![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
313 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
12: Elements in the same group... |
often have similar properties |
|
|
How does metallic character (readiness to lose electrons in reactions) change across periods and groups? |
Decreases across a period, increases down a group |
|
|
There are trends in properties down a group as well as across a period |
sadf |
|
|
What are the trends of group I elements (alkali metals)? |
As you go down, they get softer, more reactive, denser and their m&b points decrease |
|
|
What is the product of a reaction between a group I metal and water? |
Hydrogen, and a solution of that alkali metal's hydrogen oxide. E.g. 2Li (s) + 2H2O (l) -> 2LiOH (aq) + H2 (g) |
|
|
Group VII is... |
the halogens: F, Cl, Br, I, At. |
|
|
As you go down Group VII (halogens), what happens? |
Reactivity decreases, m&b points increase (subsequently it goes gases -> liquids -> solids), the colour gets darker. |
|
|
What are halides? |
Salts formed when metals react with halogens. E.g. 2Na (s) + Cl2 (g) -> 2NaCl (s) |
|
|
What happens in a reaction between a halogen with a halide ion? |
If the halogen is more reactive it will displace the halide. E.g. Cl2 (g) + 2KBr (aq) -> 2KCl (aq) + Br2 (aq) |
|
|
What is group 0? |
the noble gases
|
|
|
Traits of group 0? |
Unreactive (full outer shell), density and boiling points increase down the group |
|
|
Uses of group 0? |
Argon is used for an inert atmosphere in light bulbs. Neon is used for neon lights because it lights up when an electric current goes through. Helium is used in weather balloons and airships because it is lighter than air and not flammable. |
|
|
What are the trends in groups III-VI? |
In general, they change from non-metals to metals down the group. |
|
|
What are the trends in group II? |
Increased reactivity with oxygen and water down the group. Solubility of the hydroxides increases down the group. |
|
|
What are the properties of metals? |
malleable, ductile, shiny, sonorous |
|
|
What are the traits of transition metals? |
High m&b points and densities, their compounds are highly coloured, have several different oxidation states in their compounds, they are hard and strong. |
|
|
13: What are alloys and why are they made? |
Alloys are mixtures of metals, they are made to create metals with more desirable qualities. |
|
|
What are the uses, properties and elements of some alloys? |
Brass: copper + zinc, strong & malleable, instruments and ornaments. Bronze: copper + tin, statues and bells Stainless steel: iron + chromium + nickel, doesn't rust, cutlery and surgical instruments |
|
|
What are smart/memory alloys? |
An alloy that, if bent, goes back to its original shape when heated, e.g. nitinol (nickel and tin). |
|
|
Recite the metal reactivity series. |
K Na Ca Mg Al Zn Fe Pb H Cu Ag Au |
|
|
What metals can react with hydrochloric acid, steam or water? |
only metals above hydrogen in the reactivity series can react with hydrochloric acid, steam or water |
|
|
What is the 'thermit' reaction? |
Fe2O3 + 2Al -> Al2O3 + 2Fe The aluminium displaces the iron in the iron oxide. This is used for welding railway lines and breaking into industrial warehouses in Breaking Bad. |
|
|
When does a metal displace another metal in its salt? |
If the metal is more reactive than the one in its salt, then it will displace it. E.g. Zn + CuSO4 -> ZnSO4 + C |
|
|
What is the difference between a more reactive and less reactive metal? |
A more reactive metal loses its valency electrons more easily |
|
|
Explain what makes a metal lose its valency electrons more easily than others |
There are fewer protons in the nucleus to draw the electrons back. There are more electron shells between the nucleus and the valency electrons. These shells shield the valency electrons from the charge of the nucleus. The valency electrons are further away from the pull of the nucleus. |
|
|
When can a metal oxide be reduced by carbon? |
When carbon is more reactive than it. E.g. 2CuO + C -> 2Cu + Co2 |
|
|
Explain the terms oxidation and reduction. |
Oxidation is gain of oxygen. Reduction is loss of oxygen.
Oxidation is loss of electrons. Reduction is gain of electrons. OILRIG |
|
|
Why does aluminium seem unreactive? |
The outside layer reacts with the air to form aluminium oxide, this is a very unreactive layer that does not flake off. |
|
|
What is thermal decomposition? |
The breakdown of a compound when under heat. |
|
|
What affects the stability of a metal nitrate, carbonate or hydroxide? |
The more reactive the metal the more stable it is in these states |
|
|
Metal hydroxides thermally decompose to form... |
metal oxides and water. E.g. Zn(OH)2 -> ZnO + H2O |
|
|
Alkali metal nitrates (apart from lithium) thermally decompose to form... |
a nitrite and oxygen. E.g. 2KNO3 -> 2KNO2 + O2 |
|
|
Non-alkali metal nitrates (and lithium nitrate) thermally decompose to form... |
an oxide, nitrogen dioxide and oxygen. E.g. 2Mg(NO3)2 -> 2MgO + 4NO2 + O2 |
|
|
How does calcium carbonate decompose? |
CaCO3 (s) -> CaO (s) + CO2 (g) the calcium oxide is used to purify metals and form slag in certain metal extractions |
|
|
How does copper carbonate decompose? What does the experiment look like? |
CuCO3 -> CuO + CO2 goes from green to black |
|
|
14: What metals are extracted by electrolysis? Why? |
Metals that are more reactive than carbon. Otherwise, electrolysis is unnecessary because carbon can be used to displace the metal from its metal oxide. |
|
|
How is zinc extracted? |
zinc ore aka zinc blende aka zinc sulfide Roasted with air to form zinc oxide Put into a blast furnace with coke (carbon) Air comes in from the bottom of the furnace, reacts with the coke to form carbon monoxide. Carbon monoxide reduces zinc oxide to zinc and carbon dioxide. Also, the carbon dioxide may react with coke to form more carbon monoxide. Sometimes the zinc oxide can react directly with the carbon, to leave zinc and carbon monoxide. Zinc vapour then goes up with the carbon mon/dioxide, it condenses into trays. |
|
|
How is iron extracted? |
iron ore aka haematite aka mostly iron (III) oxide Raw materials are haematite, coke, limestone and air. Haematite, coke and limestone put in blast furnace, hot air blasted through bottom. Coke reacts with oxygen to form carbon dioxide Carbon dioxide reacts with coke to form carbon monoxide Carbon monoxide reduces the iron (III) oxide to iron via Fe2O3 + 3CO -> 2Fe + 3CO2 Sometimes the iron (III) oxide can react directly with the coke Haematite has sand (silicon (IV) oxide) as a major impurity. The limestone helps remove this CaCO3 thermally decomposes to leave CaO + CO2 CaO + SiO2 (the sand) -> CaSiO3 (calcium silicate aka slag) Slag is run off, used for road building. |
|
|
How pure is extracted iron? What are the impurities? |
95% pure. The other 5% is mostly carbon, though there is phosphorus, sulfur and silicon too. |
|
|
How is steel made? |
Using a basic oxygen converter. Molten iron is poured in An oxygen lance is lowered in. The lance blows oxygen and powdered calcium oxide onto the iron The oxygen oxidises most of the impurities. Carbon dioxide and sulfur dioxide are gases so they escape. However, silicon and phosphorus oxides (acidic) are solid, so they react with the calcium oxide (basic) to form a slag, which is run off. The amount of carbon in the steel is controlled by how long oxygen is blown on Finally, other elements like chromium and nickel are added to form the right type of steel.
