![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
115 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
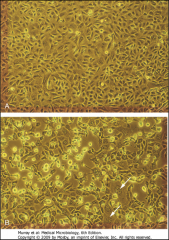
Virus Isolation and Growth: How does this test work?
|
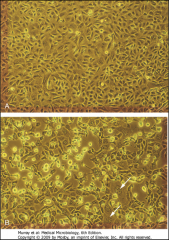
Infected cells with CPEs die and sink to the bottom of the culture. Syncytia can be seen in this HSV culture.
Bright Yellow cells are healthy and alive. |
|
What type of CPE (cytoplasmic inclusion) is pictured here?
What virus is this sample from? |
Syncytia (Multinucleated Giant Cell)
Sample is from measles virus |
|
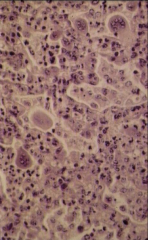
What are the multinucleated cells in this respiratory viral infection called?
|
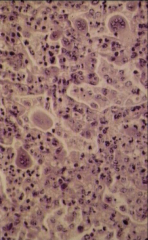
Syncytia
|
|
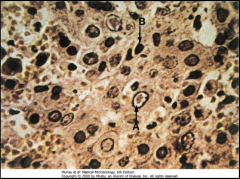
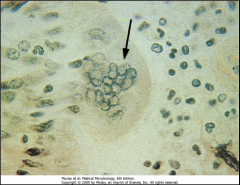
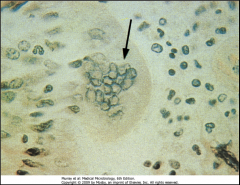
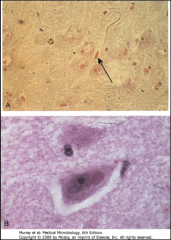
1. What is the CPE to which the arrows are pointing?
2. What virus causes these and what are they? 3. What tissue is depicted here and what test is being performed? |
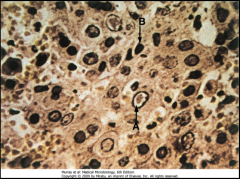
1. Cowdry Type A bodies
2. Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV). They are acidophilic intranuclear inclusion bodies 3. Liver - Tzanck Smear of Vesicle Base |
|
1. What type of CPE is depicted above?
2. What disease is this associated with? |
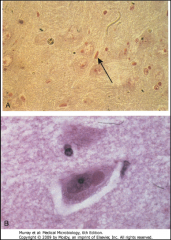
1. Negri Bodies
2. Rabies |
|
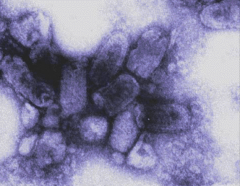
Why is this not done in clinical testing?
|
EM of Viruses are too expensive to run
|
|
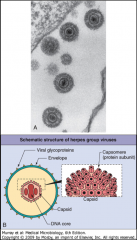
1. What is surrounding the capsid of the Herpes Virus?
2. What is the morphology of this virus? 3. Where does it replicate? 4. What cells do HSV 1 and 2 target and how do they spread? 5. Where is the virus contained so that it can be transmitted? 6. What other CPE do HSV strains cause? |
1. Envelope
2. LInear, dsDNA 3. Replicates in the nucleus - Intranuclear Inclusion bodies (Cowdry Type A) 4. Mucoepithelial Cells - Direct contact, sexual contact 5. Vesicle fluid, Saliva, Vaginal Secretions 6. Syncytia |
|
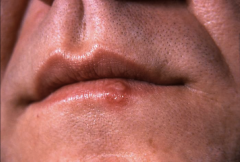
1. What symptom is pictured here?
2. What virus causes this? 3. Where is this virus latent? 4. Where can this symptom also be found? |
1. Cold Sore (Gingivostomatitis)
2. Herpes Simplex 1 3. Trigeminal Ganglia 4. Hard and soft palate, Gingiva, Tongue, Lip, Face |
|
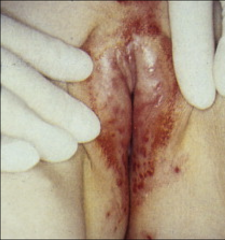
1. What is pictured here and what causes this?
2. Where is this virus latent? 3. If a patient had Meningoencephalitis from this, what would differentiate this from bacterial infection? 4. What can a baby get if it contracts this from its mother during birth and how do you treat it? 5. What other symptoms can you get from this? |
1. Genital Herpes - Herpes Simplex 2
2. Sacral Ganglia 3. Bacterial Infection would have Neutrophils in the CSF. HSV should causes Elevated Protein, Lymphocytosis, and normal glucose 4. Meningitis Encephalitis - Encyclovere (otherwise 70% mortality) 5. Clear mucoid discharge and Dysuria |
|
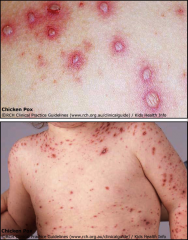
1. What is pictured here and what causes it and what is the morphology?
2. What differentiates this from Small Pox? 3. Where is this virus latent? |
1. Chicken Pox from Varicella Zoster Virus (VZV), Linear, dsDNA, Enveloped
2. The rash is Asynchronous AND covers mostly the torso and face. 3. DRG and Trigeminal Ganglia |
|
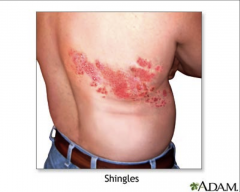
1. What is this and what causes it?
2. When in life is this most common? 3. What is the morphology? 4. What symptoms are associated with this? |
1. Shingles - Reactivated VZV
2. Under stress and in the 5th and 6th decade of life 3. Linear, dsDNA, Enveloped 4. Post-herpetic Neuralgia - Chronic pain syndrome for moths to years |
