![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
89 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The 4 most frequently occurring chemical elements in living things |
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen |
|
|
Organic compounds |
Compounds which contain CARBON and are found in living organisms (Except hydrogencarbonates, carbonates and oxides of carbon) |
|
|
Carbon Atom |
Forms 4 covalent bonds with other atoms -carbon molecules are stable |
|
|
Covalent bond |
2 adjacent atoms share a pair of electrons, with one electron contributed by each atom -The strongest type of bond |
|
|
Carbohydrates |
composed of C,H and O. Hydrogen and oxygen are in the ratio of 2:1 |
|
|
Lipids |
Class of molecules including steroids, waxes, fatty acids and triglycerides -insoluble in water |
|
|
Triglycerides at room temperature |
fats-if they are solid at room temperature oils- if they liquid at room temperature |
|
|
Proteins |
composed of one or more chains of amino acids -Composed of C, H, O, N (sometimes S) |
|
|
Nucleic Acids |
-DNA and RNA -Contain C, H, O, N, P -subunit nucleotide |
|
|
Metabolism |
is the web of all the enzyme catalysed reactions in a cell or organism |
|
|
What is the site of metabolic reactions? |
Cytoplasm and extracellular space |
|
|
Anabolism |
Reactions that build up larger molecules from smaller ones -Requires energy (ATP) ex: protein synthesis, DNA synthesis |
|
|
Catabolism |
A reaction in which larger molecules are broken down into smaller ones -Releases energy ex: Digestion, cell respiration |
|
|
Hydroxyl Simplified notion |
-OH |
|
|
Amine Simplified notion |
-NH2 |
|
|
Carboxyl Simplified notation |
-COOH |
|
|
Methyl Simplified notation |
-CH3 |
|
|
Ribose |
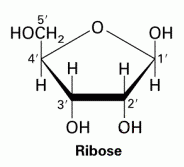
C5H10O5
Molecule is a 5 membered ring |
|
|
Glucose |
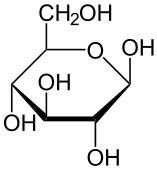
C6H12O6
Six membered ring |
|
|
Saturated Fatty Acids |
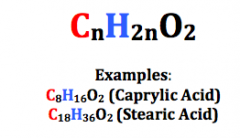
Carbon atoms form an unbranched chain Carboxyl group |
|
|
Difference between saturated and unsaturated fatty acids... |
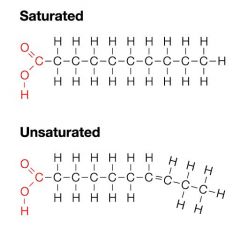
Saturated fats have no double bond and remain solid at room temperature |
|
|
Amino acid |
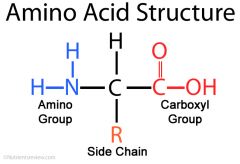
Central C atom is bonded to: Amine group(-NH2) , Carboxyl group(-COOH) ,hydrogen atom, R group |
|
|
IDENTIFYING MOLECULES |
-Proteins contain: C, H, O and N (Some Sulphur) -Carbohydrates contain H and O atoms in a ration of 2:1 -Lipids contain relatively less O than carbohydrates |
|
|
Nucleic Acid |
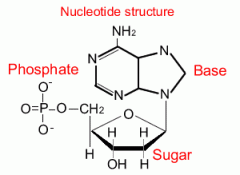
Each nucleotide has three components: a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base if the sugar is ribose it is RNA
|
|
|
Difference between Nucleotide and Nucleic Acid |
Nucleotides are the subunit that is polymerized (connected into a long chain) to make nucleic acids (DNA and RNA).