|
|
|
Why is pure iron not useful? |
too soft and weak |
|
|
Why is iron straight from the blast furnace not useful? |
too much carbon, which makes it too brittle. |
|
|
What is done to iron to make it useful? |
Controlled amounts of carbon and other metals (chromium, nickel etc.) are added to make steels |
|
|
What is mild steel and what is it used for? |
Low carbon (0.25%) steel. Used for car bodies. |
|
|
What is high carbon steel and what is it used for? |
0.5-1.4% carbon. Becomes harder and more brittle. Used for hammers |
|
|
What are low alloy steels and what are they used for? |
1-5% of other metals such and chromium, nickel, manganese and titanium. Hard and don't stretch. Nickel steels are used for bike chains, tungsten steel is used for high-speed tools because it doesn't change shape at high temperatures. |
|
|
What is stainless steel and what is it used for? |
High alloy steel: 20% chromium, 10% nickel. Strong and resist corrosion. Cutlery and surgical instruments. |
|
|
What is aluminium used for? |
It's light so it gets used for aircraft bodies. It has an unreactive layer of aluminium oxide so it gets used for food containers. |
|
|
How is zinc used for galvanising iron or mild steel? |
Dip the iron/mild steel object into liquid zinc. The zinc forms a coating. This means the metal will not rust as easily. This helps for roofs because it is weather resistant. |
|
|
What is copper used for? |
Wires, because it is very conductive and can be drawn into shape easily. Also, cooking pans because it conducts heat well. |
|
|
What is brass used for? |
Copper and zinc. Gold colour makes it pretty so it is used for instruments and ornaments. |
|
|
15: What is water used for? |
In the home: drinking and washing. In industry: coolant and solvent. |
|
|
What are the tests for water? |
Add the liquid to anhydrous copper sulphate (white), if it goes blue then there is water. Add the liquid to anhydrous cobalt chloride (blue), if it goes pink then there is water. Cobalt chloride also comes in the form of handy test papers (a la litmus test papers) specifically for this purpose. |
|
|
How is water purified? |
Filtration and chlorination. Water goes through metal grids to get the big bits out. Then through the sedimentation tank where largish bits are deposited. Aluminium sulphate is added to make the little bits stick together and fall to the bottom. It goes through a filter of sand and gravel or crushed coal. Chlorine is added to kill germs. pH is adjusted and it goes to homes and factories. |
|
|
What is air made up of? |
78% nitrogen 21% oxygen 1% mainly argon with small amounts of CO2 and other noble gases |
|
|
How are nitrogen and oxygen separated? |
Fractional distillation. Water is removed by passing it through a drying agent and carbon dioxide is removed by reacting it with sodium hydroxide. Air is cooled until liquid Argon, xenon and neon and removed since they are still gases at this temperature When the liquid is warmed the nitrogen boils off first, this leaves an impure mix of nitrogen and oxygen, which becomes a gas It goes to the top column where the temperature is below the boiling point of oxygen but above the boiling point of nitrogen, so the oxygen condenses at the bottom and the nitrogen gas is removed at the top. |
|
|
Carbon monoxide is... |
a poisonous gas that is formed by incomplete combustion with carbon |
|
|
Acid rain is caused by... |
When coal is burnt, the sulphur impurities react with oxygen to form sulphur dioxide which escapes into the atmosphere. This then reacts with the air to form sulphur trioxide, and then reacts with water vapour (like in clouds) to form sulphuric acid. |
|
|
Acid rain's effects are: |
kills trees and fish, corrodes metals and limestone buildings and acidifies soils |
|
|
Lead pollution... |
from old sources like petrol and paint (it doesn't break down easily) can hinder brain development |
|
|
How is nitrogen oxide formed? |
in car engines by nitrogen and oxygen reacting under high pressures and temperatures |
|
|
What are the problems with nitrogen oxide? |
can cause smog, breathing difficulties and acid rain |
|
|
What do catalytic converters do? |
Fitted to car exhaust to cleanse it of poisonous gases. They have a 'honeycomb' of catalysts like palladium, platinum or rhodium. In the first compartment nitrogen oxides are decomposed to nitrogen and oxygen, in the second compartment carbon monoxide is reacted with oxygen to form carbon dioxide. |
|
|
List some greenhouse gases and their sources |
Methane: cows and swamps and rice paddy fields. Carbon dioxide: cars and industry processes (like the thermal decomposition of calcium carbonate to make cement and lime) CFCs: refrigeration and spray cans Nitrous oxide: produced by bacteria in soils |
|
|
What is global warming? |
Short-wavelength UV rays from sun pass through atmosphere and hit earth. Earth absorbs it and warms up. Some is bounced back to leave the atmosphere as long-wavelength infra-red radiation, but it can struggle to get out because of greenhouse gases absorb some of it, thereby making the world hotter than it should be |
|
|
How will global warming affect the planet? |
polar ice caps melt -> sea levels rise less rain -> more deserts + less food more violent weather -> damage of property and crops |
|
|
What does the carbon cycle do? |
Keeps the concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere approximately constant. |
|
|
What are some things in the carbon cycle? |
CO2 emitters: fossil fuels, oceans, decaying of organisms CO2 receivers: photosynthesis, oceans
|
|
|
How is the carbon dioxide produced in respiration balanced? |
by the carbon dioxide taken in during photosynthesis |
|
|
How is the carbon cycle being unbalanced? |
Deforestation and burning fossil fuels. |
|
|
What is required for something to rust? |
oxygen and water |
|
|
What is rust? |
hydrated iron (III) oxide aka 2Fe2O3.H2O (s) |
|
|
How can rusting be prevented? |
painting, plating (galvanising), coating with plastic or greasing. |
|
|
How does galvanising prevent rusting? |
Galvanising is sacrificial protection. The metal is coated with a more reactive one (usually zinc) which reacts with the water/oxygen instead. The iron remains protected because the electrons on its surface are being accepted - meaning it is in a reduced state. The thing being protected doesn't have to be completely coated, blocks of zinc can work too |
|
|
1: How can the properties of solids, liquids and gases be explained? |
particle theory |
|
|
What are the terms for changing states? |
melting, boiling, condensing, freezing and (rarely) subliming |
|
|
During a change of state... |
energy is absorbed or released |
|
|
Diffusion is... |
the random movement of particles, which leads to them spreading out. |
|
|
The rate of diffusion depends on... |
The relative molecular mass. Higher mass = slower diffusion |
|
|
In chemistry, what is mass measured in? |
grams |
|
|
The apparatus you select for an experiment depend on... |
the accuracy required in your experiment |
|
|
How can you measure volumes of gas? |
a gas syringe or by water displacement (upside-down water-filled measuring cylinder in a tub of water thing) |
|
|
What is chromatography? |
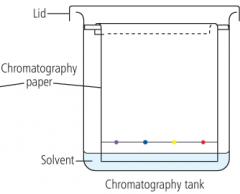
A way of separating and purifying coloured compounds using filter paper and a solvent. Ink is put on paper, which is dipped in solvent, the solvent moves up the paper gradually, separating the dyes making up the inks due to their differing solubility |
|
|
What are locating agents? |
they are used to make colourless compounds visible on chromatography paper. The colour is developed by warming the paper in an oven. |
|
|
How compounds be identified using chromatography? |
By finding he Rf (that's a subscript f) value and comparing it to a table of known values.