|
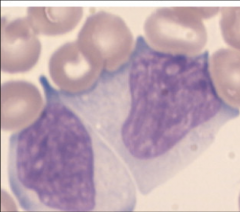
1. What are these and what causes them?
2. Why do they have this appearance? 3. What clinical manifestation of this would result in white patches on the side of the tongue and hyperproliferation of lingual epithelial cells? What patient population would this be seen in? |
1. Downey Cells (Atypical T-Lymphocytes) - Epstein Barr Virus (EBV)
2. T-Cells are made quickly to go after the over-abundance of B-Cells and they are exhausted. Downey cells result. 3. Hairy Oral Leukoplakia - Beginning stage HIV |
|
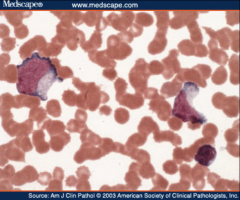
1. Name the abnormal cell and the causative intruder.
2. What chromosomal mutation causes this? 3. What causes the hyperproliferation of B-cells? 4. What receptors does the virus bind to on B-cells? 5. What receptors does the virus bind to on Epithalial cells? |
1. Downey Cells - EBV
2. T(8:14)Translocation joining c-myc with IgH (Immunoglobulin Heavy Chain) 3. c-myc causes proliferation of B-cells. When IgH is activated to make a B-cell, c-myc is also activated, causing B-cell proliferation. Repeat. 4. B-Cells - CR2 Receptors 5. Epithelial Cells - CD21 Receptors |
|
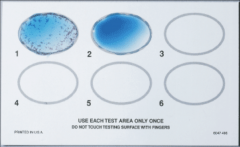
1. What test is this and what disease does it test for?
2. How does this test work? 3. What is the morphology of the virus that this tests for? |
1. Monospot test - Tests for heterophile antibodies - EBV
2. Mixes syrum from the patient with color-enhanced sheep/horse RBC. If EBV, then B-cell proliferation creates Heterophile antibodies. A positive test results in agglutination of RBC. 3. Linear, Enveloped, dsDNA |
|
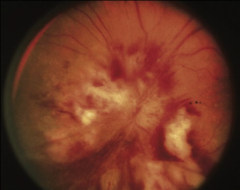
1. What is this and what virus causes it?
2. What patient population is this seen in? 3. What else can be seen in this population with this virus? 4. How does one contract this virus? 5. What is the morphology of this virus? |
1. Retinitis caused by Cytomegalovirus (CMV)
2. HIV and Immunosuppressed 3. Interstitial Pneumonitis 4. Saliva, Sex, Birth 5. Linear, Enveloped dsDNA |
|
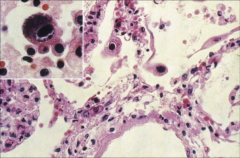
1. What virus causes this and what is this CPE called?
2. Where is this virus latent? 3. When can this cause severe congenital symptoms and what are the symptoms? |
1. CMV - Owl's Eye Inclusion
2. Monocytes and Macrophages, Epithelial Cells 3. Infection during the 1st Trimester - Cytoplasmic Inclusion Disease - Jaundice, Hepatosplenomegaly, Petechial Rash, Multiple organ involvement, Organ transplant rejection |
|
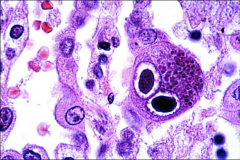
1. What CPE is this and what causes it?
2. How can primary infection be differentiated from recurrent/chronic infection? 3. How is this treated? |
1. Owl's Eye Inclusion - CMV
2. Presence of IgM means NEW infection. Presence of IgG w/o IgM means you cannot tell how long the patient has been infected. 3. Supportive Care |
|
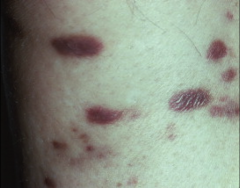
1. What is depicted above and what causes it?
2. What patient population is susceptible to this? 3. What is the morphology? |
1. Kaposi's Sarcoma - Human Herpes Virus 8 (HHV8)
2. AIDS patients 3. Linear, Enveloped, dsDNA |
|
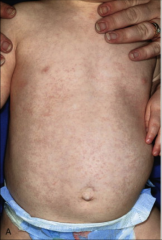
1. What is depicted above and what causes it?
2. What disease is this characteristic of? 3. What population is most often affected? 4. What is the morphology? 5. What precludes this rash? |
1. Lacy Body Rash - HHV6 (Human Herpes Virus 6)
2. Roseola 3. Children (pediatrics) 4. Linear, Enveloped, dsDNA 5. High Fever |
|
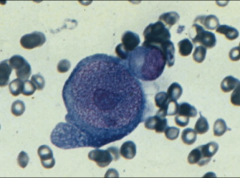
1. What cell is this and what virus often infects it?
2. What is the morphology of this virus? 3. What symptoms are associated with it? 4. How can you determine if the infection was recent? 5. Describe transmission. |
1. Replicating Erythroprogenitor Cell - Parvovirus B19
2. Linear, ssDNA, Naked 3. Anemia from lysis of erythroprogenitors and Aplastic Crisis in Sickle Cell Patients 4. Recent infection shows IgM in Serology. IgG shows that the infection is not new. 5. Inhaled, Replicates in Upper Resp Tract --> Blood --> Marrow |
|
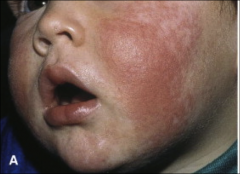
1. What is the symptom depicted above and what virus causes it?
2. What else can this virus cause in adults and what is the mechanism? 3. What can this virus be confused with and why? |
1. Slapped Cheek Rash - Parvovirus B19
2. Arthralgias - Antibody/Antigen complex accumulation in Joints 3. Rubella - They both have a facial rash and arthralgia |
|
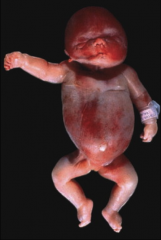
1. What virus causes this and what are the possibilities that caused this outcome?
2. How does a fetus get this virus? 3. What is another name for this virus? |
1. Parvovirus B19 - Hydrops Fetalis, Spontaneous Abortion, Severe Anemia
2. Vertical Transmission from mother to fetus 3. Fifth Disease |
|
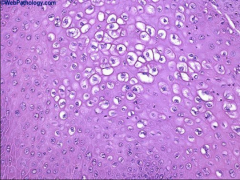
1. What is pictured above and what virus causes it?
2. What is the histological description of the pictured cells? 3. What is the morphology of the virus that causes this? |
1. Koilocytes - HPV
2. Enlarged Keratinocytes with clear halos around shrunken nuclei and a vacuolated cytoplasm 3. Small, Naked, Circular, dsDNA |
