![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
48 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
FEATURES OF MAMMOGRAPHIC UNIT:
|
Adequate contrast
Fine details Easy positioning of breast with firm compression Low radiation dose to breast tissues Consistency of exposure factors |
|
|
What are the benefits of the high frequency generator?
|
Allows precise control of kVp, mA, and
exposure times; Excellent linearity & reproducibility of X-ray exposures; More efficient x-ray production; Do not require an autotransformer or line compensation circuit – compact |
|
|
What is the range of kVp used in mammography?
|
KVp selections range from 22 to 40 KVp
- commonly used in clinical practice varies between 25 & 32 KVp (Breast tissue has low inherent subject contrast) |
|
|
What is the exposure time, ma and mAs?
|
mA varies from 2 to 180
Short exposure times to reduce motion Exposure times : 0.4 to 2 sec (standard projections) 2 to 4 sec ( magnification technique) - low mA & small focus |
|
|
What is the AUTOMATIC EXPOSURE CONTROL used for?
|
To provide consistent film density for the various
thickness & density compositions of breast tissues Radiation-sensitive detectors |
|
|
where is the optimal placement of the photocell/detector?
|
beneath the most dense area of the breast.
|
|
|
a fatty breast/area would produce ____ image.
|
- Less dense
|
|
|
a glandular breast/area would produce _____ image.
|
– Dense (Increased in density)
|
|
|
study the parts of the mammographic unit
|
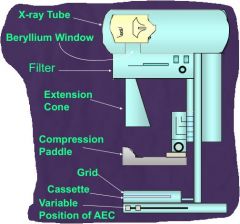
study!
|
|
|
Study the parts of the mammographic unit x-ray tube
|
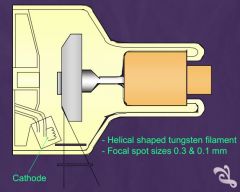
- Helical shaped tungsten filament
- Focal spot sizes 0.3 & 0.1 mm |
|
|
When using conventional X-ray tube, will have missed tissue
|
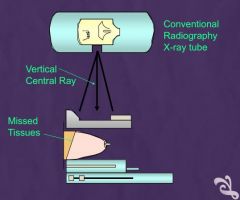
study!
|
|
|
Make sure no missed tissue, use mammo unit where anode at the side
|
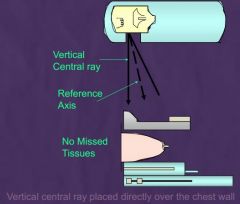
study
|
|
|
X-ray tube
|
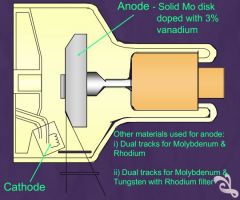
Anode - Solid Mo disk
doped with 3% vanadium |
|
|
what is the range of the rahodium Rh target?
|
s x-rays with a higher
energy range of about 20.2 and 22.8 keV |
|
|
For very dense breasts, what target is the best option?
|
Rhodium
|
|
|
What are the type of filters that are most commonly used?
|
Molybdenum & Rhodium
|
|
|
What is an advantage of using different type of combinations of target and filter material?
|
allows improvement
in penetration and reduction in the mean glandular dose in dense breasts. |
|
|
What is the main goal of mammograpy imaging?
|
The goal is to obtain the highest possible image quality while using the lowest
radiation dose. |
|
|
the choice of target and filter combination will affect ________ (3 things)
|
-High contrast
-Low dose -Compromise between dose and contrast |
|
|
what are the advantages of using Molybdenum?
|
- Increased number of low-energy
photons - High radiographic contrast |
|
|
What are the disadvantages of using Mo?
|
Less X-ray photons output
Increased mAs required Increased dose |
|
|
what is the energy if the Mo filter?
|
20 keV K-edge energy
|
|
|
If Mo has an energy of 20 keV K-edge, radiation above ____keV will be removed.
|
20
|
|
|
what is the thickness of an Mo filter?