Rf = distance from base line to the centre of the spot / distance of solvent front from the base line
(the solvent front is the line of dampness that rises up the paper when dipped in the solvent) |
|
|
How can you identify a pure substance? |
Find its boiling or melting points, since they will be at definite temperatures. |
|
|
What is decanting? |
It is a method of separating a liquid from a solid, by simply pouring the liquid off. |
|
|
What is filtration? |
Another method of separating a liquid from a solid. ;lsdaflk;sdfj |
|
|
What is centrifugiation? |
Another method of separating a liquid from a solid. A centrifuge is a machine that spins test tubes around very quickly, which pulls the solid to the bottom, you can then decant it. |
|
|
How does crystallisation occur? |
When a solution of a crystallised solid is partially evaporated and allowed to cool. You heat it to make it evaporate (water vapour usually) until it reaches its crystallisation point, you can tell when this is by periodically placing a drop of solution onto a cold tile, if it evaporates quickly then the point has been reached. Then u let it cool. |
|
|
What is fractional crystallisation? |
It is a method of separating a mixture of two compounds with differing solubilities. A warm concentrated solution containing the two solutes is cooled, the solute with the lower solubility forms crystals, the one with the higher solubility remains in solution. They can then be separated by filtration |
|
|
What is solvent extraction? |
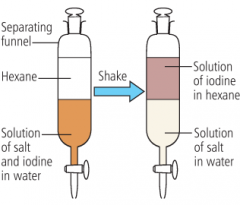
A method of separating two solutes by using a second solvent, especially useful if one of the solutes is volatile (evaporates readily). The second solvent (hexane here) must not mix with the first - it is immiscible |
|
|
What is simple distillation? |
Used to obtain a solvent from a solution. E.g. when a solution of salt and water is heated, the water boils off as steam, leaving salt behind. |
|
|
What is fractional distillation? |
It is used to separate a mixture of liquids with differing boiling points. There is a column, where the bottom is at a high temperature, which decreases as you go up. When the liquid with the lower boiling point boils, it is able to reach the top without condensing, once there it goes through a tube into the condenser and is taken away - pure now. The liquid with the higher boiling point also boils, but will not reach the top before the temperature is below its boiling point, so it will condense and go back to the bottom. |
|
|
Sometimes, several methods of purification need to be used. |
faadfdfasfh6t |
|
|
What is a condenser? |
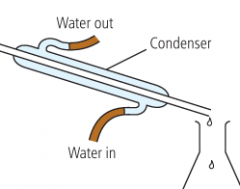
It is a piece of equipment that looks like this. It functions similarly to water-coolers in gaming PCs. |
|
|
2: What are the subatomic particles in atoms? What are the charges of each of them? |
Proton: +1 Electrons: -1 Neutrons: 0
Protons and neutrons make up the vast majority of the atom and its mass. The electrons have negligible mass. |
|
|
Why are atoms neutral? |
Because the positive charge of the protons is balanced out by the negative charge of the electrons. |
|
|
Using a periodic table, how do you work out how many neutrons an atom has? |
Subtract the proton number from the nucleon number. |
|
|
What are isotopes? |
They are different versions of elements that have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons. Different isotopes of the same elements have identical chemical properties but may have different physical properties. |
|
|
What can be done with radioactive isotopes? |
Medical uses: gamma knives for cancer treatment, locating tumours in the body, sterilising medical equipment
Industrial uses: beta particle emitters with a Geiger counter can be used to measure the thickness of paper in paper mills. |
|
|
What do the valency electrons of an element determine? |
Its chemical properties. |
|
|
What do the group numbers on the periodic table show? |
The amount of valency electrons of each element in that group. |
|
|
What are the properties of non-metals? |
Brittle and don't conduct heat/electricity well. |
|
|
What are some common exceptions to the general properties of metals/non-metals? |
Graphite is a non-metal that conducts electricity, because the way that it is bonded lets a free electron pass between its layers. The group I metals and mercury have low melting/boiling points, unlike most metals. |
|
|
3: What does an ionic bond form between? |
A metal and a non-metal. E.g. NaCl |
|
|
How can you show ionically bonded compounds? |
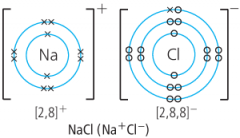
The Na has lost an electron so it is a positive ion now. The Cl has gained an electron (the x) so it is a negative ion now. This is a dot and cross diagram |
|
|
How are ions similar to noble gases? |
They have full outer shells. |
|
|
What does a covalent bond form between? |
two non metals |
|
|
How can you show a covalent bond? |
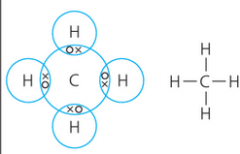
The atoms share electrons to have full outer shells. In the diagram to the right, the '-' between elements means a covalent bond, i.e. H-C |
|
|
What are more complex covalent bonds like? |
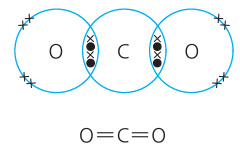
There can be double bonds and even triple bonds. Double bonds are signified with O=O, triple bonds are signified with N≡N. |
|
|
What kind of structure does ionic bonding result in? |
The attractive forces between the pos and neg ions form a giant ionic structure. The ions are arranged regularly in a crystal shape. This three-dimensional network is a crystal lattice. |
|
|
What are the properties of a giant ionic structure? |
The electrostatic attractive forces are very strong, therefore it has high melting and boiling points. Soluble in water but insoluble in organic solvents. Conduct electricity when molten or dissolved in water, because the ions are free to move. |
|
|
What are the properties of covalently bonded molecules? |
The bonds are strong, but the forces between separate molecules are weak (intermolecular forces), therefore they have low m&b points. They do not conduct well. |
|
|
What are giant covalent structures? |
They are sometimes described as macromolecules. They are rigid three-dimensional crystal structures, so they have high m&b points. Examples are graphite, diamond and silicon (IV) oxide. |
|
|
What are diamond's properties and why is it like that? |
It is very strong because it has a tetrahedral crystalline lattice, so it is used for drilling. It is shiny and glittery, so it used for jewellery. |
|
|
What are graphite's properties and why is it like that? |
It conducts electricity, this is because it is arranged in layers where each carbon atom is joined to three other carbon atoms, leaving one free electron (a delocalised electron) to travel between the layers. Therefore it is used for carbon electrodes. The bonding between the layers is weak, so the layers slide off easily, therefore it is used in pencils and as a lubricant. |
|
|
What is silicon (IV) oxide? |
