![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
64 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Nutrition |
The way that organisms obtain + use food to provide energy + carry out characteristics |
|
|
Heterotrophic |
Organisms cannot make their own food. Obtain nutrients by eating other animals. |
|
|
Autotrophic |
Organisms can make their own food through photosynthesis |
|
|
Herbivores |
Animals that feed on plants e.g. Rabbit |
|
|
Carnivores |
Animals that feed on other animals e.g. Fox |
|
|
Omnivores |
Animals that feed on plants + animals e.g. Badger |
|
|
Balanced Diet |
A diet that has correct amount of nutrients for body's needs |
|
|
Digestion |
Physical + chemical breakdown of food into soluble particles that can be absorbed into the body |
|
|
Mechanical Digestion |
Breakdown of food into smaller particles by teeth, churning of stomach or peristalsis |
|
|
Chemical Digestion |
Breakdown of food into smaller particles by enzymes, stomach acid or bile |
|
|
Stages of Human Nutrition |
1. Ingestion 2. Digestion 3. Absorption 4. Egestion |
|
|
Ingestion |
Food is taken into the body through mouth |
|
|
Digestion |
Food broken down into small molecules |
|
|
Absorption |
Nutrients (e.g. Amino acids) taken into bloodstream through walls of intestines |
|
|
Egestion |
Removal of unabsorbed materials known as faeces through anus |
|
|
Peristalsis |
Wave like contraction + relaxation of alimentary canal causing food to move through |
|
|
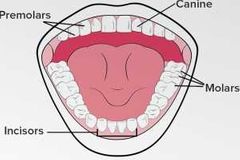
Types of teeth |
|
|
|
Function of incisors |
Cutting, biting |
|
|
Function of canines |
Tearing |
|
|
Function of Premolars + Molars |
Grinding |
|
|
The Human Dental Formula |
Amount of teeth in a human I 2/2, C 1/1, PM 2/2, M 3/3 (half mouth) |
|
|
Areas of Mechanical Digestion |
Mouth, oesophagus, stomach |
|
|
Oesophagus |
A muscular tube 25cm long which connects mouth to stomach |
|
|
Stomach |
Muscular J shaped bag |
|
|
How long does stomach store food? |
4 hours |
|
|
Chyme |
Semi-solid liquid formed when stomach churns + mixes food with gastric juices |
|
|
Components of Saliva |
- Water > softens food - Salts > make pH alkaline (pH 7.5) > optimum pH for salivary amylase - Salivary amylase > breaks down starch into maltose |
|
|
Chemical Digestion in Mouth |
- Secretes saliva - Food turned to bolus (easy swallow) |
|
|
Epiglottis |
Flap of skin that covers windpipe when swallowing which prevents food entering into it |
|
|
What ring of muscle does food enter the stomach through? |
Cardiac sphincter muscle |
|
|
What produces gastric juice in the stomach? |
Gastric glands in the stomach wall |
|
|
Components of Gastric Juice |
- Mucus > protects stomach lining as it is alkaline - Hydrochloric acid > acid (pH2) that kills bacteria - Pepsin > protease (breaks down protein) enzyme > breaks proteins into peptides |
|
|
Through what does chyme enter duodenum? |
Pyloric sphincter muscle |
|
|
Small Intestines |
25 ft long tube made up of: > duodenum > jejunum >ileum |
|
|
What happens when acidic chyme arrives in duodenum? |
Hormones released > pancreas release pancreatic juice + gallbladder release bile |
|
|
Pancreas |
Feather shaped organ which lies underneath stomach |
|
|
Function of Pancreas |
Secretes pancreatic juice > contains water + alkaline salts > neutralises chyme + creates optimum pH for enzymes |
|
|
Function of Pancreatic Amylase in Duodenum |
Breaks down starch to maltose |
|
|
Function of Pancreatic Lipase in Duodenum |
Breaks down lipids to fatty acids + glycerol |
|
|
Function of Pancreatic Amylase in Duodenum |
Breaks down protein to peptides |
|
|
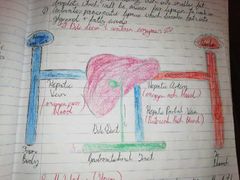
Location of liver |
Right of stomach under diaphragm connected to hepatic artery, hepatic vein + hepatic portal vein |
|
|
Functions of Liver |
- Produces bile - Detoxes blood by removing poisonous substances (e.g. Drugs) - Removes biliverdin + bilirubin pigments for breakdown of dead red blood cells - Stores excess glucose as glycogen + fat soluble vitamins - Excess proteins changed into urea |
|
|
Bile |
Yellow liquid alkaline that has bile salts which neutralises chyme from stomach |
|
|
Where is bile stored? |
Gallbladder |
|
|
How bile enters duodenum |
Through bile duct |
|
|
Functions of Bile |
- Emulsifies fats breaking them into smaller fat droplets (easier for lipase to work on) - Activates pancreatic lipase |
|
|
Despite being a big factor in chemical digestion, bile doesn't contain... |
Enzymes |
|

|
|
|

|
|
|
|
Where is food almost fully digested? |
Ileum (small intestine) |
|
|
Chemical digestion in ileum by enzymes |
- Carbohydrates broken into monosaccharides - Lipids broken into glycerol + fatty acids - Proteins broken into amino acids - Digested foods absorbed into bloodstream + lymph system through process of absorption |
|
|
Carbohydrate that cannot be broken down by enzymes |
Cellulose |
|
|
Path of amino acids + glucose to bloodstream |
Brought to liver via hepatic portal vein + to villi |
|
|
Path of glycerol + fatty acids to bloodstream |
Brought to lacteal + enter lymphatic system |
|
|
Adaptations of Small Intestines to Improve Absorption |
- Villi increase surface area for absorption - Cells of intestines one cell thick - Rich blood supply to carry digested nutrients around body |
|
|
Undigested remains of food that pass through colon (large intestine) |
Cellulose, water + bacteria |
|
|
What softens material as it moves through colon? |
Mucus secreting lining |
|
|
Functions of Large Intestines |
- Absorption of water + salts. As water is removed, waste becomes solid. Waste (faeces) passes to rectum where it is stored be removed by anus - Symbiotic Bacteria produce vitamin B + K (break down cellulose) |
|
|
Symbiotic Bacteria |
Bacteria that live off another organism where at least one organism benefits |
|
|
Alternative terms for Fibre |
Roughage or cellulose |
|
|
Where is fibre found in cell? |
Plant Cell walls |
|
|
Benefits of High Fibre Diet |
- Helps absorb water which prevents constipation + diarrhoea - Prevents bowel cancer as fibre removes carcinogens - Provides feeling of fullness to prevent overeatinf - Adds bulk to colon wall. Pressure against colon ensures waste is moved along to be removed. |
|
|
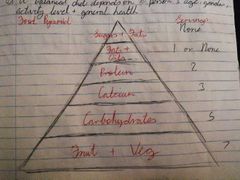
What does balanced diet depend on? |
Age, gender, activity level + general health |
|

|
|

