![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
83 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Endocarditis |
Suspect in any pt with fever & murmur (particulurily new or changed murmur) IV drug user is also suspcious for infectious endocardititis |
|
|
Management for suspected endocarditis |
Send 2-3 blood cx from different sites (sterile cx) prior to starting Abx start empiric treatment with vanc for 4-6 weeks + gentamicin for 1st week transthoracic echo (TTE), if normal, then transesophageal echo (TEE) Surgical replacement if: acute decompensation (CHF exacerbation) myocardial abscess repeated emboli very large vegetations (>10cm) fungal endocarditis prosthetic valve endocarditis If you are considering surgery, have to do TEE |
|
|
Septic emboli from endocarditis |
For IV drug users --> septic emboli from heart can go to lungs leading to nodular lesions on CXR causing pulmonary sxs (tricuspid 50%, aortic 25%, mitral 20%) For left sided endocarditisis --> can cause emboli to brain leading to stroke |
|
|
Signs of endocarditis embolus |
Mostly seen in L sided endocarditis: conjuctival petechiae splinter hemorrhages roth spots- retinal hemorrhages with white or pale centers janeway lesions- non-tender, small erythematous or hemorrhagic macular or nodular lesions on the palms or soles osler nodes- painful, raised, red lesions found on hands and feet (immune complex deposition) |
|
|
Allergic nafcillin nephritis triad |
Fever Rash Nephritis (ARF)
dx with eosinophiluria (eosinophils in urine) |
|
|
Rx for methicillin sensitive staph |
1st gen cepholosporin --> cefazolin 4-6 weeks OR oxacillin or nafcillin (4-6 weeks) + gentamicin for 1st week (contraindicated in pts with renal failure) |
|
|
TTE then TEE |
If TTE is negative, can consider doing TEE if high prob of looking for thrombus Even if TTE is positive, still need to do TEE if: considering surgical replacement of valve new conduction delay on EKG aortic valve endocarditis persistent bacteremia or fever with proper coverage |
|
|
Bugs in endocarditits in IV drug abusers |
S aureus --> 60-90% large portion are due to healthcare-associated bacteremia vanc and gentamicin good empiric coverage until the results of blood cx rx for 4-6 weeks |
|
|
Bugs in subacute endocarditis |
Streptococci --> 50-60% S viridans acct for 75% of this (found in mouth flora) --> rx with Penicillin G or ceftriaxone (2 wks) S bovis --> 20% assoc with colon cancer Staphylococci --> 30% S aureus acct 90% of this Enterococci --> 5-10% --> rx with b-lactam + aminoglycoside (4-6 wks) |
|
|
Culture negative endocarditits |
HACEK --> < 2% of cases Haemophilus --> H parainfluenzae, H aprophilus, H paraprophilus Actinobacillus Cardiobacterium hominis Eikenella corrodens (human bites) --> amox+clavulanic acid Kingella rx with ceftriaxone, ampicillin-sulbactam, or cipro (4 wks) |
|
|
Prosthetic valve endocarditis |
Staph epidermidis is most common in first 2 months after replacement Strep viridans becomes more common after that |
|
|
Uses for Pencillin |
Strep viridians --> endocarditis Syphilis Group A strep --> strep throat Actinomyces Clostridium species |
|
|
Rx of MRSA |
Vancomycin (but is bacteriostatic) If allergic to vanc or resistant to vanc--> daptomycin DO NOT USE DAPTOMYCIN FOR PNEUMONIA (surfactant inactivates daptomycin) --> use either vanc or linezolid |
|
|
Side effect of daptomycin |
myositis --> monitor CK daptomycin inserts into cell membrane of bug & causes ion leak (particularily Ca) |
|
|
Endocarditis prophx |
Give amox 30-60 mins prior to procedure (if allergic, give clindamycin, cephalexin, or macrolide) previous episode of endocarditis prosthetic cardiac valve CHD cardiac transplant with cardiac valvulopathy Prophx for: dental procedures respiratory tract procedures involving incision or bx procedures on infected skin, skin structures, & musculoskeletal tissue |
|
|
Libman-Sacks endocarditis |