It is what a large quantity of sand is made of. Each silicon atom is bonded to four oxygen atoms, but each oxygen atom is only bonded to two silicon atoms. Its structure are properties are similar to diamond. It forms hard colourless crystals and it has high m&b points. It does not conduct electricity. |
|
|
What is metallic bonding? |
Metal atoms are packed closely together, because of this, their valence electrons move away from their atoms - a sea of delocalised electrons. The now positively charged ions are held together by their strong attraction to the mobile electrons which move between the ions. This is metallic bonding. The attraction acts in all directions. |
|
|
Why do metals conduct electricity? |
Because the sea of delocalised electrons can move about freely. |
|
|
Why do metals conduct heat well? |
The vibrations of the atoms pass around more easily than say, in a covalent structure |
|
|
Why do metals have high m&b points? |
It takes a lot of energy to pry apart strong forces of attraction between the positive metal ions and the delocalised negative electrons in the lattice. |
|
|
Why are metals malleable and ductile? |
They are arranged regularly in layers. The layers can slide over each other because the attractive forces between the ions and delocalised electrons can act in any direction, meaning that new bonds can easily form. |
|
|
16: Why are fertilisers needed? |
Plants need not only water and sunlight to grow, they also need nitrogen to make amino acids and proteins. They take in nitrogen (as well as other things they need, such as potassium and phosphorus) from the soil (they cannot take nitrogen directly from the air because it is quite unreactive, they have to take it from compounds). When the plants are harvested, they take their nitrogen with them, meaning the soil will not grow plants as well because less nitrogen is left. Fertilisers are added to replenish the soil of nitrogen and other things. |
|
|
What is the most common type of fertiliser? |
NPK fertilisers. Dung can also be used, but there is a limited amount of it. NPK fertilisers contain compounds that have N, P and K in them, such as ammonium nitrate, ammonium phosphate and potassium chloride. |
|
|
How are the ammonium salts in NPK fertilisers made? |
By neutralising ammonia (made with the Haber process) with acids. E.g. NH3 + HNO3 -> NH4NO3 |
|
|
Using standard laboratory equipment, how can you make ammonium sulphate? |
Titrate ammonia with dilute sulphuric acid using methyl orange. Once it turns pink, record the burette reading and start over again, this time without using methyl orange, adding the same amount of dilute sulphuric acid as before. Then, pour the solution from the flask into an evaporating basin, evaporate some water and allow the fertiliser to crystallise. |
|
|
What is the problem with NPK fertilisers? |
Many are slightly acidic, but a lot of plants do not grow well in acidic conditions. Therefore, lime (calcium hydroxide) is added to neutralise it a bit. However, if there is too much lime, it reacts with the ammonium salts to release ammonia gas that escapes - this should be avoided. |
|
|
How are the raw materials for the Haber process obtained? |
Hydrogen: Either 'cracking' ethane under a high temp with a catalyst or reacting steam with methane using a nickel catalyst.
Nitrogen: air |
|
|
What reaction takes place in the Haber process? |
N2 (g) + 3H2 (g) ⇌ 2NH3 (g) |
|
|
Describe the Haber process. |
Nitrogen and hydrogen are compressed. Goes into a large tank called a converter where there are trays of iron catalyst, the temp is 450 degrees and the pressure is 200 atmospheres. Under these conditions, about 15% of the N and H react in the reversible reaction of N2 + 3H2 ⇌ 2NH3. The mixture passes into a cooling chamber, where the ammonia condenses and is removed. The leftover N and H goes back to the converter so it is not wasted. |
|
|
Explain the ideal conditions for the Haber process. |
N2 (g) + 3H2 (g) ⇌ 2NH3 (g) '⇌' indicates it's an equilibrium reaction. It is exothermic in the forward direction (since it is making bonds), therefore lower temps are better. Increasing pressure helps too. Since it is a gas reaction, increasing the pressure will favour the side with less moles (4 moles on left side, 2 on right). |
|
|
Why aren't the ideal conditions of the Haber process realized optimally? |
It favours coldness, but if the reaction is too cold then the rate will be too slow, therefore a compromise of 450 degrees is used. It favours high pressure, but if it is too high then a lot of money is needed for fuel to keep the pressure that high and to make a tank sturdy enough to contain it. Therefore a compromise of 200 atmospheres is used. |
|
|
What is sulphur used for? |
90% is used to make sulphuric acid. The rest is used to make tyres more flexible (vulcanising) and for making dyes. |
|
|
What is sulphur dioxide used for? |
Bleach, used in the manufacture of paper and for materials like silk and straw that are too weak for stronger bleaches. |
|
|
What is sulphuric acid used for? |
Most produced chemical in the world. Fertilisers, detergents, car batteries, paints and fibres. |
|
|
What are the properties of sulphuric acid? |
It is a strong acid that has typical acidic properties. Reacts with metals that are more reactive than hydrogen to form salt + hydrogen. With metal oxides to form salt + water With metal hydroxides to form salt + water With carbonates to form salt + water + CO2 |
|
|
What are the raw materials of the Contact process (manufacturing of sulphuric acid)? |
Sulphur from beneath the ground (mines), sulfide ores or hydrogen sulfide from petroleum Air Water
|
|
|
Describe the Contact process. |
Molten sulphur is burned in a current of dry air, forming sulphur dioxide. It is cooled and reacted with excess air in a convertor, with a catalyst of some trays of vanadium (IV) oxide. Temp is about 450 degrees, forms sulphur trioxide. The sulphur trioxide goes to the absorber and gets absorbed into a 98% solution of sulphuric acid. Sulphur trioxide dissolves into the acid to form oleum. SO3 + H2SO4 -> H2S2O7 (oleum) The oleum dissolves in a little water to make 98% pure sulphuric acid. H2S2O7 + H2O -> 2H2SO4 |
|
|
Explain the ideal conditions for the Contact process. |
2SO2 ⇌ O2 -> 2SO3 The reaction of sulphur dioxide to sulphur trioxide is an equilibrium reaction. The sulphur trioxide yield increases as the pressure increases, but the yield is already high enough so atmospheric pressure is used. The reaction is exothermic, so the yield increases with temp. Therefore 450 degrees is used. The catalyst does not effect the equilibrium, it speeds up the reaction both ways the same amount. |
|
|
How is calcium oxide (quicklime) made? |
Calcium carbonate thermally decomposes to form calcium oxide and carbon dioxide. Quicklime is made in a rotary lime kiln. It is a big cylinder that is suspended horizontally and angled slightly towards the ground. At the higher end (the colder end), limestone (calcium carbonate) is added, it runs down and increases with heat gradually (since the bottom end is hotter), thereby decomposing to quicklime. Hot air is constantly being blasted through. The quicklime is taken out at the bottom. |
