![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Definition Of indifference curve analysis |
This is a theory of consumer behaviour based on the analysis of individual preference. This was developed because of the difficulty in measuring utility obtained from a product |
|
|
What is it possible to develop with this theory |
It is possible to develop an individual scale of preference. A scale of preference means it is able to compare satisfaction obtained from different utility of a product |
|
|
Definition of indifference curve |
This is a curve that shows all possible combinations of two products between which an individual is in different is indifferent |
|
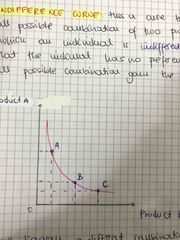
Explain point A, B, C |
From the above diagram ABC on the curve give the consumer the same satisfaction. Therefore an individual is in different after any combination |
|
|
Name the 3 properties of an indifference curve |
1) The indifference curve is convex to the original simply because of the marginal rate of substitution. In order for an individual to obtain the same satisfaction for any combination of goods or consumer is prepared to give up less of one product to obtain more of another product. 2) The higher the indifference curve the higher the satisfaction. And any individual prefer consuming higher combination on the highest indifference curve. It also enables consumers obtain greater quantities of both products 3) The indifference curves will never intersect |
|
|
Name the 3 properties of an indifference curve |
1) The indifference curve is convex to the original simply because of the marginal rate of substitution. In order for an individual to obtain the same satisfaction for any combination of goods or consumer is prepared to give up less of one product to obtain more of another product. 2) The higher the indifference curve the higher the satisfaction. And any individual prefer consuming higher combination on the highest indifference curve. It also enables consumers obtain greater quantities of both products 3) The indifference curves will never intersect |
|
|
Definition of individual indifference map |
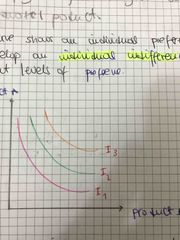
This shows different levels of preference |
|
|
Name the 3 properties of an indifference curve |
1) The indifference curve is convex to the original simply because of the marginal rate of substitution. In order for an individual to obtain the same satisfaction for any combination of goods or consumer is prepared to give up less of one product to obtain more of another product. 2) The higher the indifference curve the higher the satisfaction. And any individual prefer consuming on the highest indifference curve ad It enables consumers to obtain greater quantities of both products 3) The indifference curves will never intersect |
|
|
Definition of budget line |
This is a curve that shows the combination of two products that an individual can produce in a given level of income. This theory assumes that consumers are rational have a limited income and aim of maximising their total utility |
|
|
Definition of budget line |
This is a curve that shows the combination of two products that an individual can produce in a given level of income. This theory assumes that consumers are rational have a limited income and aim of maximising their total utility |
|
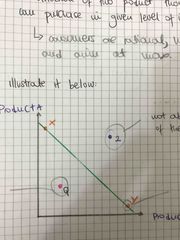
Explain the following points on the budget line |
1) Q there is no full use of his income 2) Z, he’s not able to buy any of the combination as it is above the budget line 3) X and Y are maximising their income but only of either of the two products |
|
|
What can cause the budget to shift or pivot |
This can happen whenever there is changes of the price of the product or changes in the income of individual. |
|
|
What causes the budget line to pivot and why |
A change in price will always affect the real income or purchasing power of an individual. This is causing a pivot on the budget line |
|
|
What causes the budget line to pivot |
A change in price will always affect the real income or purchasing power of an individual. This is causing a pivot on the budget line |
|
|
Show what happens when the price of the product falls |
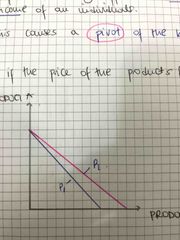
Back (Definition) |
|
|
What causes the budget line to pivot |
A change in price will always affect the real income or purchasing power of an individual. This is causing a pivot on the budget line |
|
|
Show what happens when the price of the product falls |
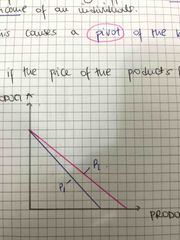
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Draw what happens on the price of product a decreases and the price of product be increases |
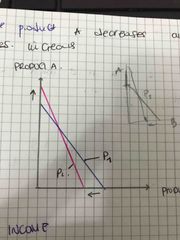
Back (Definition) |
|
|
What causes a paddle shift of the budget line |
Whenever there is a change in the nominal income of an individual, it causes a paddle shift of the budget line. This is because the change in income also affects the individual is purchasing power and services |
|
|
What causes a paddle shift of the budget line |
Whenever there is a change in the nominal income of an individual, it causes a paddle shift of the budget line. This is because the change in income also affects the individual is purchasing power and services |
|
|
What will happen when the budget increases and when the budget decreases |
When the budget increase this to be a shift to the right of the budget line. While when there is a fall in the budget there will be a shift to the left of the budget line |
|
|
Def of optimum consumption point and where does it happen |
There is a point where consumers maximise satisfaction or utility it is also known as the equilibrium point of the consumer This is a point where the budget line is tangential to indifference curve |
|
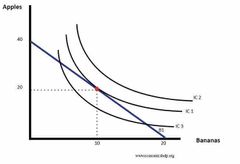
Why is the red point the optimum consumption point |
1) At IC3, it is within the budget line but it gives less satisfaction compared to IC1 2) At IC2, Given the. The current income it is unobtainable . However it gives a high satisfaction 3) Given a budget line of B1, the consumer will maximise utility where the highest indifference curve is tangential to the budget line |
