicing. So The way I would think about habituation is that experience, actually this gets easier, is enough for them to keep them doing their home work. |
|
|
Habituation/psycho education |
Psycho educate patient Now Let’s imagine that you are at the beech and your getting into the sea. And your dipping your toes in the water and it is freezing cold. and you stand there for 30 mins, just going huh huh it’s cold. Is the sea going to start to feel warmer?, no, what do you need to do, you need to properly emerse yourself. Look when we are doing this work, don’t just dip your toes in the water, when we are doing this work, you need to fully throw yourself into it. |
|
|
Edna foa
With PTSD you have a memory of the event and flashbacks. With social phobia people are not haunted by the image of what happened to them. Many people who phobias don’t know where they are coming from and don’t identify an event. You don’t. Have a memory with phobias. Memory haunts people with ptsd, it haunts them with nightmares, intrusive thoughts, flashbacks and avoidance. |
With PTSD you have a memory of the event and flashbacks. With social phobia people are not haunted by the image of what happened to them. Many people who phobias don’t know where they are coming from and don’t identify an event. You don’t. Have a memory with phobias. Memory haunts people with ptsd, it haunts them with nightmares, intrusive thoughts, flashbacks and avoidance. |
|
|
In vivo exposure |
Exposure in reality Exposure in real life |
|
|
Operation behaviours |
Are learned strategies |
|
|
Ptsd |
Asking about the traumatic event What is the memory that haunts you the most. What did you learn from today? Which trauma haunts you the most? Did you learn anything new? |
|
|
PTSD book components |
Education Breathing imaginable exposure In vivo exposure |
|
|
Vicarious learning |
Learning from others experiences. |
|
|
Hierarchy |
Rating fear level of problem? Problems that she is having difficulties facing that course her worry and anxiety. You don’t have to start at the bottom, you can start at the top. Repeat them also Number them In order I’m not going to ever force you to do anything The morning show The servant Harlot Pennywirth. |
|
|
Gad I’ll box |
When people have gad, the believe they are either I’ll or well. But that is not the case as we all worry and it is a process. |

