![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Adipose tissue stores about
|
95% of body's triacylglycerols
|
|
|
Following a meal, the liver does what?
|
Converts glucose --> glycogen for storage
|
|
|
Excess glucose after a meal goes to ? to synthesize ?
|
Acetyl-CoA to synthesize fatty acids
|
|
|
Fatty acids are esterified to ?
|
Glycerols
|
|
|
During a fast, the liver does what?
|
Converts glycogen --> glucose and releases it into circulation
|
|
|
Triacylglycerols and acetyl-coa during a fast can go to ?
|
Ketone bodies
|
|
|
Amino acids during a fast can go to ?
|
Glucose via gluconeogenesis or ketosis
|
|
|
Muscles store glucose --> glycogen to?
|
A limit
|
|
|
During exercise, what is broken down for glycolysis for what?
|
Glycogen is broken down for ATP production
|
|
|
Heart muscles burn primarily what?
|
Fatty acids
|
|
|
Adipocytes turn what to what? Stored where?
|
Glycose --> glycerol and store in fat globules
|
|
|
Metabolites travel between tissues in ?
|
Interorgan metabolic pathways
|
|
|
The Cori cycle does what?
|
Transports lactate from muscle to liver
|
|
|
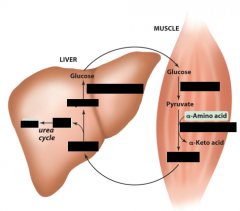
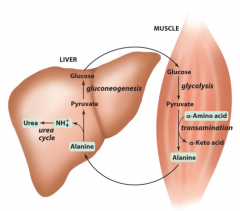
Glucose-alanine cycle does what?
|
Alanine is transported from the muscle to liver?
|
|
|
In the glucose-alanine cycle:
1) Pyruvate is produced by ? 1) Pyruvate is transaminated to make ? |
Muscle glycolysis
Alanine |
|
|
What two organs can carry out gluconeogenesis?
|
Liver and kidney
|
|
|
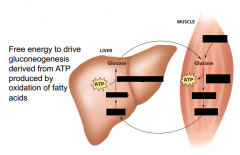
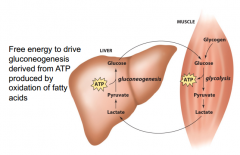
Free energy to drive gluconeogenesis is derived from ? by oxidation of ?
|
ATP produced by oxidation of fatty acids
|
|
|
Cori Cycle: Glycogen ---> ? which goes through ??? for ATP
|
Glyocgen --> Glucose which goes through glycolysis
|
|
|
In the Cori Cycle, NADH cannot be ? which generates ?
|
NADH cannot be re-oxidized, creates lactate
|
|
|
|
|
`
|
|
|
|
Pancreatic cells release ? in response to high glucose
|
Insulin
|
|
|
Insulin stimulates uptake of ? and storage of ?
It inhibits what? |
Glucose
Metabolic fuels Glycogen breakdown |
|
|
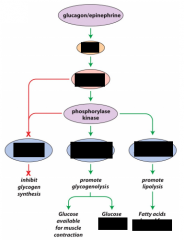
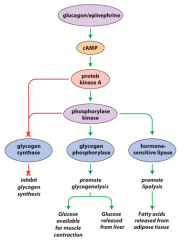
Glucagon and epinephrine promote ? and ?
|
Glycogenolysis and lipolysis
|
|
|
Hormones produced by ? and ? regulate appetite and fuel metabolism
|
Adipose tissue and digestive organs
|
|
|
AMPK actives ? and inhibits ?
|
Actives ATP-producing pathways and inhibits ATP-consuming pathways
|
|
|
Normal concentration of glucose in blood is ?
|
3.6-.5.8 mM
|
|
|
Insulin is synthesized in ? cells in ?
|
beta islet cells in pancreas
|
|
|
Glucagon is synthesized in ? cells in ?
|
Alpha islet cells in pancreas
|
|
|
Glucokinase vs Hexokinase
|
Hexo: Low km so enzymes saturate with substrate
Gluco: Higher km (in liver), never saturated, sensitive to glucose concentration |
|
|
Glucokinase appears to be a ? sensor, triggering ?
|
Glucose sensor, triggering insulin release
|
|
|
The liver is more responsive to ?
Muscle is more responsive to ? |
Glucagon
Epinephrine |
|
|
Glucagon is released from beta-cells of pancrease when blood glucose drops below ?
|
5mM
|
|
|
|
|
|
AMPK acts as ?
|
Fuel sensor
|
|
|
AMPK is activated by ? and ?
And inhibited by ? |
AMP/ADP
ATP |

