![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
66 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Infrastructure
|
the essential facilities and services such as roads, airports, sewage treatment, water systems, railways, telecommunications, and other utilities that are necessary for economic activity.
|
|
|
capital widening |
increase at the same rate as the labour force and lead to a constant labour productivity per worker |
|
|
Relative Poverty
|
They do not reach some specified level of income
|
|
|
Absolute Poverty
|
Basic necessities for survival and the amount a person needs of them to live.
|
|
|
gini coefficient
|
measure of inequality of a distribution. defined as a ratio with values between 0 and 1. Numerator is the area between the Lorenz curve of the distribution, denominator is area under distribution
|
|
|
Import Substitution
|
developing country should produce goods domestically rather than import them --domestic industries will grow, as will economy.
|
|
|
Foreign Direct Investment
|
long term investment by private multi-national corporations in countries overseas.
|
|
|
Humanitarian Aid
|
given to alleviate short-term suffering, which may be caused by war, draught, or natural disasters.
|
|
|
Types of humanitarian aid
|
food, medical, emergency
|
|
|
Development aid
|
alleviates poverty in the long run and improves welfare
|
|
|
Tied Aid
|
given to a developing country but on condition that they spend it on goods and services from the donor country.
|
|
|
Project Aid
|
given for specific project in a country, given in the form of a grant aid that requires no repayment.
|
|
|
Technical Assistance
|
raises level of technology by bringing in foreign technology and technicians. Raises the quality of human capital by provision of training facilities and expert guidance.
|
|
|
Commodity Aid
|
given by countries to increase productivity in developing countries--provides funds to purchase commodities including consumer items intermediate inputs, and industrial raw materials.
|
|
|
Bilateral Aid
|
given directly from one country to another
|
|
|
Multilateral Aid
|
given by rich countries to international aid agencies---they decide where it goes.
|
|
|
Lorenze curve |
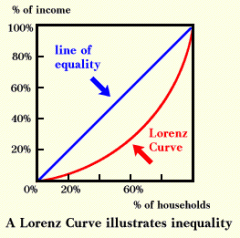
|
|
|
subsidy graph |
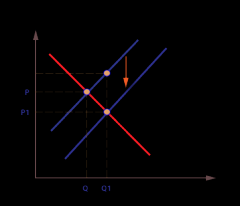
|
|
|
quota graph |
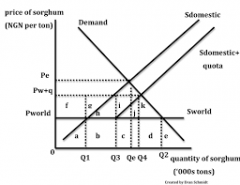
|
|
|
tariff graph |
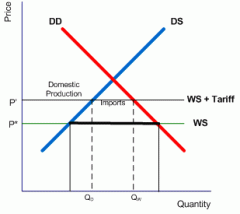
|
|
|
supply side shock |
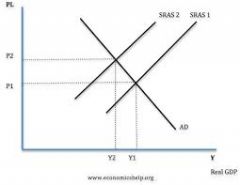
|
|
|
production possibility frontier |
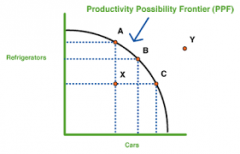
|
|
|
current account |
The sum of the balance of trade, goods and services, net income from other countries |
|
|
financial account |
a country's balance of payments that covers a company's financial assets. Components include direct investment, portfolio investment and reserve assets. |
|
|
capital account |
National account that shows the net change in ownership of a nation. Result of public and private international investments flowing in and out of a country. |
|
|
appreciation graph |
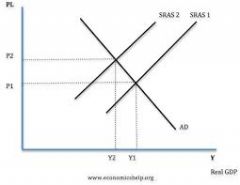
|
|
|
depreciation graph |
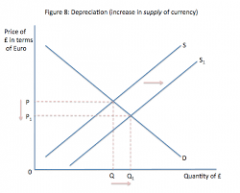
|
|
|
National account that shows the net change in ownership of a nation. Result of public and private international investments flowing in and out of a country. |
tax imported on goods, in order to protect the domestic industry |
|
|
Quota |
numerical limit to a good that can be imported |
|
|
Capital deepening |
increase output through better technology and output per worker; leads to rising labor productivity |
|
|
Specialization
|
occurs when a country or a firm concentrates production on one or a few goods
|
|
|
Exchange Rate
|
the rate at which one currency can be exchanged for another, or the number of units of foreign currency that corresponds to one unit of domestic currency
|
|
|
Trade protection
|
government intervention in international trade through the imposition of trade restrictions to prevent the free entry of imports into a country
|
|
|
Infant Industry
|
a new domestic industry that has not had time to establish itself and achieve efficiency in production and may therefore be unable to compete with 'mature' competitors
|
|
|
Dumping
|
the practice of selling goods in international market at a price that is below the cost of production
|
|
|
Appreciation
|
refers to an increase in the value of a currency in the context of floating/managed exchange rate system
|
|
|
Depreciation
|
refers to a decrease in the value of a currency in the context of a free floating managed exchange rate system.