|
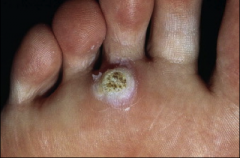
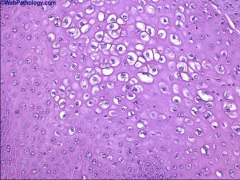
1. What is this and what virus causes it?
2. What histological feature causes this feature? 3. How long does it take for this to develop? 4. What serotype is common on the hands and feet? Plantar? |
1. Cutaneous Wart - HPV
2. Thickening of the Stratum Corneum 3. 3-4 months for the wart to develop 4. Hands and Feet (2 & 4), Plantar (1) |
|
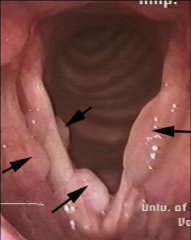
1. To what are the arrows pointing and what serotype causes this?
|
1. Laryngeal Papillomas (most common benign epithelial tumors of the larynx) - HPV 6 & 11
|
|
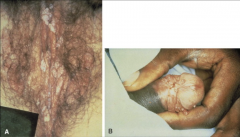
1. What is depicted above and what serotypes cause them?
2. What serotypes are preneoplastic? 3. What viral proteins are associated with malignancy and why? |
1. Genital Warts - HPV 6 & 11 (90% of the time)
2. 16, 18, 31, 35 3. E6 blocks P53 and E7 blocks Rb |
|
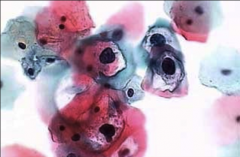
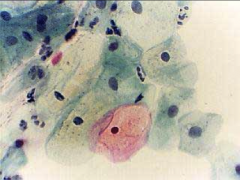
1. What test would this show up on and what does this indicate?
2. What are these cells called? 3. Describe these cells. |
1. Pap smear - HPV
2. Koilocytes 3. Clumped, Rounded Keratinocytes (squamous) with clear halos around shrunken nuclei and a vacuolated cytoplasm. |
|
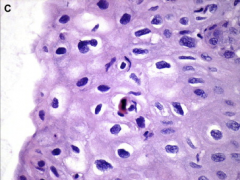
1. This is a pap smear: What is the diagnosis?
|
1. Normal
|
|
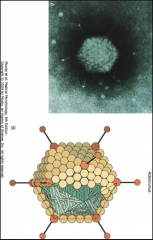
1. What virus is pictured here?
2. What are the projections from the capsomere and what is their function? 3. What is its mode of transmission and why is is so easily spread? |
1. Adenovirus
2. Penton fibers - Toxic - Bind receptors 3. Fecal-Oral Route - Most are asymptomatic |
|
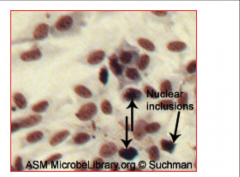
1. To what are the arrows pointing and what virus causes this?
2. What is the morphology of this virus? |
1. Central intranuclear inclusions (Viral DNA and Protein) in an infected epithelial cell - Adenovirus
2. Naked, Linear, dsDNA with Penton Fiber projections |
|
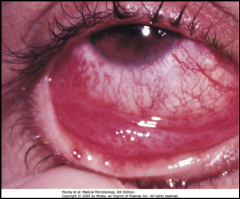
1. What is this, what virus causes this, and what are the two types of this seen with this virus?
2. What population does the Acute Respiratory Disease and Pneumonia serotype affect and what are the serotypes? |
1. Pink Eye - Adenovirus - Pharyngoconjunctivitis (Swimmer's) and Epidemic Keratoconjunctivitis (Shipyard)
2. Children, Military Recruits, College Students - 4, 7, 21 |
|
|
1. What serotypes of Adenovirus cause Gastroenteritis?
2. What population does it affect? 3. What is the most common cause of this symptomology in this population? 4. What symptom is associated with these strains? |
1. 40 - 41
2. Daycare 3. Rotavirus 4. Watery Diarrhea |
|
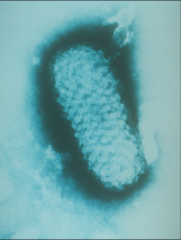
1. What virus is pictured above?
2. Describe the morphology. 3. Where must this virus multiply and why? 4. What are the inclusion bodies in which this type of virus multiplies? What does it acquire there? |
1. Pox Virus
2. Complex oval-to-brick-shaped with internal structure, Enveloped, Large, dsLinear DNA 3. Cell Cytoplasm - must encode enzymes for mRNA and DNA synthesis 4. Guarnieri Bodies - Where it acquired the outer membrane |
|
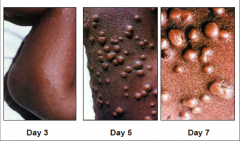
1. What is pictured above and what causes it?
2. What is the preferred mode of transmission and incubation period? 3. What version of this can you get from Prairie Dogs? 4. When is infectiveness greatest? |
1. Smallpox - Variola (Orthopoxvirus)
2. Respiratory - 14 days incubation 3. Monkey Pox 4. During the 1st Week of illness (fever) |
|
|
What is the pathogenesis of smallpox?
How do you treat it? |
1. Inhaled
2. Replicated in upper respiratory tract 3. Incubation 14 days 4. Flu-like symptoms 2-4 days 5. Mouth Rash --> Then Body Rash 24 hours later 6. 2nd Viremia gives pox to tissues 7. Synchronous Rash Treatment - Supportive care to prevent secondary bacterial infection |
|
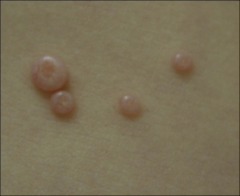
1. What is pictured here and what causes it?
2. What population is usually affected? 3. How is this spread? 4. What differentiates this from HPV warts? |
1. Wart-like Tumors - Molluscum Contageosum (Molluscipoxvirus)
2. Children 3. Skin-to-skin contact --> WRESTLERS, and Sexual Contact 4. Painless (HPV warts can be itchy) |
|
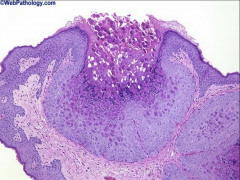
1. What is pictured above and what causes it?
2. What stands out, histologically? 3. How is this treated and why does this work? |
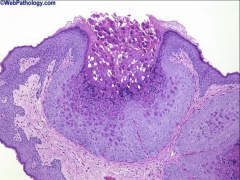
1. Wart from Molluscum Contagiosum
2. Eosinophilic cytoplasmic inclusion bodies. Dimple in the center of the wart 3a. Cryotherapy - Virus is limited to the dermis 3b. Curretage - Scraping removal of nodules 3c. Iodine Solution |
|
|
Which viruses are (+)RNA?
|
Calciviruses
Picornaviruses Flaviviruses Togaviruses Coronaviruses |
|
|
What makes (+)Sense RNA viruses not need RNA Dependednt RNA Polymerase (reverse transcriptase) like the (-)RNA viruses?
|
(+)RNA viruses are 5'-3', so they can be used as mRNA and translated immediately.
