![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Importance of Carbohydrates |
- source of energy - bread, pasta, potatoes |
|
|
Importance of Fats |
- imp for protection - make cell membranes - store of energy - butter, vegetable oil |
|
|
Protein |
- building & repairing tissues (muscle, skin) - meat, eggs, beans |
|
|
Importance of Fibre |
- keeps food moving through digestive system - whole grain bread, pasta, rice, oats, beans |
|
|
Importance of Water |
- necessary pour chemical reactions - waste removal - temperature regulation |
|
|
Importance of Vitamin D |
- absorbs calcium & phosphorus (imp to keep bones healthy) - egg yolks, oily fish |
|
|
Importance of Calcium |
- imp for growing bones and teeth - dairy, green veggies |
|
|
Vitamin C |
- imp for making collagen (imp protein in blood vessels & skin) - repairing bones & teeth - citrus fruits |
|
|
Iron |
- makes hemoglobin - red meat, liver, nutsb |
|
|
Dietary needs - gender |
- Men need more calories then women bc have larger muscle mass - Menstruating women need more iron as they lose blood - Pregnant women need more protein, calcium, iron for baby - Breast-feeding women need more fats, calcium, water to produce milk |
|
|
Dietary needs - age |
- elder ppl need fewer calories bc they have smaller muscle mass & metabolic rate - children & teenager need more calories, protein as they are growing |
|
|
Dietary needs - activity |
Ppl who exercise need more calories & protein for energy and muscle development |
|
|
Malnutrition |
Disease where persons dietary needs aren’t met |
|
|
What causes constipation |
- lack of water and/or fibre |
|
|
What causes starvation |
- not enough food eaten and body’s energy needs not met - lead to marasmus when cells don’t receive enough energy for respiration - can cause diarrhea and death |
|
|
What causes obesity |
- too much fat stores in body - caused by eating too much - lead to diabetes and heart disease |
|
|
What causes coronary heart disease |
- eating too much fat - block arteries around heart and can’t receive enough O2 |
|
|
Scurvy |
- deficiency of vitamin C - not enough collagen - bleeding, swollen gums, tiredness, muscle pain |
|
|
Anaemia |
- lack of iron in diet/ blood loss - can’t make enough hemoglobin & RBC - tiredness, pale skin, shortness of breath |
|
|
Vitamin D deficiency |
- can get rickets (bones are malformed) - severe bone pain called osteomalacia |
|
|
Kwashiorkor |
- severe protein deficiency - can’t grow/repair tissue and weakens immune system - stunted growth & swollen belly |
|
|
Human alimentary canal |
Where food is processed for use in the body - mouth - salivary glands - oesophagus - stomach - pancreas - liver - gall bladder - duodenum (small intestine) - colon (large intestine) - ileum (small intestine) - rectum - anus |
|
|
Digestion 6 steps |
- ingestion - mechanical digestion - chemical digestion - absorption - assimilation - egestion |
|
|
Ingestion |
- good, drink taken in body - in mouth |
|
|
Mechanical digestion |
- food broken down into smaller pieces - teeth, mouth, stomach contraction, bile |
|
|
Chemical digestion |
- food broken down into smaller and soluble particles by digestive enzymes - salivary glands, stomach, pancreas, small intestine |
|
|
Absorption |
- movement of small food molecules through wall of intestine to blood - food in ileum and small intestine - water in large intestine |
|
|
Assimilation |
- movement of digested food molecules into cells and are used becoming part of cell - any body cells that need it |
|
|
Egestion |
- passing out food that hasn’t been digested, absorbed as feces - rectum and anus |
|
|
Cholera |
- disease caused by bacteria causing severe diarrhea - bacteria causes small int to secrete chloride ions - treatment is oral hydration |
|
|
Tooth structure |
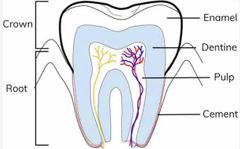
- crown covered by enamel - pulp contains blood vessels - cement covers surface of tooth’s roots |
|
|
Incisors (teeth) |
- Sharp, flat edges - in the middle of upper and lower jaw - cut through food |
|
|
Canines (teeth) |
- next to incisors - tear food |
|
|
Premolars & molars |
- broader surface - premolars next to canines and molars at the back of the mouth - grinding and crushing |
|
|
Enzymes in digestion |
- amylase - protease - lipase |
|
|
Why do we need to break down large molecules into small |
Large insoluble molecules can’t be absorbed into the bloodstream but small can |
|
|
Amylase |
- produced in small intestine, pancreas, salivary glands - breaks starch into maltose and other simple sugars - Maltase breaks maltose down into glucose so it can pass through bloodstream - action sites small intestine, mouth |
|
|
Protease |
- protein —> amino acids - pepsin in stomach - trypsin in small intestine - made in small intestine, pancreas, stomach |
|
|
Lipase |
- Lipids —> glycerol + fatty acids - produced in small intestine & pancreas |
|
|
Bile |
- produced in liver - stored in gall bladder - resealed in small intestine - breaks large fat droplets into small fat droplets (emulsification) |
|
|
Gastric juices |
- in stomach contains HCL - HCL kills harmful organisms |
|
|
Villus |
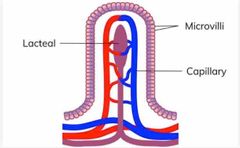
- Wall of small intestine - for water and food digestion - capillary maintains conc gradient - microvilli creates large SA - lacteal for fat absorption
|