Young F with rash, joint pain, and MR w/o fever Sterile vegetation assoc with SLE --> no fever vegetations present on and under surface of mitral valve --> mitral valve regurg |
|
|
Chronic rheumatic dz |
caused by group A strep infection during childhood bacterial M protein resemble proteins in valve leading to autoimmune destruction fibrosis and scarring of valve leaflets leads to abnormalities causing stenosis or regurg mitral valve almost always involved causes mitral stenosis with "fish mouth" appearance |
|
|
Acute rheumatic heart dz |
JONES criteria elevated ASO and a-DNase B titers migratory polyarthritis pancarditis (endocarditis, myocarditis, pericarditis) subcutaneous nodules erythema marginatum (involving trunk and limbs) sydenham chorea --> rapid involuntray muscle movements |
|
|
Lower extremity edema w/u |
Duplex u/s --> look for DVT pt with warm, tender, unilateral swollen leg with neg u/s has cellulitis until proven otherwise |
|
|
Rx for cellulitis |
most likely gram + --> either Staph or group A strep (S pyogenes) elevation of leg and warm soaks For mild cases: oral dicloxacillin --> mild penicillin allergy then use cephalexin if severe penicillin allergy --> clinda, macrolides, fluoroquinolones For moderate cases resistant to oral rx: IV cefazolin For severe cases: IV antibiotics with oxacillin or nafcillin or cefazolin q4 hr for MSSA |
|
|
High risk community assoc MRSA groups |
Household contacts of pt with MRSA children MSM IV drug users athletes engaged in contact sports native american and pacific islanders |
|
|
Rx of MRSA cellulitis |
Treat when there is an abcess or purulent cellulitis Vancomycin drug of choice Daptomycin Ceftaroline Tigecycline (doesnt cover pseudomonas and actinomyces) Telavancin Linezolid (common side effect is thrombocytopenia & dont give with SSRIs) For mild infections: Clinda Doxycycline Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole |
|
|
Cellulitis abscess |
Surgical drainage small abcess with no surrounding erythema does not need Abx ALWAYS DRAIN AN ABCESS |
|
|
Necrotizing fasciitis |
Extreme pain and tense edema with dark bullae fever systemic toxicity maybe septic |
|
|
Initial w/u of necrotizing fasciitis |
CBC Chemistry Lactic acid level (if low --> sepsis) Broad spectrum IV Abx SURGERY CONSULT IMMEDIATELY If PE is uncertain, then can think of CT to look for gas formation |
|
|
Rx of necrotizing fasciitis |
Immediate surgical debridement Send to OR w/o imaging! Clindamycin + Penicillin for group A strep for mixed flora: cover MRSA (vanc or daptomycin or tigacycline or ceftaroline or linezolid) PLUS cover gram - and anaerobes (imipenem/meropenem or pipercillin/tazobactam or ticarcillin/clavulinate or cefepime + metronidozole) PLUS toxin production inhibition --> clinda |
|
|
Bugs of necrotizing fasciitis |
destruction of fascia and muscle through the release of toxins, which include S pyogenic exotoxins most cases are polymicrobial with anaerobes and aerobes Group A strep (any serious skin infection gets 2 drugs with one being clinda) S aureus C perfringens Bacteroides fragilis Pseudomonas |
|
|
Clostridium perfringens |
rare cause from deep stab wounds black tar heroin abuse Rx with surgical debridement along with penicillin + clinda |
|
|
w/u of suspected menigitis |
blood cxs dexamethasone (specifcally in case of pneumococcal or Tb meningitis) empiric Abx (ceftriaxone + vanc) head CT (if required) LP |
|
|
Menigitis vs encephalitis |
encephalitis HAS to have AMS --> coma, lethargic, altered, confused |
|
|
CT before LP |
papilledema confusion focal neurologic findings seizures immunocompromised |
|
|
Bugs of bacterial meningitis |
Most common cause --> Strep pneumonia Neisseria meningitis In neonates --> gram - bacilli & group B strep is most common Consider Listeria in: neonates > 50 yr DM immunocompromised liver or kidney dz If Listeria --> add ampicillin to empiric ceftriaxone |
|
|
Viral meningitis |
neutrophilic predominance in first 24 hrs but then lymphs WBC in 100s vs bacterial in 1000s |
|
|