|
|
|
Fixed Exchange Rate
|
refers to an exchange rate that is fixed by the central bank of a country and is not permitted to change in currency supply & Demand
|
|
|
Managed exchange rate
|
exchange rate that are for the most part free to float to their market levels over long periods of time, but there is some intervention of the government to reduce short-term fluctuations
|
|
|
Balance of Payments
|
a record of all transactions between the residents of a country and the residents of all other countries, showing all payments received from other countries and all payments made to other countries
|
|
|
Current Transfer
|
item in current account: refers to inflow and outflows of funds for items involving gifts, foreign aid and pension
|
|
|
Balance of current account
|
sum of all inflows-outflows of funds the current account of payments
|
|
|
Current Account
|
balance of payments, including balance of trade, balance of service, plus inflows minus outflows of income and current transfer
|
|
|
Capital Transfer
|
a part of the capital account, that includes inflow-outflows of debit forgiveness, non-life insurance claims and investment
|
|
|
Direct Investment
|
inflows-outflows of funds for the purpose of foreign direct investment
|
|
|
Portofolio Investment
|
financial investment, including Investment in stocks and bonds
|
|
|
Trading Bloc
|
a group of countries that have agreed to reduce tariff and other barriers to trade for encouraging freer trade and cooperation between them
|
|
|
Free trade area
|
type of trading bloc - eliminate trade barriers between them
|
|
|
Customs union
|
fre trade between countries in union, ADDITIONAL common policies towards non-members
|
|
|
Common Market
|
no restriction on any factors of production + freer trade + common policy towards non-members
|
|
|
Purchasing Power parities
|
special exchange rates between currencies that make the buying power of each currency equal to the buying power of 1 US Dollar
|
|
|
Composite Indicator
|
a summary measure of more than one indicator, often used to measure economic development
|
|
|
Human Development Index (HDI)
|
composite indicator of development which includes that measure 3-Dimensions of development: Income, level of education and Health
|
|
|
Empowerment
|
creation of conditions for equality of opportunities
|
|
|
Export Promotion
|
refers to a growth and trade strategy where a country attempts to achieve economic growth by expanding its export
|
|
|
Trade Liberalization
|
the policy of freeing up the international trade by eliminating trade protection and barriers to trade
|
|
|
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)
|
refers to investment by firms based in one country, but in productive activity based in another country
|
|
|
Multinational Cooperation
|
a firm involved in foreign direct investment
|
|
|
foreign aid
|
consists of concessional financial flows from the developed world to economically less developed countries
|
|
|
Humanitarian Aid
|
a type of foreign aid extended in regions where there are emergencies caused by violent conflicts or natural disaster, intended to save lives, ensure access to basic necessities and provide assistance with reconstruction
|
|
|
Development Aid
|
foreign and intended to help economically less developed countries
|
|
|
Tied Aid
|
the practice whereby donors make the recipients of foreign aid opened a portion of the borrowed funds on the purchase of goods and services from the donors country.
|
|
|
Official Development Assistance
|
foreign aid that is offered by countries or by organizations composed of a number of countries
|
|
|
Multilateral Development Assistance
|
lending to developing countries for the purpose of assisting their development on non-concessional terms by multilateral organizations -- IMF & World Bank
|
|
|
World Bank
|
a development assistance organization, composed of 185 member countries that extended long-term credit to developing countries for the purpose of promoting economic development & structural change
|
|
|
International Monetary Fund (IMF)
|
an international financial institution composed of 185 member countries, whose purpose is to make short-term loans to governments on commercial terms in order to stabilize exchange rates, alleviate balance of payments difficulties and help countries meet their foreign debt obligations
|

