![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
75 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
3 common bacteria causing gastroenteritis
|
Champylobacter
Salmonella E.coli 0157 |
|
|
S&Ss of food poisoning/ gastroenteritis
|
D&V
abdo pain malaise ?fever- salmonella, e.coli ?blood |
|
|
commonest bacterial cause of food poisoning/ gastroenteritis ?
- source - incubation - S&Ss |
CHAMPYLOBACTER- raw milk, poultry
LONG incubation 2-5days BLOODy, abdo pain, fever |
|
|
how champylobacter prevented/ treated
|
food hygiene
NO Rx- oral fluids at risk Rx: ciproflaxacin/ erythromycin |
|
|
salmonella:
- source - incubation - S&Ss - type of bacterial infection |
meat, eggs, poultry
MED incubation- 1-2d D&V, abdo pain, fever, SEPTICAEMIA TOXIN-producing |
|
|
treatment of salmonella infection
|
NO Rx
at risk: ciprofloxacin |
|
|
how is salmonella serogrouped
why |
- antigens on flagella& body
- identify source, identify outbreaks |
|
|
E.coli:
- source - incubation - S&Ss - mechanism of infection |
PERSON-person spread from ANIMAL contact, food (beef, raw milk) or water bourne
- 1-3d LONG incubation - BLOOD d, - VTEC toxin producing |
|
|
which bacteria can cause outbreaks and which are toxin producing:
- champylobacter, salmonella, E.coli |
salmonella and E.coli - OUTBREAKS & toxin-producing
E.coli= VTEC |
|
|
what's the commonest cause of acute renal failure in children
|
E.coli 0157 complicated by haemolytic ureamic syndrome (HUS)
|
|
|
dangerous complication of E.coli 0157 infection?
- Ix's to Dx |
HUS;
- thrombocytopaenia ↓plt - blood film fragmented RBCs - ↓Hb - ARF: ↑creatinine & ↑urea, haematuria, proteinuria - neurological involvement |
|
|
abx for e.coli 0157 may precipitate HUS, how do you treat HUS
|
seek expert advice
treat hypovolaemia &HTN DIALYSIS |
|
|
bacteria incubation;
- SHORT - MED - LONG |
SHORT- staph aureus, bacillus cereus
MED- Salmonella, Cl.perfringens LONG- Champylobacter, E.coli |
|
|
q's to ask in clinical dx of gastroenteritis/ food poisoning
|
Hx: travel, contact, food, animals, camping
anyone else? TIME- incubation DIARRHOEA: blood, severity PMH: risk comorbidities |
|
|
what bacterial cause of gastroenteritis do you have to notify HPY about
|
suspicion of HUS
|
|
|
Dx of causative org
|
STOOL culture (48h)
|
|
|
management of pt's with D&V suspected gastroenteritis/ food poisoning
|
oral rehydration
supportive AVOID antimotiligy agents IMMUNOCOMPROMISED- abx's, e.g. ciprofloxacin isolation |
|
|
what's amoebic dysentery by definition (1 important symptom)
|
BLOODy diarrhoea
|
|
|
what causes pseudomembranous colitis
how is dx confirmed |
overgrowth of Cl.difficile following Rx with braod-spec abx's
STOOL culture |
|
|
common pathogen causing food poisoning 1-2hrs after indigestion.
abdo cramps, vomiting, watery diarrhoea. gram +ve aerobic bacilli. Pathogenicity due to enterotoxin, usually self-limiting. |
Bacillus cereus
|
|
|
what pathogen is cause of diarrhoea due to broad spec abx's.
enterotoxin A&B = pseudomembranous colitis. high mortality in elderly. Rx? |
Cl. diff
oral metranidazole/ vancomycin |
|
|
what are coliforms:
- loc - gram stain - aerobes or anaerobes - e.g |
LARGE AEROBIC BACILLI
GUT commensals E.coli, Klebsiella, proteus |
|
|
what are strict/ obligate aerobes
- eg - gram stain |
REQURIE O2 for growth
gram +ve - bacilli: legionella, pseudomonas aeruginosa (exac bronchectasis) |
|
|
what are strict/ obligate anaerobes
- e.g's - gram stain |
WILL NOT grow in presence of O2
-Gram +ve: bacteroides bacilli |
|
|
normal mouth flora
|
Gram +ve aerobic:
- streptococci: strep viridans - staphylococci Gram -ve aerobes: - neisseria Candida |
|
|
flora of stomach / duodenum (low pH) & bile ducts
|
usually sterile
stomach/ duod.- (some Candida & Staphylocicci) |
|
|
normal flora of jej & ileum (small bowel)
|
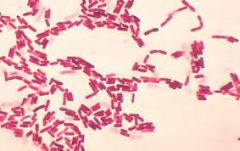
Gram -ve:
- aerobes: coliforms (pic) - anaerobes |
|
|
normal flora of colon
|
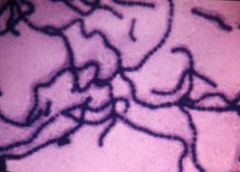
Gram -ve:
- aerobes (coliforms) - anaerobes Gram +ve: - aerobes: (streptococci) ENTEROCOCCUS FAECALIS (pic) |
|
|
micro-organisms that leak/ perforate into peritoneal cavity can cause abscesses (pus cells + orgs).