(-)RNA viruses are 3'-5', so they have to make a template strand 5'-3' that can be used for translation |
|
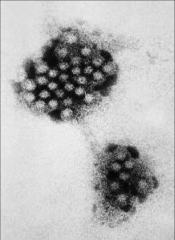
1. What kind of organism is this?
2. What is the morphology? 3. What are examples of this kind of organism? |
1. Calciviridae
2. (+)ssRNA, Naked, Icosahedral 3. Norwalk Virus - Norovirus, Hepatitis E, Noro-like Virus |
|

1. What virus is linked to the above image?
2. What is the reservoir for this virus? 3. What interventions do not work on this virus? 4. What are the symptoms? |
1. Norwalk Virus - Norovirus
2. Human GI tract 3. Desiccation (Dryness) and Chlorine Solutions 4. Damage to intestinal brush boarder --> Watery Diarrhea |
|
|
1. What is the incubation period for Norwalk Virus?
2. What is the duration of it? 3. How long does immunity last afterward? 4. What disease does it cause? |
1. Incubation - 24-48 hours
2. Duration - 12-60 hours 3. Short-lived immunity 4. Acute Gastroenteritis |
|
|
1. What are the two genera of Picornaviridae?
2. What is the morphology of Picornoviridae? 3. How does the virus get out of cells? 4. Where in the body does it replicate? |
1. Enterovirus and Rhinovirus
2. Small, Naked, Icosahedral, (+)ssRNA 3. Cytolytic - multiplies in the cytoplsm and bursts out of the cell 4. Pharynx, Gut, Submucosal Lymphoid Tissue |
|
|
1. What is the morphology of Enterovirus?
2. What are the Enteroviruses? 3. Why are enteroviruses called that if they do not cause diarrhea? 4. Where are they most often found? 5. What conditions are enteroviruses immune to? |
1. Same as the other Piconoviruses - Small, Naked, Icosahedral, (+)ssRNA
2. Polio, Coxsackievirus A and B, and Echovirus 3. They replicate in the GI tract 4. Schools, Daycares, Contaminated Water Supply 5. pH3-9, Detergents, Sewage Treatment, Heat |
|
|
1. Where do enterovirus treatments work?
2. What is the primary immune response? 3. Why do enteroviruses have the ability to target various different tissues? |
1. Antibody Blockage Point is at Primary Viremia
2. Antibody 3. Virus has tropism for cells based on receptors. The disease is dictated by the organ/target tissue. |
|
|
1. What is the reservoir for Polio Virus?
2. What kind of virus is Polio Virus? 3. What diseases are caused by Poliovirus? 4. Describe the morphology of Poliovirus. |
1. Humans
2. Enterovirus - Picornaviridae 3. Aseptic Meningitis, Paralytic Polio, Bulbar Paralytic, and Asymptomatic 4. (+)ssRNA, small, icosahedral, naked |
|
|
In aseptic meningitis, what shows up on a gram stain?
What causes Aseptic Meningitis? |
Nothing
Coxsackie A and B, Polio |
|
|
1. What is the worst case scenario for Poliovirus?
2. What are the treatments for Polio? |
1. Paralytic Polio - Hyperextension of knees/joints, Contractures, Muscle weakness
2. No drugs. Prevention only: Inactivated Vaccine in US. Oral, Active vaccine (CHEAP - Can Mutate) |
|
|
1. What kind of virus is Coxsackievirus A and B?
2. What diseases are caused by Coxsackie A and what are their symptoms? |
1. Enterovirus - Picornaviridae
2a. Hand-Foot-and-Mouth-Disease - Vesicular Exanthem (Serotype A16), mild fever - Children 2b. Herpangina (summer time) - Pain on swallowing, Anorexia, Vomiting, Sore throat, fever, VESICULAR ULCERATED LESIONS AROUND SOFT PALATE AND UVULA |
|
|
1. What diseases are caused by Coxsackievirus B and what are their symptoms?
2. What disease is caused by Coxsackie A AND B? 3. What is the treatment for Coxsackie? 4. How is it diagnosed? |
1a. Pleurodynia - DEVIL'S GRIP on the Thoracic Cage
Can test for it up to 2 weeks after symptoms relieve 1b. Myocardial and Pericardial Infection - Replication of virus in Myrofibers, Scattered myofiber necrosis, Migration of WBC to heart, Myocarditis, Heart Failure (RARE) 2. Aseptic Meningitis - Increased Lymphocytes and Protein. Normal Glucose 3. Supportive care ONLY 4. Stool samples, rectal swab, Culture (CPE 2-6 days) |
|
|
1. What kind of virus is Rhinovirus?
2. What is the morphology? 3. Why dose it grow best in the nose/airway? 4. When is it most common? 5. Why can it live anywhere for weeks? |