|
|
How is calcium hydroxide (slakelime) made? |
Adding water to quicklime (calcium oxide). |
|
|
Apart from flue gas desulphurisation, what are limestone products used for? |
Limestone: building, extraction of iron, roads, neutralising soil, making glass, manufacturing cement. Quicklime: lime mortar (quicklime hardens in contact with the CO2 in the air) Quicklime & slakelime: treating excess acidity in lakes and soil. |
|
|
How are limestone products used in flue gas desulphurisation? |
Calcium oxide, hydroxide or carbonate can be used for flue gas desulphurisation - they are sprayed through the waste gases of fossil fuels combustion to get rid of sulphur dioxide (which causes acid rain). This reaction forms hydrated calcium sulphate, which can be used to make plasterboard, but it's often dumped because transporting it is expensive. |
|
|
4: Each chemical element... |
has a symbol. |
|
|
When naming a compound containing two elements... |
the second name often changes to -ide. |
|
|
How can you work out the formula of a simple compound? |
The formula of a simple compound can be worked out from the valency of the elements present. |
|
|
How can you work out the formula of a molecular compound? |
The formula of a molecular compound can be worked out from a diagram of the full structural formula by counting the number of each type of atom. |
|
|
How can you work out the formula of an ionic compound? |
The formula of an ionic compound can be found by counting the ions and finding the simplest ratio. It can also be worked out using the charges on the ions. |
|
|
There is the same number of each type of atom on each side of a chemical equation. |
sneil |
|
|
In a chemical reaction, the mass of the products always... |
equals the mass of the reactants. |
|
|
How are equations balanced? |
Equations are balanced by writing numbers in front of particular reactants or products. |
|
|
The state symbols (s), (l), (g) or (aq) are added after... |
the formula of each reactant and product. |
|
|
What are ionic equations? |
Ionic equations are simplified symbol equations showing only those ions that react and the products of their reaction. |
|
|
What are spectator ions? |
In reactions involving ions, not all the ions take part in the reaction. Those that are not involved are called spectator ions. |
|
|
17: What is a functional group? |
The part of an organic compound that gives the compound its organic properties. E.g. -O-H in the alcohol homologous series. |
|
|
What is a homologous series? |
A group of organic compounds with the same functional groups and similar properties. |
|
|
How can you tell if something is an organic compound? |
It burns or chars when heated, unlike inorganic compounds which melt. |
|
|
How are members of each homologous series similar to each other? |
They follow a general formula in compound names: all the alkanes end in -ane, alkenes in -ene etc. They have similar chemical properties. Their compounds follow a pattern (e.g. alkanes have n carbons and 2n+2 hydrogens). The physical properties change in a regular way as the amount of carbon increases, e.g. the boiling point of alkanes. |
|
|
What prefixes tell you the amount of carbon atoms in organic compounds? |
meth- 1 eth- 2 prop- 3 but- 4 pent- 5 hex- 6 hept- 7 etc. |
|
|
Structural isomers are... |
compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural formulae. |
|
|
What are branched-chain compounds? |
As opposed to straight chain, they have parts of their structural formula branching out. E.g. 2-methyl propane is branched but butane is no, though they are both structural isomers of each other. The parts that are sticking out are called alkyl groups. |
|
|
What is a fuel? |
Something which is burnt for heat energy. |
|
|
What are the attributes of a good fuel? |
Lots of heat energy per gram, non-polluting, easy to transport. |
|
|
Name some common fuels (not including ones from crude oil) |
Wood, biofuel (plant oils from plants like oilseed rape and corn), solid waste, hydrogen and methane. |
|
|
What are the products of the complete combustion of a hydrocarbon fuel? |
carbon dioxide and water |
|
|
How is petroleum separated? |
fractional distillation. Each fraction has hydrocarbons with similar melting points. |
|
|
What are the uses of each fraction of petroleum? |
under 40 degrees: bottled gas for heating/cooking 40-100: petrol 80-180: making chemicals, esp. plastics 160-250: kerosene (aka paraffin) - jet fuel and heating 250-300: diesel for lorries and tractors 350-500: fuel oil for powerstations and ships. Residue: lubricants, waxes and polishes |
|
|
5: What does stoichiometry mean? |
The calculation of the quantities of chemical elements or compounds involved in chemical reactions. |
|
|
What is meant by relative atomic mass? |
The mass of an atom in comparison to one atom of carbon-12, which is said to be 12 units in weight. The relative formula mass of a substance, shown in grams, is called one mole of that substance. So one mole of carbon monoxide has a mass of 28g, and one mole of sodium oxide has a mass of 62g. |
|
|
What is meant by relative molecular mass? |
The sum of relative atomic masses in the formula of a molecule. |
|
|
When given enough information, how might you go about calculating the mass of a product formed in a reaction? |
Using simple proportion. So if 9.6g of magnesium gives 48g of magnesium sulphate, then 1.2g of magnesium 1.2/9.6 x 48 = 6g of magnesium sulphate. |
|
|
What is a mole? |
A unit representing the amount of a substance expressed in grams containing as many atoms/molecules/ions as the number of atoms in 12 grams of carbon-12
Moles = mass / RFM |
|
|
In a reaction, what is the limiting reactant? |
The one that is not in excess. |
|
|
How can the limiting reactant be found? |
Comparing the necessary ratio of moles of each reactant in a reaction with the actual ratio of moles.
So if it should be 1 mole of Mg for every 2 moles of HCl, but what is present is 0.05 moles of Mg and 0.075 moles of HCl, then HCl is the limiting reactant. |
|
|
How can you use relative formula masses to find the amount of product formed in a reaction? |
You can use the relative formula masses. E.g. You have 4g of methane that undergoes this reaction: CH4 + 2O2 -> CO2 + 2H2O. CH4's RFM is 16g, which gives 2 x H2O's RFM i.e. 2 x 18g = 36g. So 4g of methane will give you 4/16 x 36 = 9g of water. |
|
|
How can you work out the percentage by mass of an element in a compound? |
% by mass = sum of RAMs of an element in a compound / RFM of compound x 100.
So, Fe2O3 has an RFM of 160, of which 112 is Fe. 112 / 160 x 100 = 70%
|
|
|
At room temperature, what is the volume of one mole of any gas? How can this information be used? |
24dm^3 or 24000cm^3. This is the molar gas volume.