|
0.03mm
|
|
|
Using Mo filter, ________ will be removed.
|
high end bremsstrahlung/X-rays
|
|
|
What is a good combination for fatty breast tissues / breast with 1:1 fatty and glandular tissues?
|
Molybdenum target and Molybdenum filter. (Mo/Mo)
|
|
|
What is the energy of a Rhodium filter?
|
Rhodium has a 23 KeV K-edge energy, so it allows
slightly higher energy x-rays to pass through. |
|
|
When is a Mo/Rh selected?
|
when imaging denser breasts
|
|
|
What is the thickness of Rh filter?
|
0.025 mm
|
|
|
Study the Moly/Rhodium spectrum
|
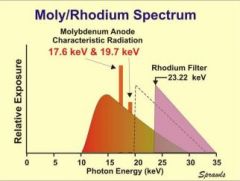
Moly target
Rh 0.025mm filter |
|
|
Study the Moly/Moly spectrum
|
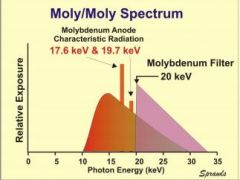
mo target
mo 0.03mm filter |
|
|
What combination combines higher energy x-rays with higher energy filter?
|
Rh/Rh
|
|
|
Rh/Rh provides more
penetration than the Molybdenum/Rhodium combination. True/false?` |
True
|
|
|
What type of breasts is Rh/Rh good for?
|
This works best for very thick breasts or very dense breasts.
|
|
|
Name another kind of filter that's ;es commonly used.
|
Aluminum Filter
|
|
|
what is a typical range of kVp for mo target?
|
24 to 30 KVp
|
|
|
what is a typical range of kVp for rh target?
|
26 to 32 KVp.
|
|
|
give advantages for magnified views
|
Increased resolution
- due to small focal spot & reduced quantum mottle. Reduction in scatter radiation reaching the film due to air-gap. Improved visibility of detail due to the larger field of view. |
|
|
what is the functionof a grid?
|
To reduce scatter radiation reaching the film
and maintain high contrast in the image. |
|
|
grid specification (mammo unit)
|
Grid ratio: 4 : 1 or 5 : 1
30 - 50 lines per cm Moving grid |
|
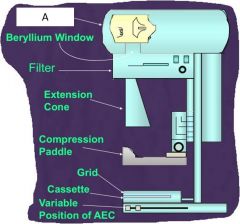
What is A?
|
X-ray tube
|
|
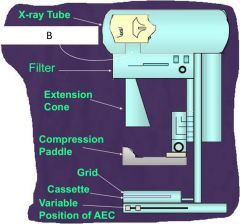
What is B?
|
Berrylium window
|
|
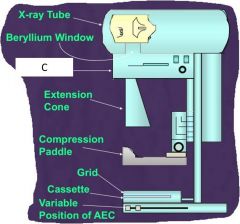
C?
|
Filter
|
|
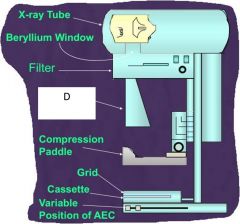
D?
|
Extension cone
|
|
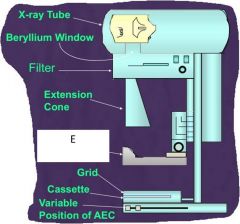
What is E?
|
Compression
paddle |
|
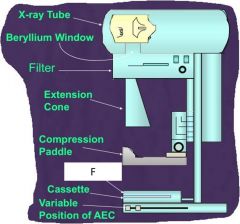
F?
|
grid
|
|
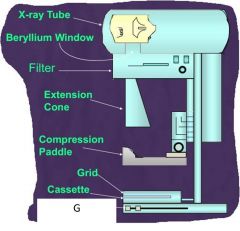
G?
|
AEC
|
|
|
What is the focal spot sizes of tungsten filament in mammo unit X-ray tube?
|
0.3& 0.1 mm
|

