![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
130 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Sound Waves are:
|
Longitudinal waves of compression and rarefaction of air molecules.
|
|
|
Sound Frequency is:
|
Number of compression/ rarefaction wave oscillations per unit time (cycles per second)
|
|
|
What sound frequencies can the human ear detect?
|
20 Hz - 20,000 Hz
|
|
|
Sound Loudness is:
|
The height (amplidude) of the sound waves
Measured by the decible scale |
|
|
How does the decible scale work?
|
Every 20 decibel inclrease in sound volume represents a 10 fold increase in the sound pressure amplitude
|
|
|
What is the threshold of hearing for humans?
|
About 20 micropascals (whispering)
|
|
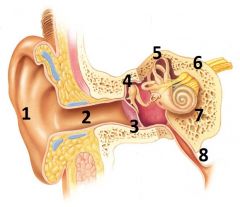
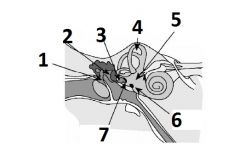
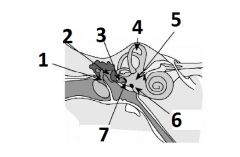
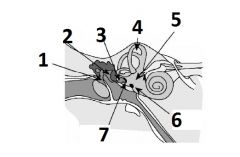
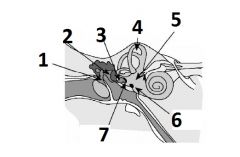
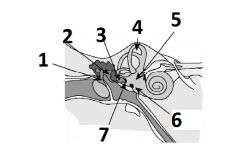
What is # 1 called?
|
Pinna (outer ear)
|
|
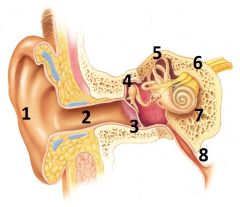
What is # 2 called?
|
Ear Canal (outer ear)
|
|
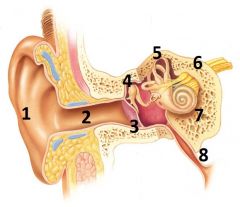
What is # 3 called?
|
Tympanic membrane (outer ear)
|
|
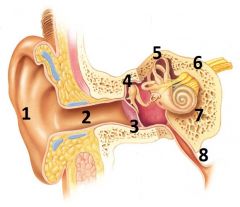
What is #4 called?
|
Auditory ossicles (middle ear)
|
|
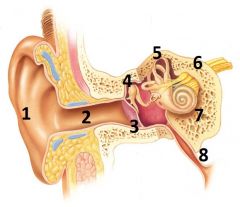
What is #5 called?
|
Semi circular cannals (inner ear)
|
|
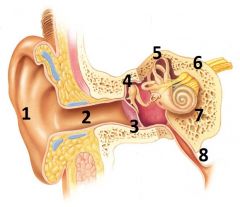
What is #6 called?
|
Vestibulocochlear nerve / cranial nerve VIII
(Inner ear) |
|
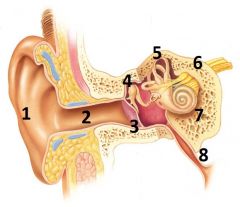
What is # 7 called?
|
Cochlea (inner ear)
|
|
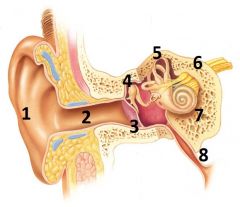
What is #8 called?
|
Auditory tube (middle ear)
|
|
What is #1 called?
|
Malleus
|
|
What is #2 called?
|
Incus
|
|
What is #3 called?
|
Stapes
|
|
What is #4 called?
|
Semicircular canals
|
|
What is #5 called?
|
Vestibular apparatus
|
|
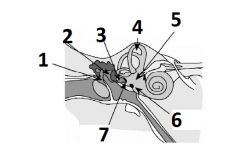
What is #6 called?