So if you want to calculate the mass of CO2 present in 60cm^3 of it, you can firstly work out how many moles there are present: 0.06 / 24 = 0.0025 moles. Then times that by the RFM of CO2: 0.0025 x 44 = 0.11g of CO2. |
|
|
How can you work out the % yield of a product? |
% yield = actual yield / predicted yield x 100
The actual yield mightn't equal the predicted yield because there may be other reactions going on at the same time or the reaction didn't follow to completion. |
|
|
How can you work out the % purity of a product? |
% purity = mass of pure product / mass of impure product x 100
This may be because of small amounts of impurities mixed in with the reactants. |
|
|
When given the percentages or weights of the elements within it, how can you find the empirical formula of a compound? |
Divide the weights by the RAMs (if %s are given instead, you can use just act as though they are weights instead, since the ratio will be the same). Divide all the outputs by whichever output came out lowest. This should leave an ordinary ratio like 1:4 or something, from this you can find the formula, which might be SnCl4 for this example. |
|
|
What does molecular formula mean? |
The actual numbers of atoms in a molecule. For example, ethane's empirical formula is CH3 but its molecular formula is C2H6. |
|
|
When given the RFM and empirical formula of a compound, how can the molecular formula be found? |
Find the mass of the empirical formula and then divide this by the relative formula mass, multiply this result by the empirical formula. So for example, the empirical formula mass of CH2 is 14, this dividing the RFM of 84 by this results in 6. 6 x CH2 = C6H12 |
|
|
How can you work out concentrations of solutions? |
conc (in mol/dm^3) = moles / volume (in dm^3)
This can be used to calculate concentrations, moles or volumes of solution when given the necessary values. Remember to convert cm^3 to dm^3 by dividing by 1000. |
|
|
What is a titration? |
Finding the amount of alkali needed to completely react with an acid. In a titration, the concentration of one of the solutions involved must be known. |
|
|
How is a titration done? |
The solution that you know the concentration of is put into a burette. Then you put a measured quantity of the other solution into a flask and add an indicator such as methyl orange or phenolphthalein. The solution is run from the burette into the mixture until it changes colour. We can then use the burette reading in tandem with its known concentration to find the concentration of the solution in the glass. |
|
|
6: What is electrolysis? |
Electrolysis is the breaking down of a compound using electricity. |
|
|
What is an electrolyte? |
a liquid which contains ions and can be decomposed by electrolysis |
|
|
When can an electric compound be electrolysed? |
When it is molten or in solution in water - an electrolyte |
|
|
At which electrodes are the metal/non-metal formed at? |
When a molten ionic compound is electrolysed, a metal is formed at the negative electrode and a non-metal is formed at the positive electrode. |
|
|
what does PANIC stand for? |
Positive Anode, Negative Is Cathode |
|
|
What happens when concentrated aqueous solutions of metal ions are electrolysed? |
Hydrogen rather than a metal is formed at the cathode. |
|
|
What happens when concentrated hydrochloric acid is electrolysed? |
Hydrogen is formed at the cathode and chlorine at the anode. |
|
|
What happens when brine (aqueous NaCl) is electrolysed in a diaphragm cell? |
Chlorine and hydrogen are formed at the electrodes, and aqueous sodium hydroxide (Na left from NaCl and OH left from water) remains |
|
|
What is formed at the negative/positive electrodes during electrolysis? |
In electrolysis, metals or hydrogen are formed at the negative electrode and halogens or oxygen are formed at the positive electrode. |
|
|
What happens when dilute aqueous solutions of acids are electrolysed? |
Oxygen is formed at the anode and hydrogen is formed at the cathode. |
|
|
What happens to the ions during electrolysis? |
Ions gain electrons at the cathode and lose electrons at the anode. |
|
|
How is copper purified? |
Copper is purified by using an impure copper anode and a pure copper cathode in aqueous copper sulphate. Impurities drop off the impure anode and form anode sludge from which rare metals can be extracted. The pure cathode increases in size. |
|
|
What happens when you use inert electrodes in electrolysis? |
During electrolysis using inert electrodes the negative ions in the electrolyte lose electrons to the anode. |
|
|
What happens when you use metal electrodes in electrolysis? |
In electrolysis using metal electrodes the metal atoms of the anode lose electrons to form positive ions. |
|
|
How can an object be electroplated? |
By making it the cathode. |
|
|
In electroplating, what is are the cathode and electrolyte? |
The metal object to be plated is the cathode and the electrolyte is a solution of a compound of the plating metal. |
|
|
|
When an article is electroplated the ions of the plating metal gain electrons at the cathode and become metal atoms. |
|
|
The electrolytic cell for the extraction of aluminium has electrodes of carbon
|
likc |
|
|
What is the electrolyte in the cell for extracting aluminium? |
The electrolyte in the cell is molten aluminium oxide, dissolved in molten cryolite to lower its melting point. |
|
|
|
Aluminium forms at the cathode and oxygen is released at the anode. The oxygen may react with the carbon anodes to form CO2. |
|
|
What is used to make cables in high-voltage power lines? |
Steel-cored aluminium cables are used in high-voltage power lines because aluminium is a good conductor and steel strengthens the cable. |
|
|
What do insulators do? |
|
|
|
Why is copper used in electrical wiring? |
It is a good conductor of electricity and it is ductile |
|
|
7: What are exothermic/endothermic reactions? |
An exothermic reaction gives out heat energy. An endothermic reaction absorbs heat energy. |
|
|
Do the products/reactants have more energy in exothermic/endothermic reactions? |
In an energy level diagram for an exothermic reaction, the reactants have more energy than the products. The opposite is the case for an endothermic reaction. |
|
|
What happens to energy when bonds are broken/made?
|
Energy is absorbed when bonds are broken. Energy is given out when bonds are made.
Bond breaking is endothermic ('gotta take it to break it') Bond making is exothermic |
|
|
In an exothermic reaction the energy absorbed when bonds are broken is less than the energy given out when new bonds are made. |
And in an endothermic reaction the opposite is true |
|
|
What are three polluting fuels? |
Coal, natural gas, and petroleum are fuels that are polluting when burnt. |
|
|
How can we compare the amount of energy released when a fuel is burnt? |
We can use a calorimeter and thermometer to compare the energy released when different fuels are burnt. (amount of heat gained by the calorimeter per 1g of fuel burnt) |
|
|
What radioisotope is used in some nuclear power stations as a source of energy? |
uranium-235 |
|
|
What does an electrolytic cell contain? |
Two electrodes of different reactivity dipping in an electrolyte. An exothermic reaction takes place and this heat is harnessed for energy. |
|
|
In an electrolytic cell, the electrode higher in the reactivity series is… |
the negative pole of the cell. |
|
|
In an electrolytic cell the electrons move from… |
the negative to the positive pole in the external circuit. |
|
|
What is the product of a hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell? |
A hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell produces only water as a product. |
|
|
What are the advantages and disadvantages of hydrogen-oxygen fuel cells? |
They are efficient and non-polluting, however the hydrogen and oxygen used are usually produced using fossil fuels. |
|
|
When a fuel cell is working… |
hydrogen loses electrons at the cathode and oxygen gains electrons at the anode. |
|
|
8: How can we follow the progress of a chemical reaction? |
By measuring how fast the reactants are used up or how fast the products are formed. |
|
|
What can we use to measure the rate of reaction? |
We can use change in volume of gas, loss of mass of reactant or the time taken for a precipitate to make a letter ‘disappear’ underneath a beaker to measure the rate of reaction. |
|
|
How is rate of reaction calculated? |
Rate of reaction is calculated by dividing the change in the amount of reactant or product by time. |
|
|
What happens as a reaction proceeds? |
The rate of reaction decreases as one or more of the reactants gets used up. |
|
|
When does a reaction stop? |
A reaction stops when the limiting reactant is completely used up. |
|
|
What does increasing the surface area of a reactant do and why does this happen? |
increases the rate of reaction
Smaller particles of solid have a large surface area than larger ones with the same total volume. |
|
|
|
A catalyst speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction but is not used up itself. Provides a surface for the reaction to take place upon |
|
|
Increasing the concentration of reactants… |
increases the rate of reaction. |
|
|
The higher the temperature… |
the greater the rate of reaction. |
|
|
Why does an increase in temperature increase the rate of reaction (collision theory)? |
The rate of reaction increases with an increase in temperature because particles have more energy so they move faster and collide more frequently. The collisions that take place are also more energetic so are more likely to result in a reaction taking place. |
|
|
The rate of some reactions is increased by increasing the intensity of light. These reactions are photochemical reactions. |
An example is photography with silver bromide on black&white photographic film. The parts exposed to light decompose to silver and bromine, this looks black. The parts not exposed to light stay white.