1. Enterocirus - Picornaviridae
2. Small, naked, Icosahedral, (+)ssRNA 3. It is 33C there 4. Summer and Fall 5. It is thermostable |
|
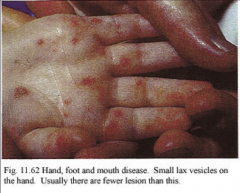
1. What disease is this and what causes it?
2. What is the morphology of this virus? 3. What strain causes Vesicular Exanthem? |
1. Hand-foot-and-mouth-disease caused by Coxsackievirus A
2. Small, Naked, Ichosahedral, (+)ssRNA 3. A16 |
|
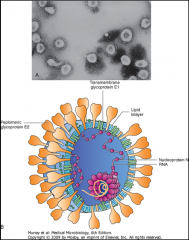
1. What is depicted above?
2. What is its morphology? 3. What is the optimum temperature for it to grow? 4. What makes this clinically distinguishable from Rhinovirus? |
1. Coronavirus
2. Enveloped, (+)ssRNA w/ Glycoprotein clubs/spikes forming a halo (corona) around it 3. 33-35C 4. Nothing |
|
|
1. What causes SARS?
2. What is the EXCEPTION to the rule about Coronavirus that makes SARS so deadly? 3. What created SARS? What is the reservoir? |
1. Coronavirus
2. Coronaviruses usually only cause URIs, but SARS causes Lower Respiratory Infections as well. This leads to ARDS 3. Animal - Bat |
|
|
1. Describe the morphology of Flaviviruses?
2. Which Flaviviruses cause Encephalitis and what are their Host and Vector? 3. Which Flavivirus is transmitted via Aedes Mosquito? |
1. Envelooped, (+)ssRNA
2a. St. Louis Encephalitis, West Nile Encephalitis, Japanese Encephalitis 2b. Host - Bird 2c. Vector - Culex Mosquito 3. Yellow Fever and Dengue |
|
|
Buzzwords:
1. Mosquito Bites 2. Staten Island 3. Old Age |
Flaviviruses
|
|

1. What is transmitted by the Aedes Mosquito?
2. What disease causes Black Vomit and how does this happen? 3. What causes Break Bone Fever? 4. What is meant by antibody mediated immune enhancement and what disease is this affiliated with? |
1. Yellow Fever and Dengue
2. Yellow Fever - Hemorrhage into the GI and then vomit it up 3. Dengue - The virus goes into the Bone Marrow and causes Hemorrhagic Fever and shock 4. Dengue - The antibodies from the first infection help the second infection get into the cells more easily |
|
|
1. What causes Encephalitis and is hosted by Equine animals (horse, goat)?
2. Describe the morphology of this virus. 3. What is the vector for this? |
1. Togavirus - Alphaviruses - Eastern, Western, Venezuelan Equine Encephalitis (EEE, WEE, VEE)
2. Enveloped, (+)ssRNA 3. Mosquito |
|
|
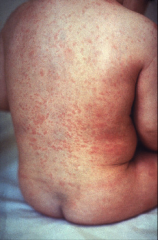
1. What causes German Measles?
2. What are the symptoms of German Measles? |
1. Togavirus - Rubella
2a. Rash that starts on the face and spreads. Caused by immune complexes. 2b. Polyarthritis on the Hands of Older Women |
|
|
1. What causes Congenital Rubella?
2. When is there the most risk for this? |
1. Togavirus - Rubella
2a. When the primary infection is gained during the first trimester b/c Rubella crosses the placenta. 2b. This is only in Unvaccinated mothers |
|
|
1. What are the (-)ssRNA Linear viruses?
|
Bring A Polymerase Or Fail Replication
Bunyavirus Arenavirus Paramyxovirus Orthomyxovirus Filovirus Rhabdovirus |
|
|
1. Describe the Morphology of Bunyaviridae?
2. What are the types? 3. What is caused by Hantavirus? |
1. Segmented, Enveloped, (-)ssRNA, Linear
2a. California Encephalitis and Lacrosse Encephalitis from a Mosquito 2b. Hantavirus (Sin Nombre) from Rodent Urine 3. Pulmonary Syndrome, Tachycardia, Pulmonary Edema, Hentapulmonary Shock - DEATH |
|
|
1. What is the morphology of Arenavirus?
2. What is special about the genome about Arenavirus? 3. What are the types of Arenavirus and what are their vectors and symptoms? 4. What are the buzzwords? |
1. Segmented, Enveloped, (-)ssRNA, linear
2. Ambisense - Part (-)Sense and Part (+)Sense 3a. Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis Virus (LCMV) - Rodents - Flu-like w/ meningial irritation 3b. Lassa Fever Virus - Hemorrhagic Fever (50% Mortality) - Rodents 4. West Africa, Huts w/ Hay roofs, Rainy Season, Rodent Urine |
|
|
Buzzwords: What virus do these go with?
1. West Africa 2. Huts w/ Hay roofs 3. Rainy Season 4. Rodent Urine |
Arenavirus - Hemorrhagic Fever
|
|
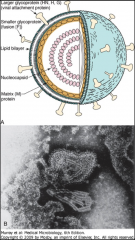
1. Describe the morphology of the virus above.
2. What is the virus above? 3. What viral proteins does it have and what do they do? 4. What does F protein do? 5. What are thy types of this virus? |
1. Enveloped, (-)ssRNA with Viral Proteins
2. Paramyxovirus 3a. HA, H, G - Viral Attachment protein 3b. F - Fusion 3c. M - Matrix 3d. N - Nucleocapsid 3e. P/L - Polymerase 4. Makes multinucleated giant cells 5. Measles, Mumps, Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV), Parainfluenza |
|
1. What disease is this?
|
1. Togavirus - Rubella - German Measles
|
|
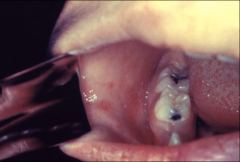
1. What is this and disease causes this?
2. What is its morphology? 3. What proteins does it have? 4. What stage is this in? |
1. Koplik Spots on the Buccal Mucosa - Measles - Paramyxovirus
2. Enveloped, (-)ssRNA 3. F protein - Fusion of Multinucleated Giant Cells HA - Attachment Protein M - Matrix Assembly 4. Prodromal Phase |
|
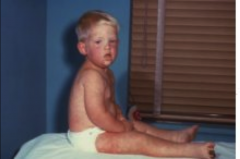
1. What is this and what causes it?
2. How does it spread? How does it fade? 3. What stage is this in? |
1. Maculopapular Rash - Measles - Paramyxovirus
2. Starts on the head and spreads to the rest of the body. Fades in the same manner. 3. Exanthematous Phase |
|
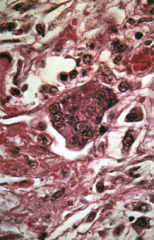
1. What is this and what causes it? What cells are these found in?
2. What is a complication of this disease? 3. What causes the Rash and in what stage? |
1. Multinucleated Giant Cell (Warthin-Finkeldey Cells) - Measles, Paramyxovirus
1a. Found in Respiratory Epithelium and Nasal Mucosa 2. Subacute Sclerosing Paraencephalitis (RARE) 3. T cells target virus-infected cells of capillaries causing the Maculopapular Rash - Exanthematous Phase |
|
1. What disease is this and what causes it?
2. What is the morphology of the virus? 3. What are the symptoms? 4. What are the complications? |
1. Mumps - Paramyxovirus
2. Enveloped w/ Hemagglutinin, Neuraminidase, Cell fusion activity 3. Parotid Gland Tenderness 4. Orchitis --> Sterility, Pancreatitis, and Meningoencephalitis |
|
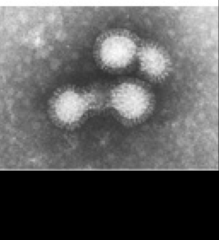
1. What is this and what causes it?
2. What is the morphology? 3. Where does this virus replicate? |
1. Influenzae A, B, C - Orthomyxoviridae
2. 8 (-)ssRNA segments, Enveloped with Neuraminidase spike proteins 3. Cell nucleus and cytoplasm |
|
|
What is the purpose of the segmented genome of Orthomyxovirus (Influenzae A, B)?