|
Round window
|
|
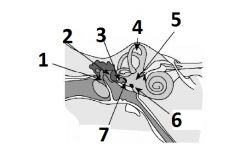
What is #7 called?
|
Oval window
|
|
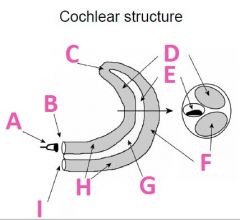
What is A called?
|
Stapes
|
|
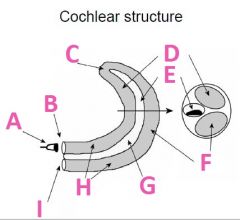
What is B called?
|
Oval Window
|
|
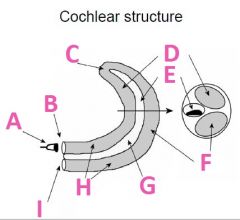
What is C called?
|
Helicotrema
|
|
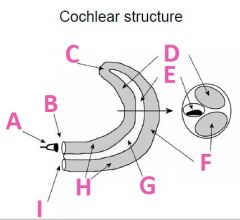
What is D called?
|
Scala Vestibuli (vestibular duct)
|
|
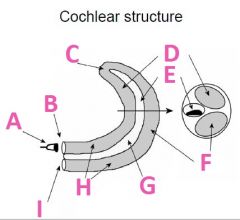
What is E called?
|
Scala media
|
|
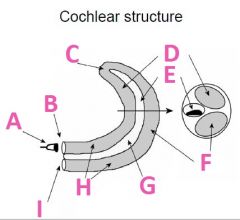
What is F called?
|
Scala Tympani (tympanic duct)
|
|
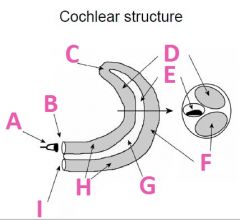
What is G filled with?
|
Endolymph fluid
|
|
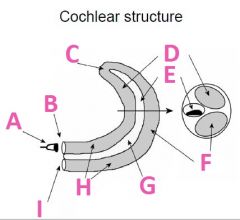
What is H filled with?
|
Perilymph fluid
|
|
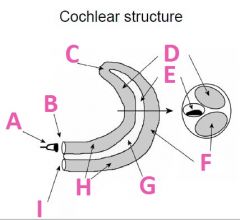
What is I called?
|
Round window
|
|
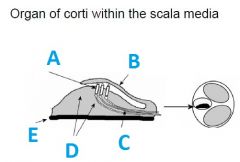
What is A called?
|
Hair cells
|
|
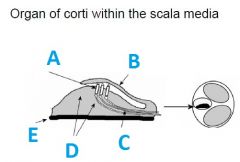
What is B called?
|
tectorial membrane
|
|
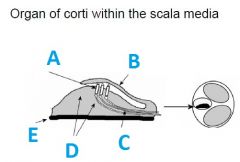
What is C called?
|
First auditory neurons (synapses outside of CNS)
|
|
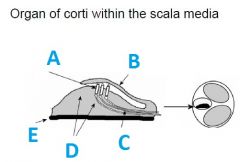
What is E called?
|
Basillar membrane
|
|
|
The basilar membrane
|
Stiff and narrow close to the ocal window, flexed by high pitches.
More flexible and wider close to the helicotrema, flexed by low pitches. |
|
|
What is the pressure release valve in the cochlea?
|
The round window.
All pressure waves are eventually dissipated out of the cochlea through the round window back tinto the middle ear. |
|
|
Endolymph and hair cells have a reversed concentration gradient of what molecule?
|
K+
High concentration in endolymph fluid Low concentration in hair cells |
|
|
The basilar membrane
|
Stiff and narrow close to the ocal window, flexed by high pitches.
More flexible and wider close to the helicotrema, flexed by low pitches. |
|
|
What is the pressure release valve in the cochlea?
|
The round window.
