![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
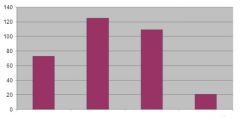
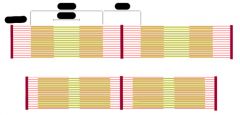
Label the bars of the spider's contact with mesh and explain.
|
Ground contact distributed along leg, not just foot
|
|
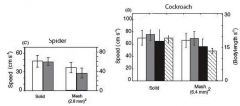
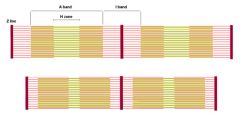
Label the bars of contact with mesh and explain.
|
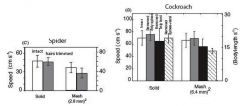
On solid surfaces and mesh, spider does better with hairs. Roaches do better on solid without spines and worse without tarsi/with spines. On mesh they do better w/o spines but do worse without tarsi
|
|
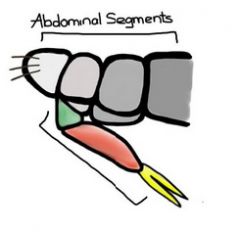
What is this structure and what is it from?
|
furcula, springtail
|
|
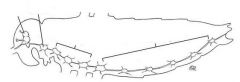
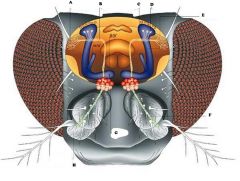
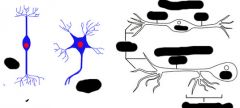
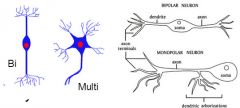
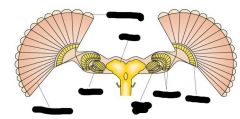
Label diagram
|
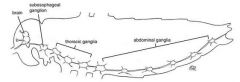
|
|
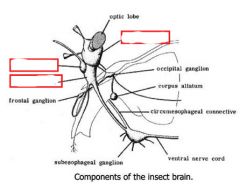
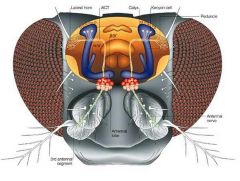
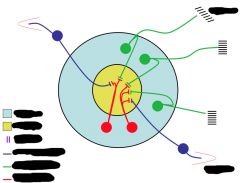
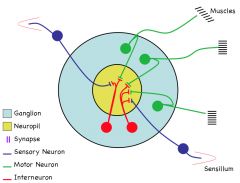
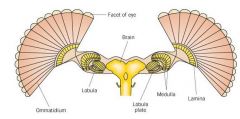
Label
|
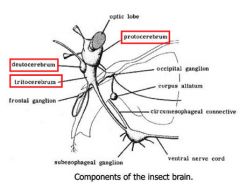
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
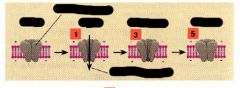
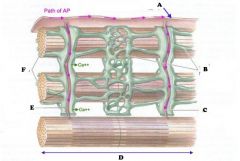
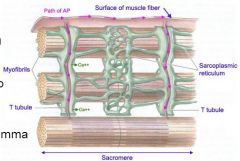
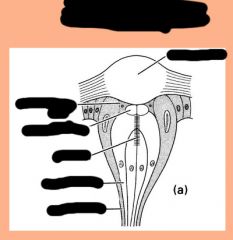
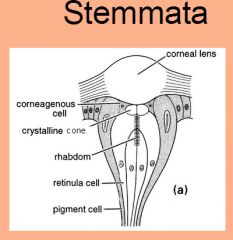
Label and what is it?
|
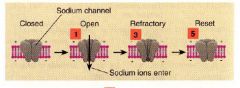
voltage gated sodium channel
|
|
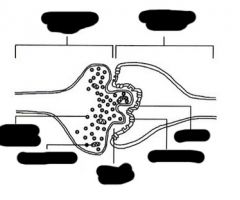
|
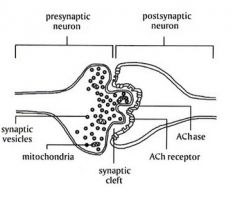
|
|
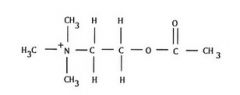
What is this?
|
acetylcholine, neurotransmitter
|
|
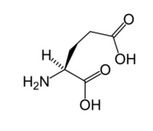
What is this?