Brain abcess |
surgical drainage PLUS metronidazole PLUS ceftriaxone w/ or w/o vanc |
|
|
Coverage for post neurosurgy |
Need to cover MRSA and pseudomonas vanc + cefepime or meropenem or ceftazidime If immunocompromised add ampicillin |
|
|
Unusual causes of meningitis |
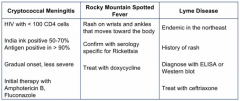
|
|
|
Spontaneous peritonitis |
thought to occur from hematologic seeding in absence of perforation first step in managment is to get u/s to confirm pt has true asciites then need to perform paracentesis --> PMN >250 or WBC >500 If low glucose (< 50), very high LDH, PMN >10,000, or polymicrobial --> secondary peritonitis from bowel perforation |
|
|
Bugs for spontaneous peritonitis |
Most common --> E coli S. pneumoniae group A strep (S pyogenes) Enterococci |
|
|
Abx for spontaneous peritonitis |
cover gram - bacilli and S pneumoniae cefotaxime or ceftriaxone Infuse IV albumin if albumin >1.5 in asciites fluid Any pt with spontaneous peritonitis gets prophx abx for life --> oral norfloxacin+cipro OR trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole Cirrhotic pts with bleeding esophageal varices are at increased risk of developing spont peritonitis --> give ceftriaxone for 1 week during the bleeding episode |
|
|
Next steps for recent dx of HIV |
RPR or VDRL --> syphilis Toxo serologies CBC & chem Pap smear PPD Hep A, B, C serology T-cell subsets Viral load & resistance testing (most important test to monitor rx) |
|
|
Latent syphilis |
Syphilis serologies convert to positive in: < 1yr --> early latency 1 dose of IM penicillin >1yr or unknown --> late latency 3 doses of IM penicillin |
|
|
HIV with close contact with Tb |
TREAT FOR LATENT Tb REGARDLESS OF PPD, g-INTERFERON RELEASING ASSAY, OR CXR RESULTS Latent Tb --> 9 months INH + Vit B6 |
|
|
PPD Guidelines |
15mm+ is positive for general population 10mm+ is positive for intermediate risk: recent immigrants from endemic countries health care personnel IV drug users <4 yrs old 5mm+ is positive for high risk pts: HIV+ recent contact with Tb Organ transplant receipients Fibrotic changes on CXR c/w prior dz |
|
|
CD4 <200 Prophx |
Pneumocystis jiroveci --> Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole --> if allergic, give dapsone or atovaquone Mycobacterium avium complex --> Azithro weekly HAART with 2 nucleosides + non-nucleoside RT inhibitors OR integrase inhibitor OR protease inhibitor Pneumococcal pneumonia vaccine Hep A & B vaccine Influenza vaccine yearly |
|
|
Rx of PCP infection |
TMP/SFX but if allergic: IV pentamidine OR Clinda + primaquine OR Atovaquone Pentamidine is very toxic --> hypo/hyperglycemia, acute pancreatitis, ATN, hepatotoxicity Give prednisone if P02 <70 or A-a gradient >35 |
|
|
Presentation of MAC |
CD4 <50 Anemia Low albumin Cachectic looking Fever Diarrhea |
|
|
Rx of MAC |
Macrolide (eg azithro or clarithromycin) PLUS Ethambutol +/- Rifabutin |
|
|
Rx of HIV |
CD4 >500: Nothing unless pregnant CD4 <500: antiretrovirals with 3+ drugs |
|
|
HIV and vaccines |
CD4 >200 --> any vaccine CD4 <200 --> no live attenuated (eg varicella) |
|
|
Drug induced hepatitis |
Acetaminophen Methotrexate Amiodarone Halothane a-Methyldopa Erythromycin Valproic acid Allopurinol |
|
|
Rx for Hep C |
First genotype strain --> type 2 & 3 are most easily treated but type 1 is most common Everyone gets Peg interferon + Ribavarin If type 1 also get: Sofosbuvir OR Simeprevir |
|
|
W/u of suspected osteomyelitis |
CBC ESR XRay If XRay normal --> CT or MRI (most accurate for osteomyelitis) MRI maybe contraindicated in pts with hardware If imaging is positive for osteo --> bone bx to identify organism prior to starting Abx NO NEED FOR CX FOR OSTEO |
|
|
Bugs causing osteomyelitis |
most common --> S aureus in diabetics: gram - bacilli (eg E coli or Pseudomonas) |
|
|
Bugs of atypical pneumonia |
b/l lung infiltrates Legionella Mycoplasma Chlamydia PCP Viral |
|
|
Abx for pneumonia |