|
Segmented genome promotes genetic diversity
Caused by mutation and reassortment of segments on infection with two different strains. |
|
|
Influenza Virus Proteins. What do they do?
1. Neuraminidase (NA) 2. Hemagluttinin (HA) 3. M1, M2 |
1. NA - cleaves sialic acid on glycoproteins - facilitates release of virus from infected cells
2. HA - Viral attachment protein - Binds sialic acid. Fusion of envelope to cell membrane 3. M1 - Matrix protein - Rigidity 3. M2 - Ion channel in Flu A |
|
|
1. What is antigenic drift?
2. What is antigenic shift? 3. Why do pigs facilitate shift so easily? |
1. Minor variations on HA ana NA encoding genes - Influenza A has the greatest rate of change
2. Major antigenic variations that make a new viral subtype - NEW HA and/or NA 3. Pigs have receptors for multiple species strains. The new virus will randomly take 8 segments to make its genome. This combines elements from various virus strains. |
|

1. What does this test for?
2. What is the treatment for this virus? 3. What is the vaccine made of? Who can have it? |
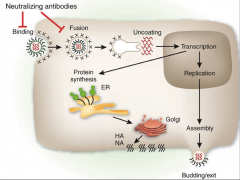
1. Rapid test to tell if it's influenza A or B. Detects viral antigen (Nucleoprotein or NA)
2a. Amantidine - Inhibits viral uncoating 2b. Zanamivir (Tamiflu) - Inhibits Neuraminidase 3. Mixture of extracts or purified HA and NA proteins from three different strains of virus - For healthy people b/w 5-49 y/o |
|
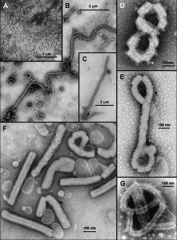
1. What is this and what does it cause?
2. What is its morphology? 3. How is it spread? 4. What are examples of this? |
1. Filovirus - Fatal Hemorrhagic Fever (Ebola, Marburg)
2. Enveloped, Filamentous, (-)ssRNA 3. Direct Contact 4. Ebola, Marburg |
|
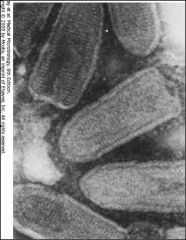
1. What is this and what does it cause?
2. What is its morphology? 3. What receptor does this have? 4. Where does replication occur? |
1. Rhabdovirus - Rabies
2. (-)ssRNA, bullet-shaped, enveloped w/ G-proteins and RNA-dependent RNA polymerase 3. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor 4. Cytoplasm |
|
|
1. What are the hosts of Rabies?
2. How is it transmitted? |
1. Unvaccinated dogs, bats, cats, raccoons
2. Minor - Droplets 2. Major - Saliva from a bite |
|
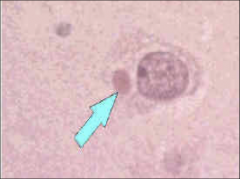
How does Rabies pathogenesis work?
2. What is pictured above? 3. What is the treatment? |
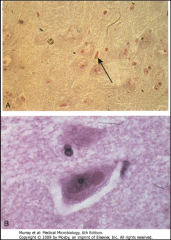
1. You get bit
2. Virus replicates, binds to Nicotinic receptors on nerve endings and muscle cells 3. Retrograde transport to DRG and spinal cord 4. Neural degeneration - NEGRI BODIES 5. Afferent neurons take the virus back to highly innervated sites 6. When you find the antibody, it's too late Treatment - HRIG at bite site and 5 doses of the vaccine |
|
|
What is the morphology of Rotavirus?
2. Which group causes human disease? 3. What protein is an enterotoxin? 4. Which inner core structural protein is an important antigenic determinant? 5. What are the inner core proteins of Rotavirus? |
1. Linear, Segmented (10-12 segments), dsRNA, Naked, Icosahedral w/ double shelled capsule (3 protein layers)
2. Group A 3. NSP4 - alters epithelial cell function and permeability 4. VP6 5. VP1, VP2, VP3, VP6 |
|
|
What is the major viral cause of infantile gastroenteritis?
2. What does it infect? 3. What differentiates this from Adenovirus? 4. How do you test for this? 5. What is the treatment? |
1. Rotavirus
2. Infect enterocytes in the villous epithelium of the small intestine The loss of absorptive villous epithelium, coupled with the proliferation of secretory crypt cells, results in secretory diarrhea. 3. Rotavirus comes with vomiting. Adenovirus DOES NOT. 4. ELISA of stool 5. Live, attenuated vaccine - For children in daycare |
|
|
Which retrovirus causes HIV?
|
Lentivirinae (HIV-1, HIV-2)
Genetically different but related HIV-1 is the most common type associated with AIDS in the United States, Europe, and Central Africa HIV-2 causes a similar disease principally in West Africa and India |
|
|
1. What is the morphology of retroviruses?
2. Why can we not make a vaccine against HIV? 3. What is the reservoir for HIV? |
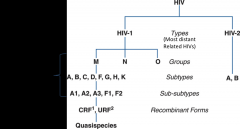
1. Sperical, enveloped, positive-strand (RNA) viruses
2. There is variability in the major protein (M) 3. Reservoir: human T cells and macrophages |
|
|
What are the essential retroviral enzymes?