|
|
|
Urea |
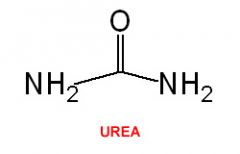
CH4N2O Nitrogen-containing compound which is produced if there is an excess of amino acids in the body |
|
|
Synthesis of Urea |
-Synthesis occurs in the liver -Then Urea is transported by the blood stream to the kidneys to be filtered -Urea can be synthesized artificially |
|
|
Friedrich Wöhler 1828
|
-Synthesized urea artificially
-the first organic compound to be synthesized artificially |
|
|
Bonds between H and O |
-involve unequal sharing of electrons -Polar Covalent Bonds |
|
|
pH (high and low) |
pH(potential hydrogen) measures the activity of dissolved H+ ions Low pH(1-6) indicates a high concentration of H+ and is acidic High pH(8-14) indicates a low concentration |
|
|
Hydrogen ions |
Used for active transport, photosynthesis, cell respiration |
|
|
Oxygen |
is used during aerobic respiration and is necessary to form water |
|
|
Water (hydrogen and oxygen as components) |
Oxygen carries negative charge while both hydrogens carry positive charges |
|
|
Hydrogen Bods |
Allow for water molecules to stick together. A weak bond compared to covalent bond. |
|
|
Cohesion |
The binding together of two molecules of the same type. Useful for water transport in plants |
|
|
Adhesion |
Hydrogen bonds can form between water and other polar molecules causing water to stick to them. Useful in leaves for keeping the cell wall moist and absorption of CO2 for photosynthesis |
|
|
High specific heat capacity |
Water can absorb or give off a great deal of heat without changing temperature greatly (hydrogen bonds restrict the motion of water molecules) |
|
|
What does water need to do in order to cool down? |
Water must lose relatively large amounts of energy |
|
|
Latent Heat of Vaporization |
The heat needed to separate a molecule from other molecules in a liquid while evaporating |
|
|
A High Latent Heat of Vaporization |
Water absorbs a great deal of heat when it evaporates.
|
|
|
Sweat |
-Secreted by glands in the skin -reduces temperature and cools the body |
|
|
The order of which the body is cooled... |
-Receptors in the skin, overheating, hypothalamus detects disturbance, sweating |
|
|
How many liters of sweat do sweat glands secrete per hour? |
2 liters |
|
|
Adrenaline |
-Secreted when our brain anticipates a period of intense activity |
|
|
Cooling the body in dogs and plants.. |
-Dogs and birds pant, heat loss occurs to to evaporation -Transpiration in plant leaves, evaporative loss of water |
|
|
High boiling point |
The highest temperature that water can reach in a liquid state |
|
|
Solvent properties of water |
Water dissolves many substances because it is polar |
|
|
Aqueous Solutions |
Fluids which are primarily water. ex: cytoplasm, blood plasm |
|
|
Solvent properties of water in plants... |
phloem transports dissolved sugars, xylem carries water and dissolved minerals |
|
|
Solvent properties of water in animals... |
blood is the most common transport medium in animals. Blood plasma transports red and white blood cells and dissolved molecules |
|
|
Sodium Chloride (blood plasma) |
-ionic compound which is freely soluble in water -dissolves to form sodium ions and chloride ions |
|
|
Amino Acids (blood plasma) |
-Have negative and positive charges -soluble in water -All amino acids can be carried in blood plasma |
|
|
Glucose (blood plasma) |
-Polar molecule and freely soluble in water |
|
|
Oxygen (blood plasma) |
-Nonpolar molecule, small size -Dissolves in water sparingly |
|
|
Fats Molecules (blood plasma) |
-nonpolar -insoluable in water |
|
|
Lipoprotein complex |
groups of molecules with a single layer of phospholipid on the outside of fats -Hydrophilic phosphate heats contact with water -Hydrophobic hydrocarbon tails face inwards and contact with fats |
|
|
Cholesterol (blood plasma) |
