![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
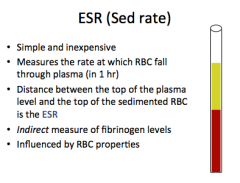
What does ESR measure? What is the distance between the top of the plasma level and the top of the sedimented RBC?
What is it an indirect measure of? What is it influenced by? |
|
|
|
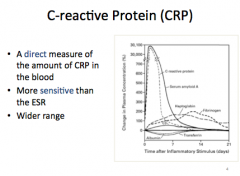
What is CRP a direct measure of? What is it more sensitive than? |
|
|
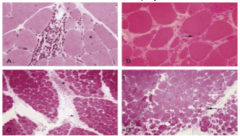
A B C D |
A = variation in fiber size and central nucleation B = inflammation and increased fibrosis C = perimysial inflammation D = perifiascicular atrophy |
|
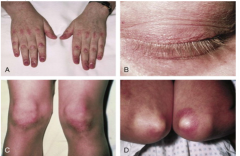
What is shown here? |
Heliotrophe rash (B) and Gottron's papules over extensive surface of MCP and IP joints of fingers |
|
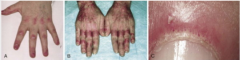
What is going on with the nails in C? |
Capillary nail fold changes in dermatomyosisit |
|
|
What are some other dermatomyositis skin changes? |
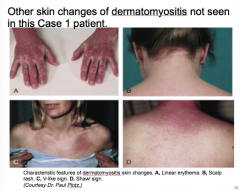
|
|
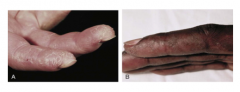
What is this characteristic lesion? |
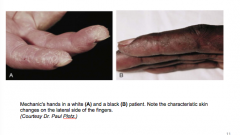
|
|
|
Are inflammatory myopathies rare? In what ages and sex does polymyositis happen? IBM? DM?
Which two are more common in females? (2:1)
Think about diseases that inflammatory myopathies can occur with.
What percent of myositis cases are associated with malignancy? |

|
|
|
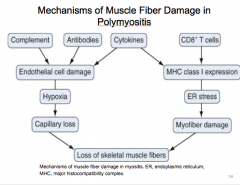
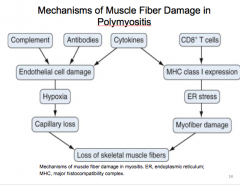
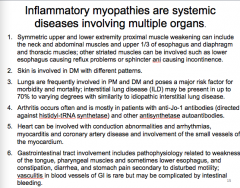
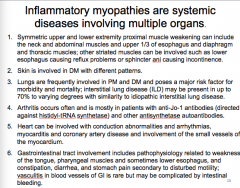
What immune response is involved in inflammatory myopathies?
What myositic associated antiboies are frequently associated with scleroderma?
In which is the cell mediated immune response?
What mediates muscle fiber damage? |

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
What are some other types of myopathies? |
|
|
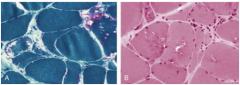
What is shown here? |

|
|
|
Inclusion body myositis:
What muscles (proximal or distal in lower or upper extremities)?
Response to corticosteroids?
Older or younger men or women? |

|
|
|
|
|
|
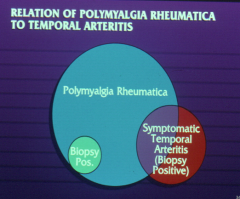
Polymyalgia rheumatic occurs in about what percent of patients with GCA?
PMR involves inflammation of what?
What can also cause carpal tunnel syndrome?
|

|
|
|
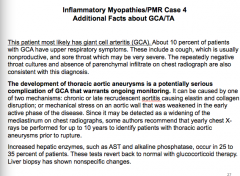
About 10% of patients with GCA have symptoms in what general region? What are some of these symptoms?
What is a serious complication of GCA that warrants ongoing monitoring?
Two mechanisms that causes it?
What enzymes will be increased? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
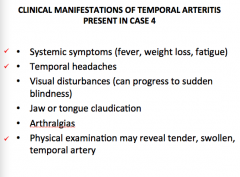
What are some clinical manifestations of temporal arteritis? |
|
|
|
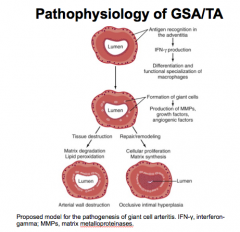
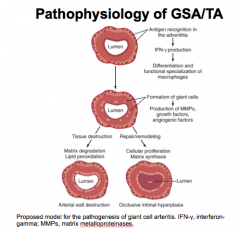
Giant cell arteritis:
Inflammation of what sized arteries? Where does it originate from? Associated with granulomas? Associated with glomerulonephritis? |

|
|
|
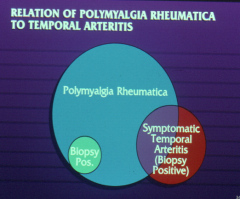
AM stiffness, pain in pelvic girdle and shoulder Associated with temporal arteritis
What is the disease? |
Polymyalgia rheumatica |
|
|
What artery does the ophthalmic artery come from? |
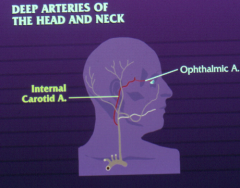
|
|
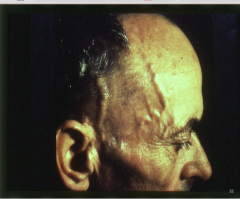
Diagnosis? |
Giant cell arteritis (temporal) |
|
|
What are the four characteristics of cranial ateritis? |
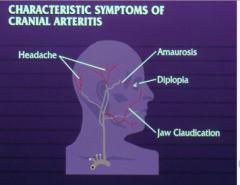
|
|
|
|
|
|
What will the labs of a temporal arteritis patient look like (blood, thrombo, ESR)
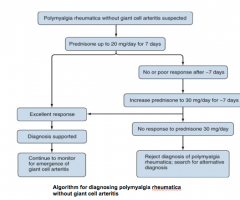
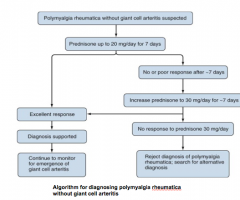
How do you diagnose temporal arteritis?
Inflammation is most marked near which membrane? |

|
|
|
|
|
|
What is the treatment for temporal arteritis? When should you begin it? Should you treat while waiting on biopsy? Prognosis is good with treatment, but what can be reversible? |

|