All pressure waves are eventually dissipated out of the cochlea through the round window back tinto the middle ear. |
|
|
Endolymph and hair cells have a reversed concentration gradient of what molecule?
|
K+
High concentration in endolymph fluid Low concentration in hair cells |
|
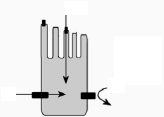
What three things happen when the stereocilia are not deflected?
|
1) some K+ channels open and partial depolarization of hair cell
2) Intermediate Ca++ influx 3) Intermediate levels of neurotransmitter release |
|
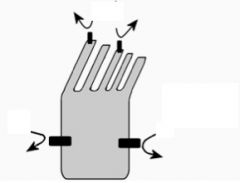
What three things happen when the stereocilium are deflected away from the kinocilium?
|
1)K+ channels close, causeing the cell to hyperpolarize
2) Less Ca++ influx 3) Low levels of neurotransmitter release |
|
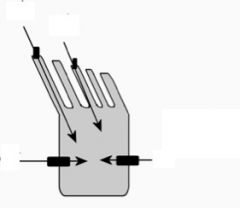
What three things happen when the stereocilia are deflected towards the tallest cilium?
|
1) K+ channels open, causing the cell to depolarize
2) More Ca++ influx 3) High levels of neurotransmitter release |
|

What volume of sound would create this kind of action potential firing frequency?
|
Silence
|
|

What kind of volumes would create this pattern of action potential firing frequency?
|
Low Volumes
|
|

What kind of volumes would produce this kind action potential firing frequency?
|
High Volumes
|
|
|
What kind of motion is the angular canal in charge of?
|
Rotation of the head up and down: "yes"
|
|
|
What kind of motion is the posterior canal in charge of?
|
Rotation of the head from side to side: "pressing ear to shoulder"
|
|
|
What kind of motion is the lateral canal in charge of?
|
Rotation of the head from side to side: "no".
|
|
|
What is angular acceleration?
|
Rotational motion
|
|
|
What is Linear Acceleration?
|
Movement straight forward (car accelerating)
|
|
|
What does the utricle do?
|
Senses horizontal acceleration and head position.
|
|
|
What does the saccule do?
|
Senses vertical acceleration and head position
|
|
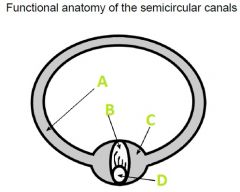
What A filled with?
|
Endolymph
|
|
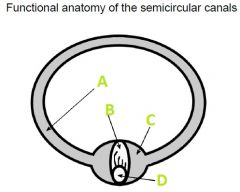
What is B called?
|
Cupula
|
|
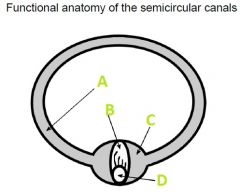
What is C called?
|
Ampulla
|
|
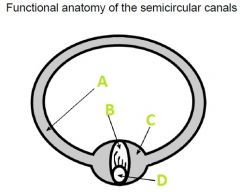
What is D?
|
Hair Cells
|
|
|
When the head moves clockwise what direction does the endolymph fluid move?
|
Counterclockwise
|
|
|
Because the semicircular canals are mirror images in each of the ears how does this affect the firing frequency during rotation of the head?
|
It causes one ear to speed up while the other one virtually stops.
|
|
|
What are the crystals that are found in the saccule and utricle?
|
otoliths
|
|
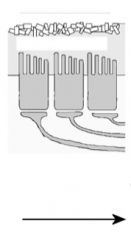
When your head moves right, what direction do the cillium on the hair cells move?
|
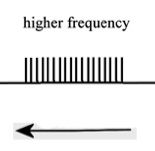
To the left (toward the cillium makes the firing frequency higher)
|
|
When your head moves left, what direction do the cillium on the hair cells move?
