![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Hypothalamus Function
|
- maintain homeostasis
subserves 3 systems 1. ANS 2. endocrine 3. Limbic |
|
|
Hypothalamic Nuclei
|
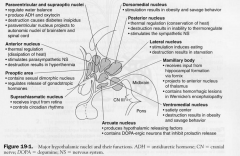
1. medial preoptic nucleus
2. Suprachiasmatic |
|
|
Medial Preoptic Nucleus
|
- regulates gonadotropic hormone release from adenohypophysis
- contains the sexually dimorphic nucleus, development of which depends on testosterone levels |
|
|
Suprachiasmatic Nucleus
|
- direct input form retina
- regulates circadian rhythms |
|
|
Anterior Nucleus
|
- thermal regulation (disspiation of heat)
- stimualtes PSNS - destruction results in hyperthermia |
|
|
Paraventricular Nucleus
|
- synthesizes ADH, oxytocin & Corticotropin-Releasing hormone
- starts the supraopticohypophyseal tract which projects to neurohypophysis. regulates water balance and project directly to Autonomic nuclei of brainstem & all levels of spinal cord - destruction results in Diabetes insipidus |
|
|
Dorsomedial Nucleus
|
stimulation results in obesity & savage behaviour
|
|
|
Posterior Nucleus
|
- thermal regulation (conservation of heat)
- destruction results in inability to thermoregulate - stimulates the SNS |
|
|
Lateral Nucleus
|
Stimulation induces eating
destruction results in starvation |
|
|
Mamillary Body
|
- input from hippocampal formation via fornix
- projects to anterior nucleus of thalamus - contains hemorrhagic lesions in wernicke's encephalopathy |
|
|
Ventromedial Nucleus
|
Satiety center
- destruction results in obesity & savage behaviour |
|
|
Arcuate Nucleus
|
- produces hypothalamic releasing factors
- contains DOPA-ergic neurons that inhibit prolactin release |
|
|
Supraoptic Nucleus
|
Synthesizes ADH & oxytocin
|
|
|
Hypophyseal Portal System
|
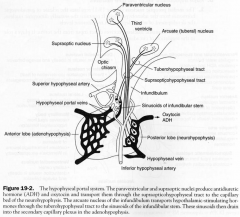
|
|
|
Major Fibres Systems in Hypothalamus
|
1. fornix; from hipocampal formation to mamillary nucleus, anterior nucleus of thalamus & septal area. then from the fornix back to the hippocampal formation
2. medial forebrain bundle; traverses entire lateral hypothalamic area. interconnects orbitofrontal cortex, septal area, hypothalamus & amygdala 3. Mamillothalamic Tract; mamillary to anterior nucleus of thalamus (papez circuit) 4. Stria terminalis; interconnects septal area, hypothalamus & amygdala 5. Supraopticohypophysial tract; supraoptic & paraventricular nuclei to neurohypophysis release site for ADH & Oxytocin 6. Tuberohypophysial tract; conducts the arcuate nucleus to the hypophyseal portal systme 7. Hypothalamospinal tract; direct descending autonomic fibres. |
|
|
Autonomic Functions
|
1. Anterior hypothalamus excites PSNS
2. Post. SNS |
|
|
Temperature Regulation
|
1. Ant. hypothalamus maintians body temp
2. Post. helps produce & conserve heat |
|
|
Water balance regulation
|
- paraventricular n. synthesisi ADJ controlling water excretion by the kidneys
|
|
|
Food Intake regulation
|
1. VM nuleus when stimulated inhibits urge to eat
2. L. induces urge to eat when stimulated |
|
|
Diabetes Insipidus
|
-polyuria & polydipsia
- lesion of the ADH pathways to the post. lobe of pituitary gland |
|
|
SIADHS
|
usually caused by lung tumor or drug therapy (carbamazepine, chlorpromazine)
|
|
|
Craniopharyngioma
|
- congenital tumor that originates from remnants of Rathke's pouch. usually calcified
1. pressure on chiasma (bitemporal) 2, pressure on the hypothalamus; hypothalamic syndrome (adiposity, diabetes insipidus, disturbace of temp regulation & somnolence) |
|
|
Pituitary Adenomas
|
- can cause endocrine abnormalities (emenorrhea & galactorrheas)
1. pressure on chiasma (bitemporal) 2, pressure on the hypothalamus; hypothalamic syndrome (adiposity, diabetes insipidus, disturbace of temp regulation & somnolence) |