What is the capsid made of and why is this important? |
RNA-dependent DNA polymerase (reverse transcriptase)
Integrase Protease If any of these don’t function, the virus will not work Capsid made of p24 First antigen we see when there is an initial infection |
|
|
Look at this repeatedly
|
|
|
How does infection with HIV work?
|
1. GP120 and GP41 bind the receptors
2. Facilitate uptake of the virus into the cytoplasm 3. Uncoating and release of the RNA genome 4. Reverse Transcriptase (RNA dependent RNA polymerase) jumps onto the genome in cytoplasm 5. Makes DNA 6. DNA is then made complementary to the first created DNA strand 7. Now you have dsDNA that encodes all of the viral genes - PROVIRUS 8. Integrase puts the dsDNA into the host genome for T-cells and Macrophages 9. Any cells that are made from this cell will be infected 10. The only way to get rid of the virus is to kill the cell that is infected |
|
|
1. How is Herpes Simplex Virus Diagnosed?
2. Where do you get the sample from for this test? 3. How is HSV treated and what does the drug do? 4. Why is this drug only active in Infected cells? |
1. Tzanck Smear for Cowdry Type A bodies (where herpes viruses replicate) and Syncytia
1b. Serology 1c. Immunofluorescence of tissue or fluid for viral particles 1d. PCR 2. Vesicle scrapings 3. Acyclovir - Competitively inhibits viral DNA Polymerase and competes w/ Nucleosides for incorporation into viral DNA. Once incorporated --> Inhibits DNA synthesis 4. Infected cells have Viral Thymidine Kinase, which alters Acyclovir into the active state |
|
|
1. What is the morphology of Varicella Zoster Virus?
2. Describe the pathogenesis of Varicella Zoster. 3. when is VZV contageous? |
1. Herpes Virus --> Linear, Enveloped, dsDNA
2a. Respiratory Droplets inhaled (Primary Infection day 1-4) 2b. Progress via Blood (Primary Viremia day 4-6) 2c. Spread to Spleen and Liver (day 6-11) 2d. Secondary Viremia (day 11- 13) 2e. Spread to skin (Asynchronous Rash (day 14 -->) 2f. Fever (day 13-15) 3. Contageous - Day 11-17 |
|
|
1. How is VZV diagnosed?
2. What CPEs can be found? 3. How is VZV treated? 4. Why can we NOT use Aspirin? 5. What methods do we have for prevention and what strain is used for it? 6. Why do we give a boosted to 60 year olds? |
1. Tzanck smear of Scrapings from the base of Vesicles for CPEs
2. Syncytia, Cowdry Type A bodies 3. Acyclovir 4. Reye's Syndrome is associated w/ Aspirin use 5. Live, attenuated vaccine (Oka Strain) 6. Prevent Shingles |
|
|
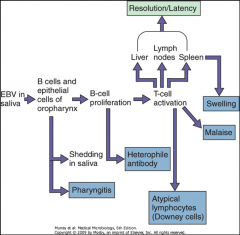
1. How is EBV transmitted?
2. What version of this do children get? 3. At what age is the peak incidence? 4. Where can EBV be latent? |
1. Saliva - 90% asymptomatic and spread it for life
2. Sub-clinical 3. 15-20 y/o 4. B-cells, Liver, Lymph Nodes, Spleen |
|
|
1. What diseases can EBV cause and what are their symptoms?
How is EBV treated? |
1. Mono - Lymphadenopathy, Splenomegaly, Sore Throat w/ HIGH Fever, Rash, Fatigue
2. Hairy Oral Leukoplakia - In Beginning Stages of HIV - Hyperproliferation of Lingual Epithelial Cells and white patches on the side of the tongue 3. Neoplasms - African Burkitt's Lymphoma, Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma, Hairy Oral Leukoplakia 4. T(8:14) Translocation Treatment - Acyclovir - for immunocompromised |
|
|
1. What is the most common cause of Intrauterine infections and congenital abnormalities in the US?
2. What is the target for this organism? 3. How many people are infected by age 15? 4. How is this diagnosed? 5. How is this treated? |
1. Cytomegalovirus (CMV)
2. Salivary Gland Epithelium and Macrophages 3. 15% by age 15 4a. Microscopy - Enlarged, Multinucleated cells with Owl-Eye Inclusions 4b. Serology - IgM vs. IgG 5. Supportive care |
|
|
1. What is Fifth Disease and why is it called that?
2. What percentage of the population is seropositive? 3. How is this virus transmitted and what is its pathogenesis? 4. How is this diagnosed? 5. How is it treated? |
1. Erythema Infectiosum - Parvovirus B19 - It is one of the five major childhood diseases
2. 65% 3a. Fomites, Vertical transmission, Respiratory Route 3b. Replicate in Nasopharynx and Upper Resp. Tract 3c. Viremia --> Bone marrow 3d. Infects actively replicating erythroprogenitor cells --> Causes Lysis 4. Serology: IgM vs. IgG 5. Supportive care |
|
|
1. How is HPV transmitted?
What histologic feature is seen on pap smear? |
1. Direct contact through small breaks in the skin or mucosa, Sexual intercourse, or Birth Canal
2. Infects basal layer Epithelium of skin or mucous membranes 3. Induces Epithelial Proliferation 4. Warts (hyperkeratosis of stratum corneum) form in 3-4 weeks On pap smear --> Koilocytes |
|
|
1. What strains of HPV cause Genital Warts?
2. Which strains are pre-neoplastic? 3. Which strains does Gardasil protect against? 4. How are genital warts treated? |
1. Warts: 6, 11, 16, 18, 31, 35
2. Pre-neoplastic: 16, 18, 31, 35 3. Gardasil: 6, 11, 16, 18 4. Cryotherapy |
|
|
1. What are the strains of Polyomaviridae?
2. What is the route of transmission? 3. What is the affected population? |
1. BK and JC Viruses
2. Respiratory 3. Immunocompromised |
|
|
1. What is caused by BK Virus?
2. What is caused by JC virus? 3. What are the symptoms of the condition caused by JC virus? 4. What is important about this condition from the perspective of immune competence? |
1. Renal Disease of all sorts and Allograft loss of kidney transplants
2. PML - Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy 3. Demyelination of white matter 4. This is an AIDS-Defining Disease |