|
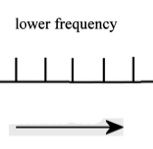
To the right (away from the kinocilium which causes lower firing frequency)
|
|
When your head moves down, what direction do the cillium on the hair cells move?
|
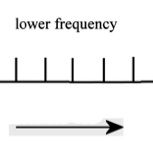
To the right (lower frequency because it's away from the kinocillium)
|
|
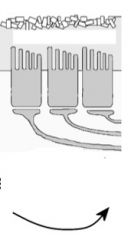
When your head moves up, what direction do the cillium on the hair cells move?
|
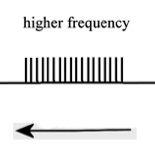
To the left (toward the kinocillium)
|
|
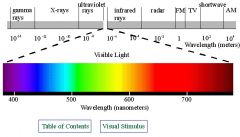
What is this called?
|
The electromagnetic spectrum
|
|
|
What is the visible spectrum?
|
Violet 400nm
Blue 500 nm Green 550 nm Yellow 600 nm Orange 650 nm Red 700 nm |
|
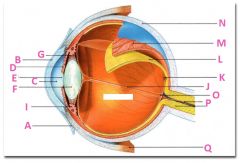
What is A?
|
Conjunctiva
|
|
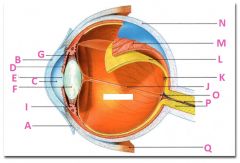
What is B?
|
Cornea
|
|
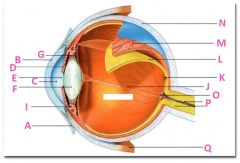
What is C?
|
Anterior cavity containing aqueus humor
|
|
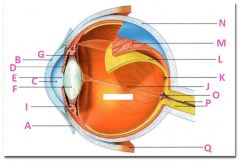
What is D?
|
Iris
|
|
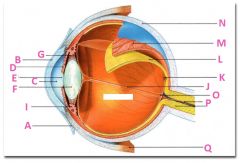
What is E?
|
Pupil
|
|
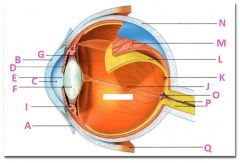
What is F?
|
Lens
|
|
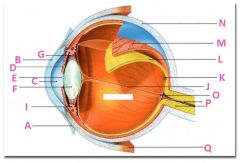
What is G?
|
Zonular fibers
|
|
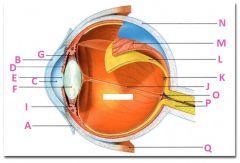
What is I?
|
Ciliary muscle
|
|
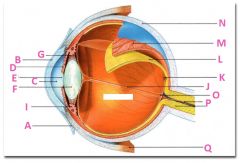
What is J?
|
Vitreous chamber containing vitreous humor
|
|
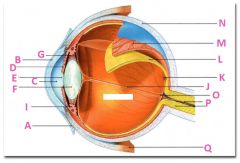
What is K?
|
Fovia
|
|
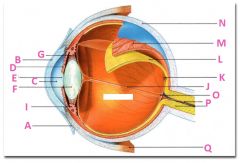
What is L?
|
retina
|
|
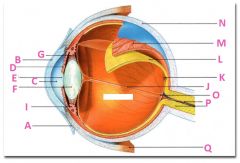
What is M?
|
Choroid
|
|
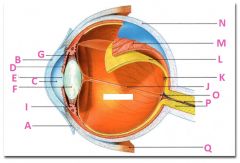
What is N?
|
Sclera
|
|
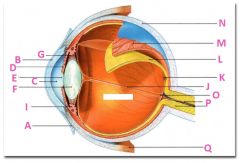
What is P?
|
Optic nerve
|
|
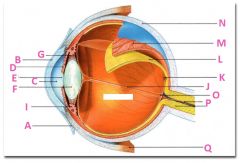
What is Q?
|
Extraoccular muscle
|
|
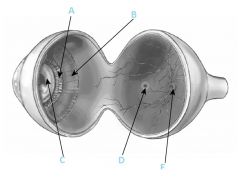
What is A?
