![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Governance of vaccination in the UK |
Joint Committee of Vaccination and Immunisation JCVI decide whether populations are vaccinated depending on: vaccine efficiacy burden of disease vaccine safety cost of vaccination |
|
|
the ideal vaccine |
safe to recipient -not cause disease -have no significant Sx prevent infection in all cases if virus has serotypes, vaccine should be cross reactive life long protection easy to administer stable relatively cheap |
|
|
Natural immunisation |
when person comes in contact with pathogen immune memory forms to prevent future infections |
|
|
Examples of different types of vaccination |
Whole microorganism -live-attenuated -dead subunit of microorganisms -inactivated toxin -recombinant proteins -polysaccharide -conjugate vaccines (polysaccharide combined with more immunogenic conjugate to get T cell help |
|
|
named vaccines from type of vaccine: live-attenuated |
BCG yellow fever VZV (chickenpox/shingles) MMR |
|
|
named vaccines from type of vaccine: dead |
Whole cell pertussis rabies |
|
|
named vaccines from type of vaccine: inactivated toxin |
tetanus, diphtheria toxoid |
|
|
named vaccines from type of vaccine: recombinant proteins |
Hep B HPV |
|
|
named vaccines from type of vaccine: Polysaccharide |
pneumococcus meningococcus haemophilus |
|
|
Live attenuated vaccines |
induce stronger immune respnose than dead more dangerous risk of vaccine infection to ↓ risk pathogen is attenuated (inactivated) small risk that attenuated → live this has happened in type 3 Sabin polio vaccine |
|
|
Adjuvant |
materials injected with vaccine → enhance immune response
most common: alum microbial agent is adsorbed onto alum soluble protein → particulate material → ↑ tendency to be phagocytosed by APC also depot of slow release of antigen |
|
|
phagocytic APCs |
DC macrophage |
|
|
Co-administring vaccines |
enhances response to vaccines e.g. co-administration of pertussis enhances Ab response to Diptheria and Tetanus |
|
|
incomplete Freund's adjuvant |
Oil-in-water emulsion |
|
|
complete Freund's adjuvatn |
when dead mycobacteria are added to the emulsion → ↑ stimulus for innate system, → enhanced expression of co-stimulatory molecules and cytokines by APCs
|
|
|
Conjugate vaccines |
possible to induce Ab response in infants to bacterial capsular polysaccharides by conjugating polysaccharide to protein antigens like Diptheria + Tetanus toxoids B cells specific for the polysaccharide internalise conjugate present peptides from toxoids on surface Thus B cells can get help from Th2 helper cells primed against the toxoids |
|
|
Conjugate vaccines diagram |
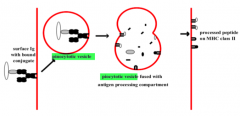
|
|
|
Graph of Ab response to 1º and 2º inoculum of infection/vacciantion |
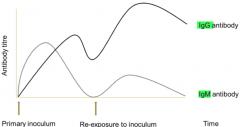
|
|
|
Ab response to 1º and 2º inoculum of infection/vacciantion |
1º inoculum IgM Abs hours -days to make Abs low affinity IgG Abs 4-6 weeks to make Abs high affinity 2º inoculum rapid boost of IgG response days higher conc. than after 1º exposure |
|
|
Vaccine safety |
allergic reactions can occur but is rare chicken eggs used to make viral vaccines → egg protein in vaccine → anaphylaxis but this is very rare |
|
|
Ca. vaccines |
HPV vaccine for cervical ca. |
|
|
Monoclonal Abs for ca. |
Herceptin for breast ca. anti-CD20 for B cell lymphoma but still very experimental |
|
|
Passive immune treatments |
1. Mother-foetus - IgG Abs enter foetal blood last trimester infant Ab protection for 4-6 months 2. Patients born without B cells/ have Ab deficiency give Ig IV or subcutaneous giving protection against range of pathogens 3. patients with immunodeficiency/particular risk pregnancy, pooled serum from donors with high tires of neutralising Ab good e.g. VZV hyper immune serum |
|
|
Passive immune treatments examples |
Human serum -Rabies -Rhesus D -VZV Animal serum -Tetanus Monoclonal Abs Anti Respiratory syncitial virus |

