![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define the term electronegativity and its trend on the periodic table. |
Electronegativity is an an atoms ability to attract electrons. Electronegativity increases as you move from left to right and bottom to top on the periodic table. |
|
|
Define the term atomic radius and its trend on the periodic table. |
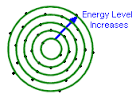
Atomic radius is the distance between an atoms nucleus and its outermost electron. Atomic radius increases as you move from right to left and top to bottom on the periodic table. |
|
|
Define the term effective nuclear charge and its trend on the periodic table. |
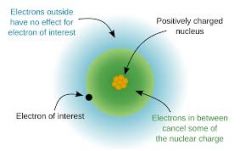
Effective nuclear charge is the net positive charge experienced by an electron in a multi-electron atom. Effective nuclear charge increases as you move from left to right and bottom to top on the periodic table. |
|
|
Define ionic bonding. |
When electrons are transferred between a metal and a non-metal. |
|
|
Define covalent bonding. |
When electrons are shared between two non-metals. |
|
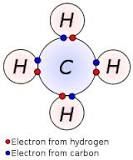
Identify what type of bond is occurring. |
Covalent |
|
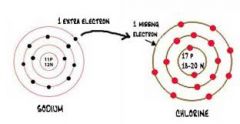
Identify what type of bond is occurring. |
Ionic |
|
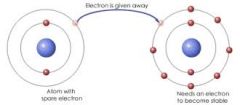
Identify what type of bond is occurring. |
Ionic |
|
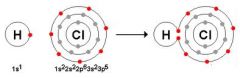
Identify what type bond is occurring. |
Covalent |
|
|
In an ionic bond, what determines which is the cation and which is the anion? |
The cation will have a slightly positive charge and the anion will have a slightly negative charge. Since electrons have a negative charge, the atom with the most valence electrons will be the anion, and the other atom the cation. |
|
|
What is the formula for Hydrogen dioxide? |
H20 |
|
|
What is the name for B2S9? |
Triboron nonaselenide |
|
|
What is the formula for tetracarbon octabromide? |
C4Br8 |
|
|
Describe the bonds within a water molecule. |
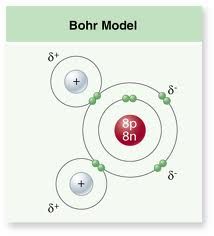
A water molecule is made up of one oxygen atom and two hydrogen atoms. The bonds that hold these atoms together are polar covalent. |
|
|
Define a polar molecule. |
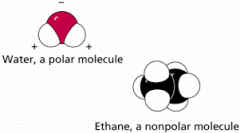
A polar molecule is a molecule in which electrons are unequally distributed, making one end of the molecule slightly negative and the other slightly positive. |
|
|
Is water a polar molecule? |
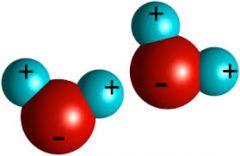
Yes |
|
|
What are the types of bonds that hold water molecules to other water molecules? |
Hydrogen bonds. |
|
|
Why/how do hydrogen bonds form to bond water molecules? |
Because water molecules are polar, the slightly negative side of one molecule is attracted to the slightly positive side of another molecule, forming the hydrogen bond. |
|
|
List the six types of chemical reactions. |
Combustion, synthesis, decomposition, double replacement, single replacement, acid-base. |