- why can small but not large abscesses be treated with abx's? - how are large abscesses treated |
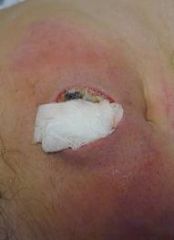
large abscess will have NO BLOOD SUPPLY so abx's won't peneetrate it.
- need incision & drainage |
|
|
which empirical abx therapy for COLIFORM infection (gram -ve large baccili = e.coli & klebsiella)
|
gram -ve aerobes
GENTAMICIN (>50% are amox-resistant) |
|
|
which empirical abx therapy for ANAEROBE infection (bacteroides -ve and cl.diff +ve)
|
(generally gram +ve bacilli eg Cl.diff)
metranidazole |
|
|
which empirical abx therapy for ENTEROCCOCAL (& staphylococcal) infection
|
aerobic gram +ve streptococci
AMOXICILLIN (think gram +ve = amoX...X looks like +) |
|
|
what 3 empirical abx's given for INTRA-ABDOMINAL sepsis
- what do each cover |
GENT..............................aerobes (coliforms)
METRANIDAZOLE......anaerobes AMOX............................enterococcus sp. (in colon) & staphyloccus |
|
|
whch prophylactic abx's for GI/HEPATO-BILIARY surgery
|
GENT......aerobic coliforms
MET........anaerobes (small bowel- colon) (not amox which covers enterococcus in colon alone & staphylococcus) |
|
|
what abx if penicillin allergy / MRSA (amox)
|
vancomycin
|
|
|
S&Ss of intra-abdominal sepsis
|
temp >38, chills/rigors
↑WCC/ CRP ↑HR, ↓BP ↑RR N&V malaise/ anorexia constipation/ diarrhoea PERITONITIS (still, no BS, board-like) pain, tenderness, guarding |
|
|
what classifies SEVERE sepsis
|
1+ acute organ dysfunction:
renal resp hepatic clotting CNS metabolic acidosis (↓HCO3-) ↓BP (↓CVS)- refractory to IV fluids |
|
|
Dx by Ix of intra-abdominal infection
|
WCC, CRP, plt, clotting, LACTATE, U/O
micro (cultures): blood, stool, urine, wound, TISSUE microscopy: stool, urine, CSF, sputum serology (atypicals/ Ab's) antigen detection- PCR |
|
|
management of intra-abdominal sepsis:
- empirical abx's - supportive |
ABX's: gent (aerobes), metra (anaerobes), amox (enterococcus & staphylococcus)
SUPP.: O2, IV fluids, anaelgesia, VTE prophylaxis (clotting), control electrolytes - ?transfusion - ?surgery |
|
|
S&Ss HUS
|
initial follow on from E.coli 0157: diarrhoea BLOODY, vomiting, severe abdo pain, fever
HUS:abdo P, F low U/O, renal failure, neurological involvement - low BP, tachycardic, fever - high urea & WCC, low plt, Hb, abnormal clotting! |
|

2 viruses causing diarrhoea
|
ROTAvirus (front pic) & NOROvirus (pic)
|
|
|
which viral cause of diarrhoea is common in kids <3
how spread time of year infectious dose |

ROTAvirus: person-person, winter
LOW infectious dose |
|
|
which virus likely cause:
<3yrs winter Vomiting first --> watery D & fever (no blood) post-infecitous malabsorption |

ROTAvirus
|
|
|
which virus:
- winter - faecal-oral/ air droplet/ direct spread - low-infectious dose - asymp shedding - outbreaks |
NOROvirus
|
|
|
avg time inc for norovirus (short/med/long)
|
SHORT
|
|
symptoms of norovirus
|
PROFUSE vomiting
SYSTEMIC SHORT incubation OUTBREAKS |
|
|
Ix for viral diarrhoea
|
PCR on STOOL
|
|
|
complication of Cl.diff infection (gram +ve anaerobe)
|
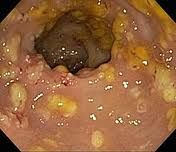
pseudomembranous colitis
|
|
|
treatment for 1st episode of UNcomplicated Cl.diff infection (gram -ve anaerobe)
|
ORAL metrinidazole
stop all other abx's review PPIs no anti-motility agents |
|
|
treatment for cl.diff if:
- poor response to SEVERE disease >1 severity marker |
get help!