Abx take up to 72 hrs to become effective CXR takes longer to show improvement IV Abx: Ceftriaxone OR Ampicillin/Sulbactam
Azithro OR Dox OR Moxifloxacin OR Levofloxacin For outpatient: fluoroquinolones or macrolide |
|
|
CURB-65 |
Confusion BUN >19.6 RR >30 BP <90/60 Age >65 1 point for each --> 2+ score should be hospitalized |
|
|
Legionella Triad |
Atypical pneumonia SIADH --> hyponatremia Diarrhea |
|
|
Contraindication for macrolides and fluoroquinolones |
pt with prolonged QT interval --> use dox |
|
|
Community acquired MRSA pneumonia |
IV drug users Concurrent or recent influenza infection Produces severe pneumonia req intubation Necrotizing (cavitary) pneumonia |
|
|
Rx MRSA pneumonia |
Ceftriaxone + Azithro + Vanc OR linezolid OR Clinda Ceftaroline + Azithro |
|
|
Hospt acquired pneumonia |
Pseudomonas or MRSA Need 2 drugs for Pseudomonas and 1 drug for MRSA |
|
|
Rx for cryptococcal meningitis |
Amphotericin B + flucytosine Casfofungin has widest coverage for fungal infections EXCEPT crypto |
|
|
Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome (IRIS) |
Pt with AIDS begins rx with HAART after dx w/another infection As CD4 rises, start to get worsening of underlying opportunistic infections Stop HAART & treat underlying infection |
|
|
Ddx for urethral d/c |
Gonococcal urethritis Chlamydia Trichomoniasis Reiter syndrome
First step --> urethral swab with gram stain and wet mount
Most accurate test --> urine PCR |
|
|
Rx for gonorrhea |
1 dose IM Ceftriaxone 1 dose Azithro or Dox for 1 week to cover Chlmydia |
|
|
Disseminated Gonococcal Infection |
1) Migratory polyarthralgia 2) Tenosynovitis 3) Skin lesions (hemorrhagic pustules on palms & soles) |
|
|
Thayer-Martin agar |
Used to grow Neisseria organisms Blood agar plate that contains: Vanc --> kills most gram + Colistin --> kills most gram - except Neisseria Nystatin --> kills most fungi Trimethoprim --> inhibits Proteus |
|
|
Recurrent Neisseria infections |
test for C5 or C9 def |
|
|
Consideration of lyme disease |
young patient in northeast camping/tick bite bradycardia or heart block |
|
|
Bradycardia with heart block DDx |
Lyme dz hypothyroid b-blocker or Ca channel blocker ischemic heart dz |
|
|
Reversal of b-blocker overdose |
glucagon |
|
|
Tx of lyme dz with heart block |
IV ceftriaxone Testing: ELISA for Borrelia burgdorferi initial test Western for confirmation |
|
|
Presentation of Lyme Dz |
Early localized lyme dz occurs 1-2 wks following infection Initial presentation is erythema migrans (erythematous skin lesion at site of tick bite) Border of erythema expands over several days, and lesion develops centrally & referred to as target or bulls-eye appearance If rash is present do not send serologies (too soon to be positive) just tx with dox OR amox |
|
|
Neuro Sxs of lyme |
Cranial nerve palsy (unilateral or b/l) --> Bell's palsy aseptic meningitis radiculopathy |
|
|
Late stage lyme |
migratory mono or oligoarticular inflammation, which improves and recurs in months or years later 85% has knee involvement |
|
|
IV ceftriaxone for lyme with... |
myocarditis 2nd or 3rd degree heart block meningitis or encephalitis |
|
|
Urinary tract infection |
febrile with dysuria high fever with flank pain --> upper urinary site perinephric abcess arises from pre-existing pyelo that is present for several weeks, particularly in assoc with stones |
|
|
Use of IV Abx for UTI |
high fever shaking chills bacteremia |
|
|
Uncomplicated UTI Abx |
TMP/SMZ for 3 days OR Fosfomycin single dose OR Nitrofurantoin for 5 days |
|
|
TMP/SMZ side effects |
TMP: type 4 renal tubular acidosis --> hyperkalemia SMZ: allergies myelosuppression |
|
|
IV Abx for pyelo |
Ceftriaxone Levofloxacin Ciprofloxacin Amp/sulbactam Gentamicin Aztreonam |
|
|
Pyelo and unstable |
Imipenem OR Meropenem bc of suspicion of extended-spectrum beta-lactamases |
|
|
Additional testing for pyelo |
if Abx is not responsive, can do:
renal u/s
OR
IV pyelography (suspcion of stone, stricture, or tumor)
OR
CT of kidney to r/o abscess |

