![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
59 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Polio virus VP2 mimics what self-antigen? |
Acetylcholine |
|
|
Myelin Basic protein is mimicked by |
Measles Virus P3 |
|
|
Insulin receptors are mimicked by |
Papilloma Virus VP2 |
|
|
Antigen attacked in Addison's disease |
Microsomal proteins of adrenal cells |
|
|
Antigen attacked on acute disseminated encephalomyelitis |
Basic protein of myelin |
|
|
Thyroglobulin and microsomal antigens are attacked in what autoimmune disease? |
Hashimoto's Thyroiditis |
|
|
Antigen attacked on Type 1 DM
|
Islet Cells |
|
|
Type 4 collagen membranes are attacked in what disease? |
Goodpastures Syndrome |
|
|
TSH receptors are attacked in what disease? |
Grave's Disease |
|
|
Acetylcholine receptors are attacked in what autoimmune disease? |
Myasthenia gravis |
|
|
Smooth muscles are attacked in what autoimmune disease? |
Autoimmune chronic active hepatitis |
|
|
Antigens attacked in Pernicious Anemia |
Gastric Parietal cell antigens, Intrinsic Factor |
|
|
Antigens attacked in Sjogren's Syndrome |
Salivary Gland nucleolar antigen |
|
|
Antigens attacked in Billiary Cirrhosis |
Mitochondria |
|
|
Striated Cardiac muscle antigens are attacked in what autoimmune disease? |
Autoimmune myocarditis |
|
|
Epidermal antigen are attacked in what disease? |
Pemphigus vulgaris |
|
|
Bullous Pemphigoid |
Attacks Epidermal Antigen |
|
|
Autoimmune rheumatic fever |
attacks heart and joint tissue organ |
|
|
In Antibiotic testing how long is the diameter of the plate and how deep is it? |
4mm depth and 6mm diameter |
|
|
Rosette uterus |
Diphylobothrium latum |
|
|
Rosette Microconidia |
Sporothrix schenkii |
|
|
Disease of Connective Tissue |
SLE |
|
|
most common manifestation of SLE |
arthritis |
|
|
Skin lesions found in SLE |
Butterfly rash or RED WOLF |
|
|
What antibody is present in SLE?
|
Anti-Nuclear Antibodies |
|
|
True or False: ANA is a specific antibody for SLE |
False |
|
|
Specific antibodies detected in SLE |
Anti-smith antibody and anti-double stranded DNA |
|
|
Specific antibodies usually found in all SLE |
Anti-dsDNA |
|
|
Cell associated with SLE |
Le cell |
|
|
Le cell appearance |
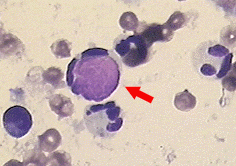
PMN leukocyte with ingested LE body, often in rosette formation |
|
|
Serologic Tests for SLE |
Antinuclear Antibody Visible Method and Indirect Fluorescent Antibody Detection of ANA |
|
|
Most commonly used and well known serologic test for SLE |
Indirect Fluorescent Antibody detection of ANA |
|
|
Nucleolar fluorescent pattern is associated with what disease? |
Scleroderma |
|
|
Pattern of fluorescence for SLE |
Homogenous, Peripheral, or Speckled |
|
|
Discrete patterned fluorescence are seen in what diseases? |
Calcinosis Reynauds Esophageal dysmotility Sclerodactyl Telangietasia |
|
|
Speckle patterned fluorescence are associated with what diseases? |
SLE, RA, MCTD |
|
|
Peripheral patterned fluorescence are associated with what diseases? |
Active stage of SLE Sjorgen's Syndrome |
|
|
Homogenous patterned fluorescence are associated with what diseases? |
Rheumatoid arthritis SLE Sjorgens Syndrome MTCD |
|
|
Autoimmune disease causing chronic inflammation of the joints and periarticular tissue |
Rheumatoid Arthritis |
|
|
What is the nonspecific marker for rheumatoid arthritis? |
Rheumatoid Factor |
|
|
What is the specific marker for RA? |
anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide
|
|
|
Sensitized Alligator Erythrocyte Test for RA was discovered by |
Cohen et al |
|
|
Rose-Waaler test for RA |
Sheep Cell Agglutination Test |
|
|
Latex Fixation Test for RA was discovered by |
Singer and Plotz |
|
|
Bentonite Flocculation Test was discovered by |
Bloch and Bunim |
|
|
Carcinoembryonic antigen |
GI cancer |
|
|
AFP |
hepatocellular cancer |
|
|
PSA |
prostate cancer |
|
|
Best and only specific tumor marker |
PSA |
|
|
Breast Cancer |
CA15-3 |
|
|
pancreas, stomach, bile duct cancers |
CA 19-9 |
|
|
Ovarian CA |
CA 125 |
|
|
Gastric Cancer |
Ca 72-4 |
|
|
Defined as the initial force of attraction between Fab and single epitope |
Affinity |
|
|
Definition of Avidity |
sum of all attractive forces between an antigen and an antibody |
|
|
Process wherein Thymocytes are presented with MHC molecules to make them single positive t cells |
Positive selection |
|
|
Process wherein T cells are selected through their lack of stimulation from self antigens in the medulla of the thymus |
Negative selection |
|
|
2 mechanisms of immune tolerance |
Clonal anergy and clonal deletion |
|
|
IgM attacking IgG disease |
Rheumatoid arthritis |

