![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
another term for antigen is _________ ___________.
|
Antibody generators |
|
|
Allogeneic means
|
an antigen that is recognized as foreign, but within the species |
|
|
autologous means |
self-recognized, unique to the individual |
|
|
TRUE/FALSE: in the transfusion setthing, is the immune respone primarly humoral |
true
|
|
|
In blood banking, which arm of the immune system is most often dealt with? (Innate or acquired?)
|
Innate |
|
|
What are the factors of antigens that influence immunogenicity?
|
Degree of foreignness: does it look like self or not? Size: >10,000kD Dosage&Ag density: # of cells and # of Ag site/cell Route of administration: intramuscular/intravenously |
|
|
Why can an
A2-typerecipient with anti-A1 antibody can be transfused A1 red cells |
Because these don't react at body temperature, so they aren't clinically significant.
|
|
|
How many fragments are created when mixing antibodies with the following enzymes: Papain: Pepsin: |
Papain: 3 frags pepsin: 2 frags |
|
|
Why do IgM not cross placenta?
|
Too big... pentamer |
|
|
At what temp are the following Ab most active? (optimal) IgM IgG |
IgM: RT or lower
|
|
|
Of what class are the antibodies that are "naturally occurring"? Examples: |
IgM Examples: Anti-A, Anti-B, Anti-A,B Hh Ii Lewis MN P |
|
|
What class are the antibodies that are only found in the plasma of individuals exposed to RBC antigens vis transfusion or pregnancy?? examples: |
IgG Examples: Rh, Kell, Duffy, Kidd, S, s Clinically significant! Detection requires AHG |
|
|
What is the isotype of the Ab generated in a primary immune response?
|
IgM |
|
|
What are the two stages of in vitro Ag-Ab reactions (hemagglutination)?
|
2. Lattice Formation (LF) |
|
|
What are the factors that effect the sensitization stage of in vitro Ag-Ab reactions?
|
1. time (increases Ab-Ag reactivity) 2. temp (optimizes Ab reactivity) 3. pH (conc. of H ions. Enhances Ab reactivity. At less than 6.5, some Ab don't even react) 4. ionic strength (low is best) |
|
|
What are the factors that effect the lattice formation stage of in vitro Ag-Ab reactions?
|
1. zeta potential (distance btwn sensitized cells) 2. zone of equivalence (Ab-Ag concentrations) 3. centrifugation (forced interaction btwn Ag-Ab) |
|
|
In a physiologic saline, what is the surface charge on RBC? What surface molecule is this attributed to?
|
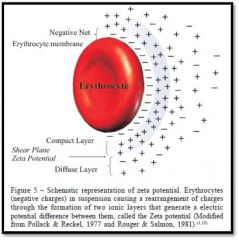
Sialic acid |
|
|
ZONE of equivalence: Prozone is due to........... Postzone is due to.................. |
postzone = antigen excess |
|
|
How does centrifugation effect lattice formation in in vitro Ab-Ag reactions
|
overcome zeta potential and augments effect of low ionic potentiators |
|
|
why should you use EDTA tubes for blood banking?
|
you want plasma, not serum. when serum in used, the complement is not able to function because the Ca has been chelated |
|
|
What gov't agency is responsible for regulating the the specificity and potency of commercial antisera and reagent RBCs? What agency is responsible for the licensing of blood banking products |
US FDA CBER (center for biologics evaluation and research) |
|
|
In blood banking, we optimize the test system in favor of what reaction? |
antigen-antibody reaction :) |
|
|
What color are the following antisera, typically> Anti-A reagent Anti-B reagent |
A- BLUE B- YELLOW |
|
|
When is it indicated to use a low protein control? |
If RBCs agglutinate with allantisera |
|
|
What is the immunodominant sugar for B specificity? |
D-galactose |
|
|
What is the immunodominant sugar for A specificity? |
N-Acetylgalactosamine |
|
|
What is the immunodominant sugar for H specificity? |
L-Fucose |

