![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
homologous chromosomes? |
Chromosomes found in pairs |
|
|
Specific location of a chromosome |
Locus |
|
|
Different versions of the locus |
Alleles |
|
|
The combination of alleles you possess at a given locus |
Genotype |
|
|
If the version on both chromosomes is the same/different |
Homozygous/Heterozygous |
|
|
Sources of genetic Variation |
Mutations (changes in DNA) are the original source of genetic diversity Reshuffling of alleles during sexual reproduction produces genetic variation (inherited variation) |
|
|
What does mutations do? |
Mutations create different versions of loci (genes) called alleles - Polymorphism |
|
|
Mechanisms of genetic Variation |
Independent assortment of chromosomes Recombination (Crossing-over) Random fertilization of gametes |
|
|
Meiosis |
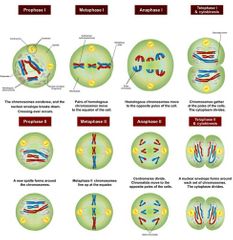
|
|
|
Mendelian laws of inheritance |
Low of segregation and Law of independent assortment |
|
|
Law of segregation |
states that the two alleles for a heritable character separate during gamete formation and end up in different gametes |
|
|
Law of independent assortment |
states that each pair of alleles segregates independently of each other pair of alleles during gamete formation |
|
|
Effects of differences in the DNA sequence? |
Differences in DNA sequence can lead to differences in protein function resulting in different phenotypes. |
|
|
Factors of expression of characteristics? |
Dominant / RecessiveCodominantAutosomal / Sex-linked |
|
|
Y linked Alleles |
Only passed through via father to son as theres is no equivialent gene on the X chromosomes all males will be affected |
|
|
Mitochondrial inheritance |
Maternal only inheritanceOnly the egg (not the sperm) contribute mitochondria to the developing embryoMutations in mitochondrial DNA can appear in every generation of a family, can affect both males and females, but fathers do not pass these disorders to their daughters or sons |
|
|
Codominant Inheritance |
Alleles are expressed equally |