oral VANCOMYCIN |
|
|
what's different about hand hygiene for control of Cl.diff and viral diarrhoea
|

HANDWASHING (no gels!)
|
|
|
4 core clinical problems in gastroenteritis
|
fever
abdo pain blood PR diarrhoea |
|
|
most common cause of bloody diarrhoea
|
champylobacter
|
|
|
what bacteria causes typhoid-fever
what is it |
ENTERIC FEVER: samlonella typhi / paratyphi
SYSTEMIC infection fever, malaise, DIFFUSE abdo pain, constipation, deleriumm, haeorrhage, perforation |
|
|
what infection gives profuse watery 'RICE-like' diarrhoea
|
CHOLERA
|
|
|
presentation S&Ss TYPHOID (enteric fever)
- Ix's |
malaise, high Fever, bradycardia, cough, CONSTIPATION (D after 1st wk)
BLOOD cultures stool & urine |
|
|
treatment for typhoid (enteric fever)
|
FLUIDS & nutrition
CIPROFLOXACIN (if resistant = chloramphenicol, ceftriaxone, azithromicin) VACCINE (incomplete protection) |
|
|
what's dysentery
|
intestinal infection = Pain , fever
severe diarrhoea, blood & mucus |
|
|
infection with c.diff, what do you suspect if:
- high WCC & creatinine colonic dilatation on AXR |
TOXIC MEGACOLON
|
|
|
which empirical treatment for...
3+ unformed stool per day & 1+: abdo pain, N&V, fever, blood in stool, tenesmus |
ciprofloxacin
|
|
|
likely cause of diarrhoea after long stay in hospital on abxs
S&Ss |
Cl.diff;
- blood D - P (complication: toxicmegacolon & pseudomembranous colitis) |
|
|
3 causes of travellers-related diarrhoea
|
amoebiasis
Giardiasis cryptosporidium |
|
|
cryptosporidium
amoebiasis giardiasis commonly cause what |
traveller's diarrhoea
|
|
|
treat travellers diarrhoea
|
self-limiting
LFUIDS single dose CIPROFLOXACIN short-term anti-diarrhoeals |
|
|
AMOEBIASIS is a PROTAZOAL infection:
- transmission - symp - Dx/ test & results - Rx |
faecal-oral, poor sanitation
acute BLOODY D HOT stool --> ova & cysts METRANIDAZOLE |
|
|
what infection is HOT stool sampled for ova and cysts
|
amoebiasis (protazoal infection)
giardiasis |
|
|
GIARDIASIS (protazoal infection);
- transmission - loc of GI tract it affects - S&Ss |
contaminated WASTE
SMALL bowel malabsorption, wt loss, fatty stool, bloating, flatulance, abdo discomfort, EXPLOSIVE diarrhoea |
|
|
dx by Ix for giardiasis
|
stool for ova & cysts
(duodenal aspirate) |
|
|
treatment for protazoal infection with amoebiasis or giardiasis
|
METRANIDAOLE
|
|
|
treatment for cryptosporidium (1 of 3 important causes of traveller's diarrhoea)
|
SUPPORTIVE
anti-microbials ineffective |
|
|
pathogens that can cause outbreaks of diarrhoea (5)
|
E.coli 0157
Norovirus cholera Cl. diff Salmonella |
|
|
geography of TYPHOID (enteric fever)
S&Ss |
india, SE asia
- HIGH fever, malaise, low HR, headache, constipation (>1wk diarrhoea), dry cough |
|
|
in a traveller, what presents with: RUQ pain, HIGH SWINGING fever & sweats, jaundice.
what Ix's would you do to confirm this? |
AMOEBIC LIVER ABSCESS
LFTs Inflam markers :WCC, CRP serology stool (often -ve) USS/ CXR/ CT |
|
|
what immune cell is raised in response to helminth (protazoal) infections
|
eosinophilia
|
|
|
3 types of parasites (helminth infections)
|
nematodes (roundworms)
tematodes (flukes) cestodes (tapeworms) |