-Hydrophobic -Is transported with fats in lipoprotein complexes |
|
|
Hydrophilic |
Water-loving substances which are chemically attracted to water -Polar molecules (ex:glucose, sodium) |
|
|
Hydrophobic |
substances insoluble in water -non polar (no positive or negative charges) (ex: lipids) |
|
|
Hydrophobic interactions |
Forces that cause non polar molecules to join together into groups |
|
|
Methane |
-CH4 Waste product of anaerobic respiration in certain prokaryotes, is a greenhouse gas -non polar |
|
|
Monosaccharides |
-Single Sugars (glucose, galactose, fructose, ribose) |
|
|
Disaccharides |
-2 sugars -Maltose= glucose+glucose -Sucrose= glucose+fructose -Lactose= glucose+galactose |
|
|
Polysaccharides |
-Consist of many sugars -starch, glycogen, cellulose -polymers of glucose |
|
|
alpha vs beta glucose... |
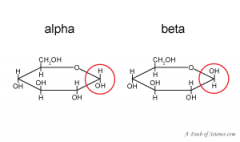
alpha C 1 points downwards, beta points upwards |
|
|
Cellulose |
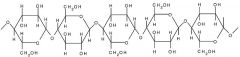
A chain of beta-glucose molecules. Very high tensile strength. Form bundles with hydrogen bonds linking the cellulose molecules - microfibrils |
|
|
Starch |
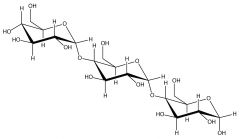
Made of alpha-glucose molecules |
|
|
the 2 components of starch are called... |
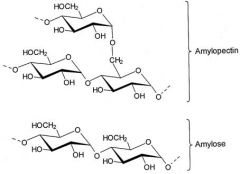
Amylose and Amylopectin |
|
|
Amylose |
Chain is unbranched and forms a helix |
|
|
Amylopectin |
Chain is branched globular in shape and made by plant cells -Hydrophillic but too large to be soluble in water -Stores glucose |
|
|
Glycogen |
-More branched than starch -Molecule more compact -Made by animals, stored in the liver (muscles in humans) |
|
|
Condensation |
Chemical reaction in which 2 molecules combine to form one single molecule -water formation, anabolic process, ATP is required -Water is A PRODUCT |
|
|
Hydrolysis |
Chemical process in which a certain molecule is split into 2 parts -Water is A SUBSTRATE |
|
|
Monounsaturated vs Polyunsaturated |
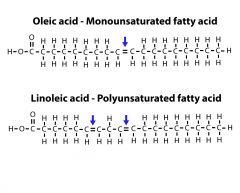
Monounsaturated has one double bond while Polyunsaturated has two. |
|
|
Cis-fatty acids vs Trans-fatty acids |
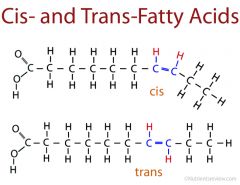
Cis have hydrogen atoms on the same side while trans have them on opposite sides. |
|
|
Energy Storage (Lipids) |
-Lipids are used for long-term energy storage -Lipids are six times more efficient in the amount of energy that can be stored per gram of body mass (than other fats) |
|
|
Energy Storage (Glycogen) |
glycogen is found in the liver and some muscles. Used for short-term energy storage. Easily transported by blood. |
|
|
BMI |

Body mass index is used to assess whether a person's body mass is at a healthy level. Can be found using a nomogram |
|
|
Causes of being underweight |
anorexia nervosa- psychological condition that involves voluntary starvation |
|
|
Causes of obesity |
excessive food intake/insufficient exercise |
|
|
People with obesity have a higher risk of... |
-Coronary heart disease -Type 2 diabetes -Significantly reduced life expectancy |
|
|
Coronary heart disease (CHD) |
-Coronary arteries become partially blocked by fatty deposits -Blood clots form causing heart attacks |
|
|
Polypeptides |
-chains of amino acids -main component of proteins (sometimes the only component) |
|
|
Condensation reaction between amino acids to form a peptide... |
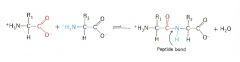
Involves -NH2 of one amino acid and -COOH of another |
|
|
Dipeptide |
Consists of 2 amino acids |
|
|
Oligopeptides |
chains of fewer than 20 amino acids |
|
|
Polypeptide |
consist of many amino acids(chains of amino acids) |
|
|
Insulin |
Small protein, contains 2 polypeptides (one with 21 amino acids other with 30) |
|
|
Titin |
The largest polypeptide, part of the structure of muscle, contains 34,350 amino acids |

