![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Hematopoiesis
|
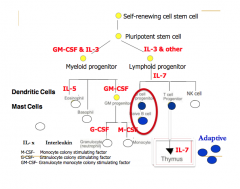
- B cell arise in the bone marrow from progenitor lymphoid cells
- During development, the progenitor B cell acquires its antigen specific receptor (immunoglobulin) |
|
|
Antigen Specific Receptors
|
B lymphocytes (B cells) express antigen recognizing receptors (membrane immunoglublin/ antibodies) on their cell surface. These receptors mediate interaction between the B cell and the intact antigen.
|
|
|
mIg
|
- Membrane immunoglobulin
- Expressed in association with a heterodimer, CD79a/CD79b (Igα-Igβ) |
|
|
Structure of immunoglobulins
|
- Composed of 2 identical heavy chains, and 2 identical light chains linked by disulfide bonds
- Each chain is made up of a variable region and a constant region - In naïve mature B cells, the heavy chain constant regions are mu (μ) and delta (δ), while the light chain constant regions are either kappa (κ) or lambda (λ) |
|
|
Light chain variable region
|
Composed of segments designated "V" and "J"
|
|
|
Heavy chain variable region
|
"V", "D", and "J" segments, where the letters "V", "D", and "J" refer to the Variable, Diversity, and Joining segments
|
|
|
Paratope
|
The antigen binding site is contained within the combined variable regions of the light and heavy chains
|
|
|
Interactive forces
|
- Non covalent - antigens can come on and off
- Attraction between the antigen binding site and an epitope determines the affinity = AVIDITY |
|
|
Somatic recombination
|
- DNA in the loci that encode the variable regions is cut and recombined to make an intact gene for the variable regions of the light and heavy chains
- The variable region genes and constant region genes are transcribed to hnRNA which is spliced to mRNA which is in turn translated to a light chain and a heavy chain - This occurs in the bone marrow during B cell development |
|
|
RAG-1 and RAG-2 genes
|
- Recombination activating genes which trigger somatic recombination
|
|
|
Light Chain Rearrangement
|
- Selection and ligation of 1 "J", and 1 "V" to form a VJ segment
|
|
|
Heavy Chain Rearrangement
|
- 1 "D" and 1 "J" are randomly selected, to form a DJ gene segment, which then combines with a randomly selected "V" gene segment to form the variable region (VDJ) of that particular heavy chain
|
|
|
Combinatorial diversity
|
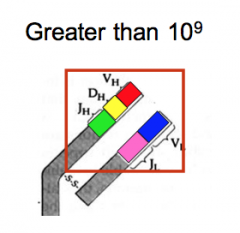
- During the recombination process of either the light or heavy chain variable region, intervening unselected "Vs", "Ds" or "Js" are deleted
|
|
|
Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase
|
Incorporation of nucleotides at junctions is mediated by a template independent DNA polymerase
|
|
|
Allelic Exclusion
|
- When there is successful rearrangement of a heavy chain variable region from one chromosome - it inhibits the somatic recombination of the heavy chain variable region on the other member of the chromosome pair, a process known as allelic exclusion
- All mIg present on the surface of any one B cell will have the same heavy chain variable region |
|
|
Stages in the Bone Marrow
|
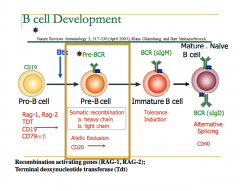
- B cell differentiation in the bone marrow occurs prior to any exposure to foreign antigen
- It is characterized both by the expression and silencing of distinct sets of genes |
|
|
Pro-B cell Stage (Transcription)
|
- Transcription of multiple genes, including RAG-1 and RAG –2, CD19, Tdt and CD79, required for differentiation of the B cell in the next developmental stage
|
|
|
Pre-B cell Stage (Expression of Pre-BCR)
|
- Pre-B cell receptor (pre-BCR) in association with the CD79a/CD79b heterodimer
- Signaling via the pre-BCR complex directs proliferation and further differentiation of pre-B cells - CD19 and CD20 is expressed at this stage of the developing B cell |
|
|
Immature B cell Stage (Tolerance Induction)
|
- Pre-BCR to BCR
- Assembly of rearranged light chains and the heavy chains with CD79 heterdomers to form the BCR - Pre-BCR is downregulated - Apoptosis or anergy of auto-reactive mIg (tolerance induction) - BCR on surface |
|
|
Mature B cell Stage (Alternative Splicing)
|
- Co-expression of cell surface IgM and IgD, which is the consequence of alternative splicing
- Mature naive B cells leave the bone marrow, enter the blood stream, migrate to peripheral lymphoid tissues, and re-circulate if they do not encounter antigen in a secondary lymphoid tissue |
|
|
Summary
|
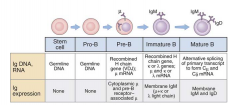
|
|
|
Exit from blood
|
- Mediated by L-selectin on B cells on high endothelial venules (HEV)
- Entry into the spleen occurs at terminal branches of the central arterioles - Failure to encounter antigen while transiting through secondary lymphoid tissues results in naive B cells entering the re-circulating pool via efferent lymphatics, en route to the thoracic duct or right lymphatic duct |
|
|
Bruton’s
|
- Mutations in the Btk kinase are associated with X-linked agammaglobulinemia
- Plays a critical role in B cell activation, differentiation, and proliferation - Btk defect occurs at the pro-B to pre-B cell transition - Patients with XLA have (DEFECTIVE) pre-B cell populations in the bone marrow such that these cells fail to mature and enter the circulation XLA - Profoundly reduced numbers of B cells in the peripheral blood, and serum Ig levels of all classes are low |