|
Zonular fibers
|
|
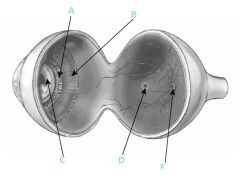
What is B?
|
Ciliary muscle
|
|
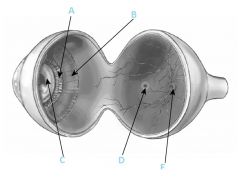
What is C?
|
Lens
|
|
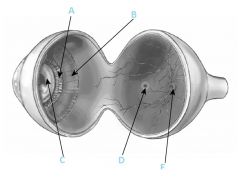
What is D?
|
Fovea
|
|
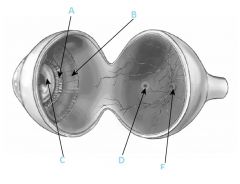
What is F?
|
Optic disc
|
|
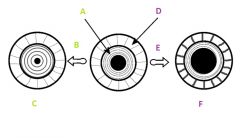
Explain A, B, and C
|
A) Circular muscle
B) Increased Light C) Parasympathetic stimulation causes circular muscle to contract |
|
|
Explain D, E, and F
|
D) radial muscle
E) decreased light F) sympathetic stimulation causes radial muscle to contract |
|
|
Explain D, E, and F
|
D) radial muscle
E) decreased light F) sympathetic stimulation causes radial muscle to contract |
|
|
Explain D, E, and F
|
D) radial muscle
E) decreased light F) sympathetic stimulation causes radial muscle to contract |
|
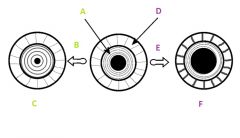
explain D, E, and F
|
D) Raidal Muscle
E) Decreased Light F) Sympathetic stimulation causes radial muscle to contract |
|
|
Pupilary diameter is controlled by _______ stimulation of muscle in the ________.
|
Autonomic
Iris |
|
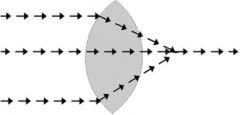
What kind of a lens is this?
|
Convex
|
|
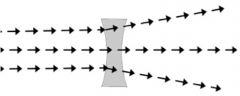
What kind of a lens is this?
|
Concave
|
|
|
How do you determine the focal length of a convex lens?
|
The power of a lens in diopters is the reciprocal of the focal length in meters.
Convex lenses will always have a positive number. |
|
|
How do you determine the focal length of a concave lense?
|
The power of a lens in the diopters is the reciprocal of the focal length in meters.
Concave lenses with always have a negative number. |
|
|
How many diopters of power does the human eye have at rest?
|
60
|
|
|
Although the cornea has _____ power optically than the lens. The cornea ______ change its shape, wherease the lense _____ change it's shape, increasing or decreasing it's optical power.
|
More
Cannot Can |
|
|
What is accomodation?
|
Allows the lens to change shape in order to correctly focus on close objects as well as far away objects.
|
|

Is the ciliary muscle relaxed or contracted?
|
Relaxed
|
|
Is the ciliary muscle relaxed or contracted?
|
Contracted
|
|
|
How do distant objects effect myopia?
|
(near-sightedness)
For distant objects the lens power is too strong (eye is too long) for the eye and the image is focused before it reaches the retina. |
|
|
How do near objects effect myopia?
|
For close objects the lens is sufficently spherical to focus the image normally.
|
|
|
What corrective lens would you use for a person who has myopia?
|
Concave
|
|
|
How do distant objects effect hyperopia?
|
For distant objects the lens flattens sufficently and the image focusing works fine
|
|
|
How do near objects effect hyperopia?
|
For close objects, the lens power is not strong enough flat (the eye is too short) and image focusig occurs beyond the length of the eyeball.
|
|
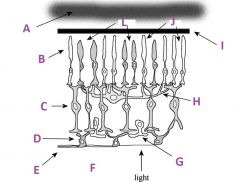
What is A called?