|
L-glutamic acid, neurotransmitter
|
|
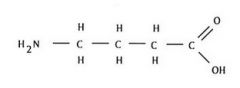
What is this?
|
GABA, neurotransmitter
|
|
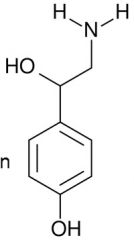
What is this?
|
Octopamine, neurotransmitter
|
|
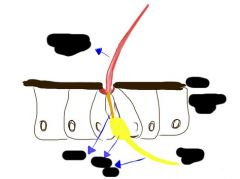
Label and what is it?
|
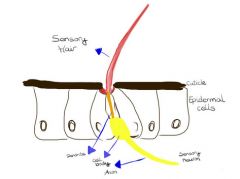
trichoid sensilla
|
|
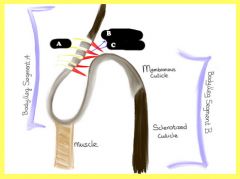
Label and what is it?
|
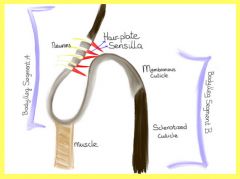
hair bed
|
|
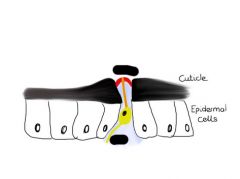
Label and what is it?
|
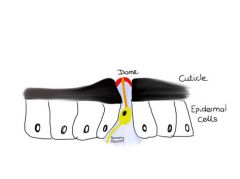
Campaniform sensilla
|
|
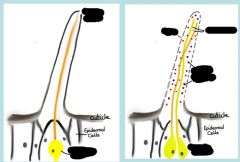
Label and what are they?
|
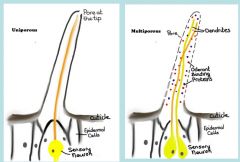
Uniporous and multiporous sensilla
|
|
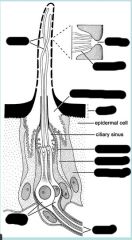
Label and what is it?
|
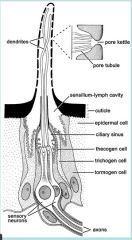
chemoreceptor
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
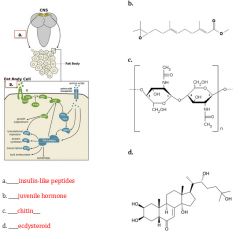
|
|
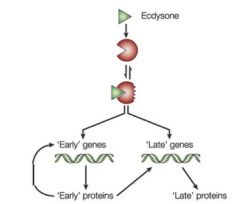
Explain the Ashburner model below and some modifications that have been made since. Describe what technique/experiment Ashburner used to support the model.
|
Puffing sequence of Drosophila polytene chromosomes initiated by moulting hormone. Model described interaction between ecdysone, its receptor, and early/late puffs during response. Ecdysone+receptor activates directly = rapid few early puffs and no late puffs. When proteins encoded by early puffs are abundant enough they repress their own promoters and activate late genes. Recent studies have IDed the different genes.
|
|
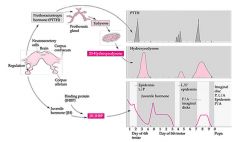
Describe
|
Parasitoids release JH and prevent JH degredation so host doesn't metamorphasize, PTTG release is stopped, PG less responsive to PTTH = decrease of ecdysone until parasitoid metamorphosis when there is a large spike
|
|
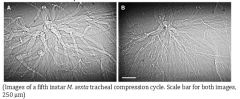
What type of equipment did researchers use to obtain these images?
|
Synchrotron
|
|
|
Draw relative positions of tracheoles, taenidiae, trachea, spiracles
|
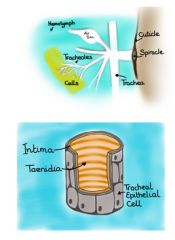
|
|
|
Draw diagram of mechanims of proteolytic digestion involving trypsin in mosquitoes. Explain in words. At least 1 hormone and 2 types of trypsin genes. Discuss why 2 types are needed.
|
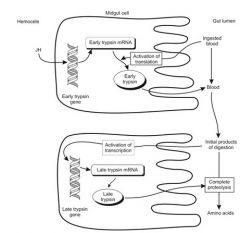
JH + blood meal activates early trypsin gene > early trypsin mRNA. Digested peptides activate transcription of late mRNA to break down peptides to aas
|