Another example is photosynthesis |
|
|
9: What happens in a reversible reaction? |
In a reversible reaction, the products can react to form the original reactants again. |
|
|
What is meant when a reversible reaction is said to be in equilibrium? |
At equilibrium, the concentrations of reactants and products remain fixed, since the forward reaction is happening at the same rate as the backward reaction. An equilibrium reaction can only take place in a closed system. |
|
|
In an equilibrium reaction, what are the effects of: increasing the concentration of a reactant increasing the pressure increasing the temperature
consider Le Chatelier's principle |
Increasing the concentration of a reactant moves the reaction in the direction of the side whose concentration was not increased until the equilibrium balance is restored. For an exothermic reaction (i.e. opposite direction to the endothermic one) increasing the temp does the opposite. |
|
|
In a redox reaction involving ions, two half-equations can be written, one showing oxidation and the other showing reduction. |
g |
|
|
How can oxidation/reduction be explained using oxidation states? |
An increase in oxidation state of an element is oxidation. A decrease in oxidation state is reduction. |
|
|
How can you test for oxidising and reducing agents? |
The colour changes of potassium manganate(VII) and potassium iodide can be used to test for oxidising and reducing agents.
When potassium manganate(VII) oxidises a substance, its colour goes from purple to colourless. When potassium iodide reduces a substance, its colour goes from colourless to brown. |
|
|
10: What is the pH scale used for? |
The pH scale is used to show the acidity or alkalinity of a solution. |
|
|
Universal indicator can be used to… |
find the pH of a solution. |
|
|
|
Acids are substances that form hydrogen ions when dissolved in water. |
|
|
|
A salt and hydrogen. |
|
|
Acids react with metals oxides and hydroxides to form… |
A salt and water. |
|
|
Acids react with carbonates to form… |
A salt, water and carbon dioxide. |
|
|
What is a base? What is an alkali? |
A base is a substance that can neutralise an acid. An alkali is a soluble base. |
|
|
|
A salt and water. |
|
|
What is released when ammonium salts is heated with alkalis? |
Ammonia gas |
|
|
|
Crushed limestone or lime is added to neutralise excess acidity in the soil. |
|
|
What is the difference between an acid and a base? |
An acid is a proton donor. A base is a proton acceptor. |
|
|
How can a strong acids and bases be distinguished from a weak one? |
Strong acids and bases are completely ionised in water. Weak acids and bases are partly ionised in water. |
|
|
Are the oxides of metals/non-metals acidic or basic? |
The oxides of most metals are basic oxides. The oxides of most non-metals are acidic oxides. |
|
|
What are examples of neutral oxides? |
Nitrogen (I) oxide, nitrogen (II) oxide and carbon monoxide are neutral oxides. |
|
|
What are examples of amphoteric oxides? |
The oxides of aluminium and zinc are amphoteric – they react with both acids and alkalis. |
|
|
11: The salt of a metal above hydrogen in the reactivity series is made by reaction of the metal with an acid. |
. |
|
|
How can salts be made? |
Salts can be made by the reaction of an insoluble base with an acid. |
|
|
When making a salt from a metal or metal oxide the acid is the… |
Limiting reactant. |
|
|
What is a titration used for? |
A titration is used to accurately make a soluble salt from an acid and an alkali. |
|
|
|
Salts of Group I elements and ammonium salts.
|
|
|
When making a salt using the titration method, the titration is first carried out using an indicator such as methyl orange to tell when the base/acid has been fully neutralised and then repeated without an indicator, using the liquid amount reading from the first time |
. |
|
|
How are insoluble salts made? |
Insoluble salts are made by mixing solutions of two soluble salts. |
|
|
All salts of Group I elements, ammonium salts (ones that have NH4 in them) and nitrates are… |
Soluble in water. |
|
|
Most chlorides, bromides and iodides are soluble. Those of lead and silver are insoluble. |
. |
|
|
What are the tests for oxygen hydrogen chlorine carbon dioxide ammonia |
The tests are oxygen: relights a glowing splint hydrogen: squeaky pop with a lit splint chlorine: bleaches damp litmus paper carbon dioxide: makes limewater cloudy ammonia: turns damp red litmus paper blue |
|
|
When sodium hydroxide is heated with a solution containing ammonium ions… |
Ammonia gas is produced. |
|
|
Aluminium hydroxide and zinc hydroxide precipitates dissolve in excess sodium hydroxide but only zinc ions dissolve in excess aqueous ammonia. |
(this is part of the anion tests) |
|
|
What is a cation? What is an anion? |
cation: positively charged ion that is attracted to the cathode in electrolysis anion: negatively charged ion that is attracted to the anode in electrolysis |
|
|
How can we identify carbonates? |
Carbonates are identified by adding a dilute acid to an unknown compound then testing the gas produced with limewater. |
|
|
How can we identify halides? |
Halides are identified by the colour of the precipitate obtained when silver nitrate is added. Chloride: white, Bromide: cream, Iodide: yellow |
|
|
How can we identify nitrates? |
Nitrates are identified by adding sodium hydroxide and aluminium foil, warming gently, then testing for the release of ammonia gas with damp red litmus paper. |
|
|
How can we identify sulphates? |
Sulphates are identified by adding dilute nitric acid followed by barium chloride to the unknown compound. A white precipitate indicates the presence of a sulphate. |
|
|
18: What are alkanes? |
Alkanes are hydrocarbons with only single covalent bonds in their structure. |
|
|
What kind of reactions can alkanes go through? |
They are generally unreactive, however they can burn or have a photochemical reaction with chlorine. |
|
|
How do alkanes react with chlorine? |
They have a photochemical reaction (only in the presence of sunlight) where a chlorine atom replaces a hydrogen atom in the alkane (a substitution reaction). CH4 + Cl2 --> CH3Cl + HCl If excess chlorine is used then multiple hydrogens will be replaced. |
|
|
What does cracking alkanes do? Why is it done? |
It breaks long-chained hydrocarbons down into small-chained ones. This is done because some of the smaller ones, such as petrol and diesel, are in much higher demand. This also produces alkenes, which are useful for making plastics. |
|
|
How is cracking carried out? |
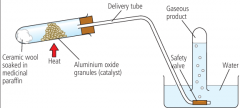
At high temperatures using a catalyst. |
|
|
What is the difference between saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons? |
saturated ones have the most amount of hydrogen molecules possible (alkanes), unsaturated ones don't because they have a C=C double bond (alkenes) |
|
|
How can you test for saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons? |
Bromine water is yellow/orange in colour. Add a few drops of it to a test-tube of the hydrocarbon you want to identify. If it decolourises the hydrocarbon then it is an alkene (unsaturated). If not, then it is saturated. |
|
|
What happens to alkenes when reacted with bromine? (one of the three addition reactions that alkenes can through) |
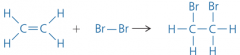
With bromine, it has been added across the double bond. |
|
|
What happens to alkenes when reacted with hydrogen? (one of the three addition reactions that alkenes can through) |
A hydrogenation reaction, can be classified as a reduction reaction. Forms an alkane. Done at 60 degrees with a nickel catalyst. C2H4 + H2 --> C2H6 (ethene to ethane) used to make margarine from vegetable oils |
|
|
What happens to alkenes when reacted with steam? (one of the three addition reactions that alkenes can through) |
Steam reacts with alkene to form alcohols. A high temp (about 300 degrees) and high pressure (70 atmospheres) is needed. The steam is passed over a catalyst of concentrated phosphoric acid. Gives a good yield of alcohol. Ethanol of a high purity is made this way. C2H4 + H20 --> C2H5OH |
|
|
What are the homologous series of alcohols and carboxylic acids? |
alcohols: -OH carboxylic acids: -COOH |
|
|
How can ethanol be made? |
by reacting steam with ethene at a high temperature whilst using a phosphoric acid catalyst or, by fermentation |
|
|
In relation to alcohols, what are isomers? |
When the -OH is attached to a place that is not the end of the structure. For example, if it was placed on the second H along it might be called butan-2-ol. |
|
|
How can ethanoic acid (vinegar) be made? |
Oxidation in the air: When left in the air, enzymes from a naturally present bacteria will help speed up the conversion.