|
|
1. What Permissive Cells does Adenovirus cause Lytic Infection in?
2. What is the effect of Adenovirus on non-permissive cells? 3. What is the histologic hallmark of Adenovirus? 4. How is Adenovirus Diagnosed? 5. What is the treatment for Adenovirus and who uses it? |
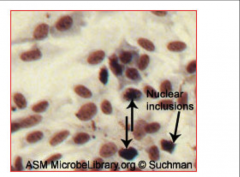
1. Epithelial Lining of Oropharynx, Respiratory, and Enteric Organs
2. Chronic or Oncogenic Changes 3. Dense, central intranuclear inclusion (Viral DNA and Protein) in an Epithelial Cell (Pictured) 4a. Isolation in vitro (2-20 days can detect cell lysis and inclusion bodies) 4b. PCR 4c. Serology, ELISA 5. Live, non-attenuated vaccine - MILITARY ONLY |
|
|
1. What is the treatment for Small Pox (variola)?
2. How is Small Pox prevented? |
1. Supportive Care - Fluids, Pain Relief, Prevention of secondary bacterial infection
2. Live, attenuated vaccine - Stabbed in the triceps 15 times and leaves a pencil-eraser scar |
|
|
How does infection with HIV work?
|
1. HIV (GP120) binds to CD4 receptor and chemokine coreceptors on whatever cell it is infecting
2. Fuse with the cell membrane by using GP41 to bind the coreceptors 3. Genome is reverse transcribed to DNA in the cytoplasm 4. DNA is now integrated into the nuclear DNA using INTEGRASE, forming a PROVIRUS 5. Provirus remains in the host cell and can be latent 6. Transcription and Translation of Genome 7. Rate of viral replication is regulated by regulatory proteins 8. Virus assembles at the plasma membrane 9. Buds from the cell and matures |
|
|
What cells can HIV infect and how does it gain entry into those cells?
|
1. HIV GP120 glycoprotein spikes bind CD$ T Cells, Macrophages, Microglia
2. GP120 also binds co-receptors 2a. CCR5 - Macrophages, Peripheral, and other T-Cells (Macrophages, M-Tropic) 2b. CXCR4 T-Cells (T-tropic) 3. Chemokine receptor binding allows GP41 to interact with and promote fusion of the 2 membranes |
|
|
How it is that people are immune to HIV?
|
1. When you have a gomozygous mutation in your co-receptors, there is nothing for HIV GP120 to bind in order to fuse with your cells
|
|
|
1. What can stimulate Latent HIV to become active?
|
1. Co-infection such as TB or EBV
|
|
|
1. Where does HIV initially infect?
2. What virus specifically infects initially? 3. What is the virus that comes later? 4. What happens once the HIV causes Viremia and Viral Dissemination? 5. What is the immune response to this? |
1. Initial infection is at the sites of entry through mucosa epithelia, in lymphoid organs (nodes), and in the circulation
2. R5-M-tropic virus --> Focuses on macrophages 3. X4-T-Tropic VIrus 4. There is a massive loss of CD4 T Cells because they become the primary target 5. Downregulation of virus replication |
|
|
1. Explain HIV Infection Syndrome. Who gets it, what are the symptoms?
2. How do these symptoms resolve? 3. How long does the latent phase last? 4. What happens during the latent phase? |
1. 40-90% of patients - Fever, malaise, myalgia, lymphadenopathy, macular rash for a few days to weeks.
2. Cellular and immune response (Downregulation of HIV) 3. Could last more than 15 years 4. CD4 cells decline slowly and opportunistic infections start coming in (non-life threatening) |
|
|
What are the 3 phases of HIV infection?
|
1. Primary HIV Infection Syndrome
2. Latent Phase 3. AIDS |
|
|
1. What are the T-cell counts for Full Blown AIDS?
2. What is a NORMAL count? 3. What happens when a person has full blown AIDS? |
1. LESS THAN 200 cells/microL
2. 1000 cell/microL 3. Virus levels climb - Person is prone to life-threatening infections |
|
|
What is the hallmark of AIDS?
How does HIV switch from binding CCR5 (M-tropic virus) to binding CXCR4 (T-tropic)? Why can more than 1 antigenic variant of HIV be found in a person? Who is most at risk for having more than 1 antigenic variant? |
1. Profound immunosuppression affecting cell-mediated immunity
2. Changes to the GP120 during infection 3. High incidence of Genetic Drift --> More than one antigenic variant 4. Those with high titers |
|
|
How do we test for HIV?
What do home kits use to do a rapid test? What is P24? |
1. Direct ELISA - rapid screening test (IgM and IgG)
2. Western Blot - confirmatory test (IgG) 3. Viral Load - RT-PCR 4. Provirus Detection - PCR 5. Early Antigen Marker - P24 antigen capture assay 6. Evaluate progress of disease - CD4:CD8 T cell ratio. CD4 cells will gradually decline Home kits use IgG from saliva P24 is an antigen that covers the nucleocapsid of HIV |
|
|
In vertical transmission, why can you not test for antibodies?
What can you test for? |
1. Antibodies came from the mother, so the child will test positive for them for up to one year
2. You can test for Provirus ONLY |
|
|
How do you treat HIV?
What is the problem with HAART? |
1. Inhibitors that target:
Reverse Transcriptase Protease Fusion Integrase 2. CCR5 co-receptor Antagonists 3. HAART (Highly Active Anti-Retroviral Therapy): 2 Nucleoside analogs and 1 protease inhibitor Problem with HAART: Increases resistance |
|
|
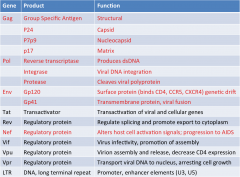
1. What are the 4 products of the Gag genes on HIV and what do they do?
|
1. P24 - Capsid - first antigen we see at initial infection
2. P7p9 - Nucleocapsid 3. P17 - Matrix 4. Group Specific Antigen - Structural |
|
|
What are the 3 products of the Pol gene in HIV and what does each one do?
|
1. Reverse Transcriptase - Produces dsDNA
2. Integrase - Viral DNA integration 3. Protease - Cleaves viral polyprotein |
|
|
What are the 2 products of the Env gene from HIV and what do they do??
|
1. PG120 - Surface protein (Binds CD4, CCR5, CXCR4) - Responsible for genetic drift
2. GP41 - Transmembrane protein - Viral Fusion |
|
|
What is the 1 product of Nef on HIV and what does it do?
|
1. Regulatory Protein - Alters host cell activation signals --> PROGRESSION TO AIDS
|

