![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what are the 2 parts of the AEC?
|
• Detector
• Comparator |
|
|
What is the Function of AEC Systems
|
to monitor the amount of radiation reaching
the image receptor, and to terminate the exposure at a preset level normally measure product of intensity (I) and time (t) |
|
|
Ionisation chamber measures radiation exposure ____ it reaches the image receptor
|
before
|
|
|
Photo-timers/Scintillator Counters are exit-type devices, meaning,
|
they measure radiation exposure after it passes through cassette
|
|
|
where is the Photo-timers/Scintillator Counters commonly found?
|
Commonly found in
fluoroscopic units |
|
What type of external mode is this?
|
side on
|
|

What type of external mode is this?
|
head on
|
|
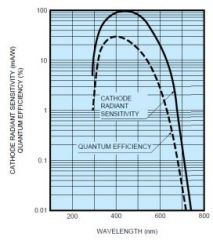
Spectral sensitivity of
photocathode MUST match wavelength of light from scintillator crystal for optimal conversion |
Only 10-30% of photons
cause emission of electrons |
|
|
) As radiation passes
through the chamber, the gas becomes ____. Ion-pairs form. Negative electrons flow to the _____. Current generated. |
ionised; anode
|
|
Study
|
study
|
|
|
difference between ion chamber & fluorescent screen
|
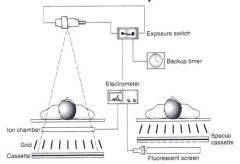
ion chamber & fluorescent screen
|
|
|
where is the detector placed?
|
Placed between patient and
film |
|
|
advantages of detector
|
• Allows actual mAs used to be displayed immediately after
exposure • Allows radiographer to become more familiar with manual exposure techniques • Use it to verify exposure charts in department • If image is suboptimal, allows of adjustment of exposure using manual technique |
|
|
what is Minimum Response Time (M.R.T.)?
|
• the length of time necessary for the AEC to respond to the
ionisation & send a signal to terminate the exposure. • Between 3 – 30 milliseconds may elapse before all the electronics & relays actually stop the exposure. |
|
|
what are Guard/Backup timers?
|
• all AEC devices are fitted with a guard timer
• A safety device which prevents the patient from receiving an excessive dose of radiation should the automatic timer fail due to mechanical or operator errors. • These terminate exposures that exceed 600mAs above 50kVp, and 2000mAs at lower potentials. |
|
|
for density settings:
|
-2: 50% decrease in density from 0 (Neutral)
-1: 25% decrease in density +1: 25% increase in density +2: 50% increase in density |
|
|
the dominant zone is where ________.
|
Positioning where a specific patient part (ROI)
should be placed over the detectors |
|
|
If the sensor is under a body part for which k is
incorrect, then an over or ______-exposure will result |
under
|
|
|
one of the largest sources of error in using AEC devices is ____.
|
poor positioning
|
|
|
Sufficient collimation demonstrates that as you increase the amount of
collimation and shielding, the amount of scattered radiation reaching the detector _____, resulting in a darker diagnostic radiograph. |
decreases
|

