![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
60 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
building blocks for every physical thing
|
atoms
|
|
|
positive charge
|
proton
|
|
|
negative charge
|
electron
|
|
|
neutral charge
|
neutron
|
|
|
what is the center of the atom
|
nucleus
|
|
|
smallest units of life
|
cells
|
|
|
proteins that speed up chemical reactions
|
enzymes
|
|
|
name the steps of the scientific method
|
make observations
form a hypothesis test hypothesis explain results repeat |
|
|
what happens during the S phase of the cell cycle
|
dna is copied
|
|
|
when does crossover occur
|
prophase
|
|
|
where does transcription occur
|
nucleus
|
|
|
where does translation occur
|
cytoplasm
|
|
|
what does the cell theory say
|
all organisms are composed of cells
|
|
|
prokaryotic cells
|
have few internal parts, simple cells
|
|
|
eukaryotic cells
|
possess organelles, complex cells
|
|
|
name the phases in order
|
interphase
prophase metaphase anaphase telophase cytokinesis |
|
|
form of asexual reproduction
|
mitosis
|
|
|
produces diploid cells
|
mitosis
|
|

|
prophase
|
|

|
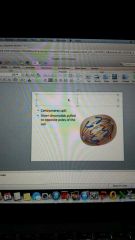
metaphase
|
|
|
anaphase
|
|

|
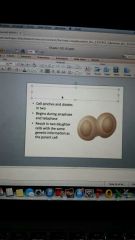
telophase
|
|
|
cytokinesis
|
|
|
what happens during interphase
|
chromosomes replicate, cell grows
|
|
|
sex cells (egg and sperm)
|
gametes
|
|
|
eggs and sperm are produced by
|
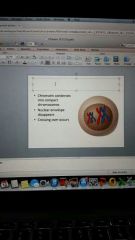
meiosis
|
|
|
prophase 1
|
|

|
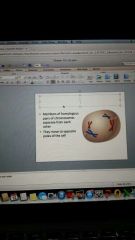
metaphase 1
|
|
|
anaphase 1
|
|
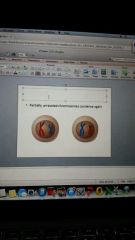
|
telophase 1
|
|

|
prophase 2
|
|

|
metaphase 2
|
|
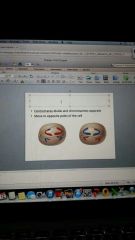
|
anaphase 2
|
|

|
telophase 2
|
|
|
cell makes copies of organelles and grows larger
|
interphase g1
|
|
|
genetic material is copied
cell chromosomes are doubled |
interphase S
|
|
|
cell grows and prepares upcoming M phase
|
interphase G2
|
|
|
the change in cells from unlimited potential to cells that are specialized
|
cell differentiation
|
|
|
hereditary unit consisting of dna
|
genes
|
|
|
cytosol and organelles together
|
cytoplasm
|
|
|
maintains shape of cell and positions of its organelles
|
cytoskeleton
|
|
|
organelle responsible for extracting energy from food molecules
|
mitochondria
|
|
|
outer cell boundary; controls movement of food molecules and waste products
|
cell membrane
|
|
|
most prominent organelle; houses chromosome
|
nucleus
|
|
|
structures that contain most of a cell's genetic information
|
chromosomes
|
|
|
membeane folds that produce proteins essential for cell structure
|
rough endoplasmic reticulum
|
|
|
site of protein synthesis; found free in cytoplasm and also studding RER surface
|
ribosome
|
|
|
membrane folds that handle synthesis of fats and lipids and break down toxic substances
|
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
|
|
|
place where proteins acquire final structure
|
golgi apparatus
|
|
|
digests waste materials and worn-out organelles
|
lysosome
|
|
|
cells move to new locations and grow into organs
cells start to specialize |
gastrulation
|
|
|
what are the three germ layers of gastrulation
|
endoderm
mesoderm ectoderm |
|
|
what did mendel study
|
pea plants determining inheritance and traits
|
|
|
process of copying genetic information from dna to rna, occurs in nucleus
|
transcription
|
|
|
process by which the information in rna is converted into amino acid sequences, happens in cytoplasm
|
translation
|
|
|
a change in the sequence of dna
|
mutation
|
|
|
disease of uncontrolled cell growth
|
cancer
|
|
|
regulate cell division
|
proto-oncogenes
|
|
|
encode for proteins that halt cell division
|
tumor suppressors
|
|
|
what are some outside causes of cancer
|
smoking
excessive alcohol use exposure to UV rays diet |