Acidified potassium manganate (VII): Refluxing - heat ethanol with sulphuric acid and potassium manganate (a good oxidant) in a flask in an upright position with a condenser. The condenser prevents the volatile alcohol from escaping.
The equation is: C2H5OH + 2[O] --> CH3COOH + H2O |
|
|
What are carboxylic acids? |
They are typically weak acids (reacts with metals, carbonates, hydroxides etc.). Ethanoic acid is an example of one. |
|
|
How can esters be made with carboxylic acids? |

Carboxylic acids react with alcohols to form esters. This is called esterifciation. When this happens, an ester linkage is formed. H2O is left over.
Esters have a fruity smell so they're used in shampoos and flavourings. |
|
|
How are esters formed? |
carboxylic acid + alcohol --> ester + water e.g. ethanoic acid + ethanol --> ethyl ethanoate + water |
|
|
19: What are polymers? |
Long-chained molecules formed when simple molecules (monomers) combine. They are macromolecules. |
|
|
What is it called when polymers are formed by addition reactions? How does this happen? |
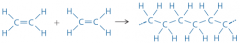
Addition polymerisation. In the case of alkenes, the C=C bond breaks and joins with its neighbouring molecule. When poly(ethene) is made, thousands join like this. |
|
|
What are the uses of poly(ethene), nylon and terylene? |

poly(ethene): bowls, plastic bags, dustbins. nylon: rope, clothes, fishing nets terylene: clothing (like pic related) |
|
|
What are the advantages and disadvantages of each method of disposing of plastic? |
Landfills: fill up quickly, use up land Burn them: heat produced can be used for electricity or heating, many plastics produce poisonous gases when burnt, also some produce poisonous 'dioxins' Recycling: not all plastics can be recycled, the ones that can't must be sorted out and processed, which takes time and money Cracking: some plastics can be melted, then cracked and polymerised into new articles |
|
|
When given the monomers, how can the structure of an addition polymer be drawn? |
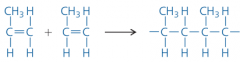
Joining several monomer units and changing the double bonds to single ones. |
|
|
How can polymer structures (and the monomers that went into them) be written in shorthand? |
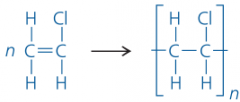
planet rock |
|
|
What is it called when polymers are formed with condensation? What happens during this? |
Condensation polymerisation. Water is eliminated as the monomers join together. |
|
|
What are polyamides? How do they link? |
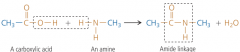
carboxylics and amines form this. There is an amide linkage of -CONH- E.g. nylon |
|
|
What are polyesters? How do they link? |
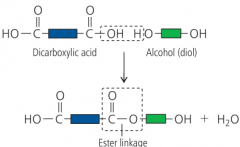
carboxylics and alcohols form this. There is an ester linkage of -COO- E.g. terylene |
|
|
20: What are the main nutrients in food? |
Proteins, fats and carbohydrates.
Proteins and some carbohydrates are macromolecules |
|
|
What do the structures of amino acids have in common? |
They all the amine (-NH2) and carboxylic acid (-COOH) groups in common, but the side chains are different. |
|
|
How are proteins formed from amino acids? |
In a condensation reaction (water eliminated). An amide link is formed between the amine group of one amino acid and the carboxylic acid group of the next. O || C -- N <-- amide linkage yes | H |
|
|
How can proteins be converted to amino acids? |
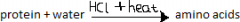
this reaction is catalysed by enzymes when it happens in the body. The proteins are converted into amino acids in the opposite to the condensation polymerisation that formed them initially. This is hydrolysis. |
|
|
What are fats? |
Fats are esters formed from glycerol and long-chain carboxylic acids (fatty acids, e.g. C15H31COOH).
Glycerol is CH2 -- OH | CH -- OH | CH2 -- OH |
|
|
How are soaps made? Why are acids not used? |
By hydrolysis of fats and oils with sodium hydroxide. An acid cannot be used because then the reaction will not go to completion (an equilibrium mixture is formed).
fat/oil + NaOH --> soap + glycerol |
|
|
What are the general formulas for: alkanes alkenes alcohols carboxylic acids and carbohydrates? |
alkanes: CnHn+2 alkenes: CnH2n alcohols: CnH2n+1OH carboxylic acids: CnH2n+1COOH carbohydrates: Cx(H2O)y |
|
|
How do monosaccharides (mono = one, saccharide = sugar i.e. simple sugars) bond to form polysaccharides (complex sugars)? How can the structural formulas of monosaccharide monomers and the polysaccharides they form be written more simply? |
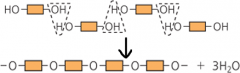
Condensation polymerisation. We can simplify their structures to show only the functional groups by using rectangles. You can use different coloured rectangles to distinguish different innards |
|
|
How are complex carbohydrates hydrolysed? |
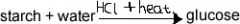
The starch is converted in the opposite way to the condensation polymerisation that formed them initially. |
|
|
What is starch? |
Found in rice, pasta and potatoes. Provides us with most of the carbohydrate in our diets. Starch is made of glucose monomers arranged in long chains or in branched chains. |
|
|
What is cellulose? |
Found in the cell walls of plants. Like starch, it is a polymer of glucose. We can't digest it. |
|
|
How can different amino acids and sugars be identified? |
Chromatography. Sugars are colourless so a locating agent must be used (do the chromatography, then spray on the locating agent and heat the paper in an oven to develop the colour). |
|
|
What is fermentation? |
the breakdown of organic material with effervescence and release of heat. This usually happens by enzymes released from yeast or bacteria. |
|
|
How is ethanol made using fermentation? What are the conditions of the reaction? What limits it? How is the ethanol extracted afterwards? |
Enzymes from yeast or bacteria (usually yeast) catalyse this reaction C6H12O6 --> 2C2H5OH + 2CO2 Must happen without air so the enzymes respire anaerobically. Can only keep going until the mixture is 14% ethanol, since after that the yeast die. Ethanol is separated by fractional distillation. |
|
|
How does producing ethanol by fermentation compare with producing it from an alkene and steam? (As and Ds of each) |
Fermentation: simpler method, needs lots of large tanks, batch process, slow rate of reaction, ethanol has to be separated by fractional distillation afterwards, uses renewable sources. Alkene (normally ethene) + steam: more complex method, less equipment, continuous process, fast rate of reaction, purer ethanol, ethene is made from the non-renewable resource petroleum |
|
|
How is ethanol used as a fuel? What are the benefits of using it? |
Made from fermentation from various plant sources. Either mixed with petrol to form the fuel gasohol or used on its own (like in alcohol burners). Does not pollute as much as petrol. Ethanol from fermentation comes from a renewable source, this means the fuel is potentially carbon neutral: CO2 released by the ethanol in burning is balanced out by CO2 taken in by the sugar cane during photosynthesis. |