|
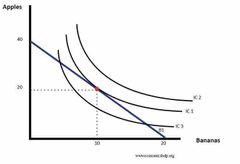
Why is the red point the optimum consumption point |
1) At IC3, it is within the budget line but it gives less satisfaction compared to IC1 2) At IC2, Given the. The current income it is unobtainable . However it gives a high satisfaction 3) Given a budget line of B1, the consumer will maximise utility where the highest indifference curve is tangential to the budget line |
|
|
Name the changes that to make the optimum consumption point move |
1) changes in income of an individual 2) changes in price of a product |
|
|
How does a change of income of an individual because the optimum consumption point to move |
Whenever there is a change in income of an individual, the changes and individuals ability to produce both products. This leads to a parallel shift of the budget line |
|
|
What happens to the optimal consumer point when Income rises |
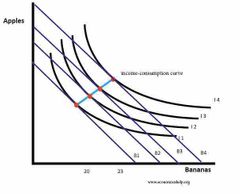
As income rises, you can afford to consume on higher indifference curves. This optimal choice will shift to the right. This we can plot consumption as income rises. |
|
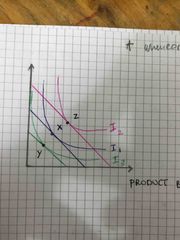
Explain point X, Y and Z |
1) At the point Y, It’s still an optimum point but it gives less satisfaction because the individual is consuming at the lower indifference curve due to a decrease in the real income 2) at point Z, it gives the highest satisfaction because the individual is consuming on the highest indifference curve this is due to an increase in the real income And therefore the consumer is still able to consume an optimum point but at a different indifference curve |
|
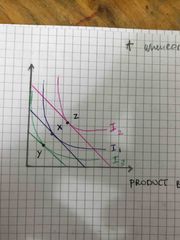
Explain point X, Y and Z |
1) At the point Y, It’s still an optimum point but it gives less satisfaction because the individual is consuming at the lower indifference curve due to a decrease in the real income 2) at point Z, it gives the highest satisfaction because the individual is consuming on the highest indifference curve this is due to an increase in the real income And therefore the consumer is still able to consume an optimum point but at a different indifference curve |
|
|
What will the the optimum Consumption point of the consumer depend on Explain |
1) This will depend on the nature of the product. Normal goods are goods which demand increases with the increase of income. From point X to Z. however the income decreases consumers will be less of a normal goods Inferior goods are goods which they demand increases when the decreases with the increase of income 2) Changes of prices of a product Whenever there is a change of price of a product, consumers real income changes This affects the optimum consumption point of the consumer. However, this will depend of the nature of the good that the consumer intendes to buy ( normal, inferior, giffen goods) Whenever there is a change in prices, there are two effects that influence the demand of the product: substitution and income effect |
|
|
Def of substitution effect |
this states that an increases in the price of a good, will encourage consumers to buy relatively cheaper alternative goods |
|
|
Def of substitution effect |
this states that an increases in the price of a good, will encourage consumers to buy relatively cheaper alternative goods |
|
|
Def of income effect |
This looks at how the the purchasing power/ real income of an individual changes due to a change in price. For example, if price rises, it reduces the consumer’s purchasing power and there would be a fall in demand of the good because of the fall the in disposable income |
|
|
Def of giffen goods and example |
These are goods which demand increases when price decreases. These are generally regarded as goods of low quality which are importante le mega of the elements in the expenditure of those of low incomes The idea is that if you’re very poor and the price of your basic food stuff , for example bread increases, then you can’t afford the more expensive alternative food ,for example meat. Therefore you end buying more bread because it’s the only thing you can afford |
|
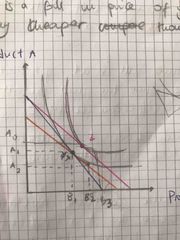
Explain the normal good on the indifference curve |
Assuming consumers want to buy a good A and good B , and there is a fall in price of good B, making it relatively cheaper than good A |
|
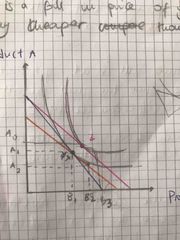
Explain the normal good on the indifference curve |
1) Assuming consumers want to buy a good A and good B , and there is a fall in price of good B, making it relatively cheaper than good A 2) From the above diagram, X is is the original consumption point. When the price of product B falls, the substitution effect will increase demand of good B and decrease demand of good A( because it is relatively cheaper than B) Consumers will still be on the same indifference curve, even though more of product an Is demanded. This causes a movement along the indifference curve from point X to Y 3) At point Y, an imagery budget line is tangent to the indifference curve. 4) the income effect will cause a parallel shift of the imaginary budget line from BL2 to BL3 on a higher indifference curve I2. This is where the new optimum consumption point, Z, will be formed when the new budget BL2 is Tangent to the indifference curve, I2. This enables individuals to consumer greater quantities of both goods( A3 and B3). This is because consumers purchasing power increased due to a fall in price and behaviours of his or her income increased.
|
|
|
Overall impact on the normal good when price falls |
In both cases the movement from X to Y represents the substitution effect of the movement from X to Z represents the income effect In both case, the substitution effect increases demand on the price falls. As well the income effect increases demand when the price falls. However the income effect outweighs the substitution effect. Therefore the demand will increase due to higher income effect when price falls. This gives a normal demand curve as shown above |