|
Choroid
|
|
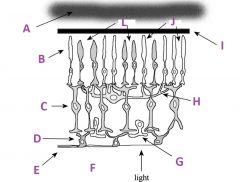
What are B called?
|
Photoreceptors
|
|
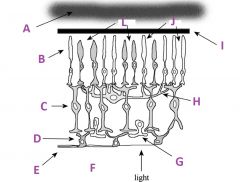
What are C called?
|
Bipolar cells
|
|
|
What are D called?
|
Ganglion cells
|
|
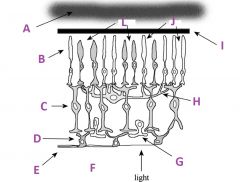
What is E?
|
Axons of ganglion cells (goes to CNS)
|
|
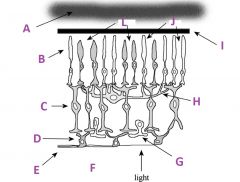
What is F?
|
Vitreous humor
|
|
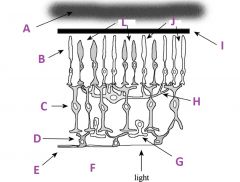
What is G called?
|
Amacrine cell
|
|
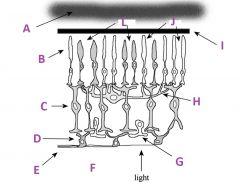
What is H called?
|
Horizontal cell
|
|
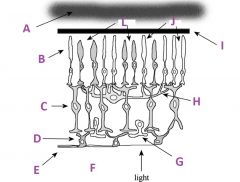
What is I?
|
Pigmented (with melanin) epithelium
|
|
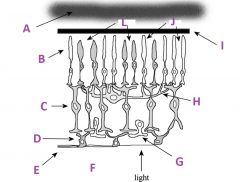
What are J?
|
Rods
|
|
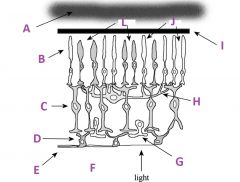
What are L called?
|
Cones
|
|
|
What is the purpose of rods?
|
To see in low light conditions; black and white
|
|
|
What is the purpose of cones?
|
To see color in bright light conditions
|
|
|
Do we have a higher light sensitivity with rods or cones?
|
Rods
|
|
|
Do rods or cones have an overall greater abundance on the retina?
|
Rods
|
|
|
Which has higher acuity rods or cones?
|
Cones
|
|
|
Do rods or cones have a higher convergence onto bipolar ganglion cells?
|
Rods
|
|
|
Where are rods found?
|
Retina periphery
|
|
|
Where are cones found?
|
Fovea
|
|
|
Describe signal transduction in rods when there are no photons present (complete darkness).
|
Retinal and opsin remain associated as rhodopsin.
cGMP is high Na+ channels are kept open by cGMP rod depolarizes Ca++ channels open Continual tonic release of inhibitory neurotransmitter onto bipolar cell Bipolar cell remains hyperpolarized and is inhibited from sending action potentials to ganglion cells. |
|
|
Describe signal transduction in rods when there is light (photons)
|
Retinal absorbs photon, changes it's conformation and dissociates from opsin.
Transducin is activated and then activates phosphodiesterase Posphodiesterase catabolizes cGMP cGMP is low Na+ channels are no longer kept open by cGMP rod hyperpolarizes Ca++ channels close Reduced release of inhibitory neurotransmitter onto bipolar cells Bipolar cell depolarizes and fires action potentials |
|
|
Do nocturnal animals have more rods or cones?
|
Rods, so they can have better vision at night. They are poor at distinguishing color.
|
|
|
Do diurnal animals have more rods or cones?
|
Cones, they are able to see colors in bright light. They have poor night vision.
|
|
|
Why do predatory animals have better depth perception?
|
Convergence
Parallax Estimation of size |

