![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
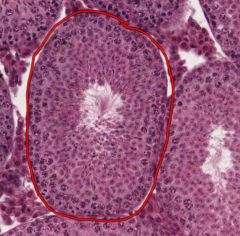
Identify the circled structure from the testes.
What cells does it contain? |
The structure is a Seminiferous Tubule, a coiled, hollow loop where Spermatozoa develop from Spermatogonia (don't worry about differentiating between the stages of sperm development).
The Sertoli Cells line the outside (circumference) epithelium of the Seminiferous Tubules. |
|
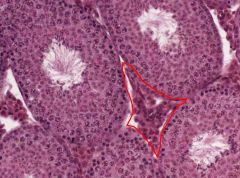
What types of cells are located in the area outlined in red?
What do they secrete? |
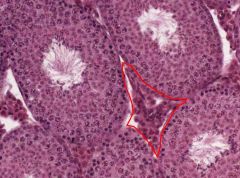
The area indicated is the Stroma, which consists of interstitial tissue between the Seminiferous Tubules.
The Leydig Cells are located there, and they secrete androgens, under the influence of Luteinizing Hormone from the Anterior Pituitary. |
|
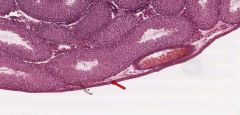
What is the layer of the testes indicated by the red arrow?
|
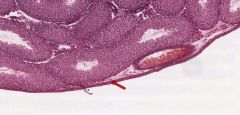
Tunica Albuginea
It is the outer part of the capsule of the testes, composed of dense fibrous connective tissue. |
|
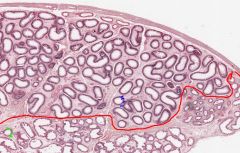
What is the function of the Epididymis?
|
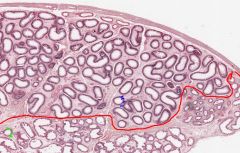
The Epididymis stores Spermatozoa matured in the testes for release during ejaculation.
|
|
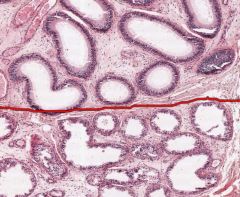
What structures are the openings below the red line in this cross-section of an Epididymis?
|
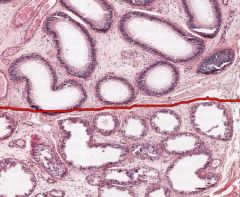
Ductuli Efferentes.
They connect the Rete Testis to the Ductus Epididymis, penetrating the Tunica Albuginea and occupying part of the head of the Epididymis. |
|
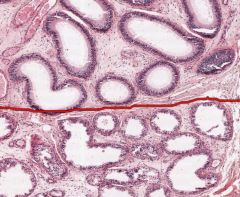
What are the round openings above the red line on this cross-section of an Epididymis?
|
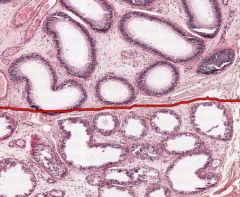
Ductus Epididymis.
It's a (single) long, very convoluted duct that connects the Ductuli Efferentes in the head of the Epididymis to the Ductus Deferens, which is connected to the tail of the Epididymis. |
|
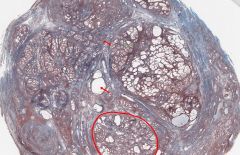
What male organ is shown in cross-section here?
What is circled in red? What structures are stained blue? |
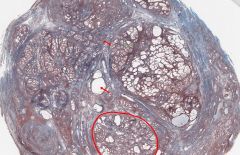
The Prostate
In this trichrome stained specimen, the glands of the Prostate are shown in the red-circled area. The blue structures are connective stroma containing smooth muscle, collagen, and elastic fibres. |
|
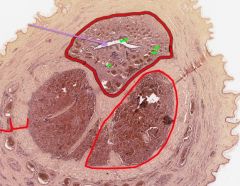
In this cross-section of a penis, what is indicated by the purple arrow?
What muscle surrounds it? What are the other muscles? |
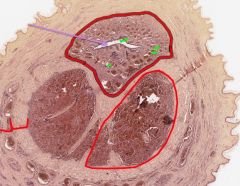
The Urethra.
Corpus Spongiosum. Corpus Cavernosa. |
|
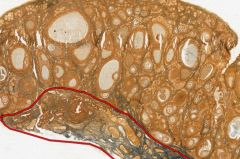
In this cross-section of an ovary, what is the structure outside (i.e above) the red outline?
What is inside the outline? |
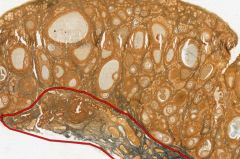
The Cortex, which contains the Follicles in their various states of development.
The Medulla, which contains richly vascularized connective tissue (that's why it's blue). |
|
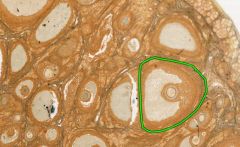
What type of follicle is circled in green on this cross-section of an ovary?
|
Mature (Graafian or Tertiary) follicle.
One mature follicle will ovulate mid-cycle following a LH surge. |
|
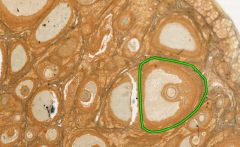
What type of follicle is circled in green?
|
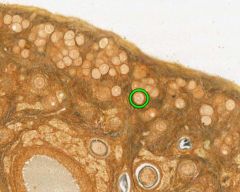
Primordial Follicle.
Consists of primary oocytes surrounded by a single layer of flat follicular cells. |
|
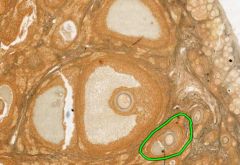
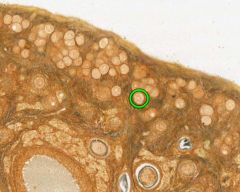
What type of follicle is circled in green?
|
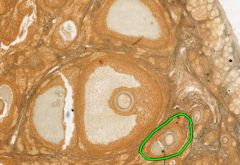
Secondary Follicle.
Step after primary, still growing until mature (like follicle beside the circled one). |
|
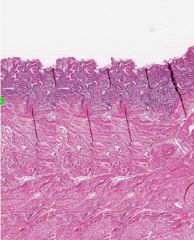
What phase of the menstrual cycle is shown in this cross-section of the uterus?
|
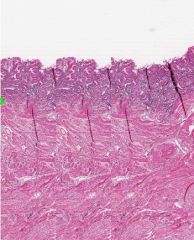
The Menstrual Stage
You can tell by the thinness of the Endometrium (Darker area), which is reduced to its basal layer. |
|
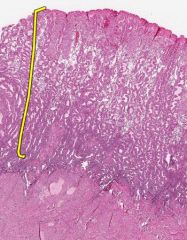
What layer of the Endometrium is indicated by the yellow bracket?
What stage of menstruation is shown here? |
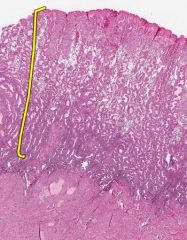
The Functional Layer.
This is the Secretory stage. |
|
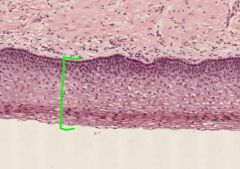
What type of epithelium from the cervix is shown here?
What side of the Os would it normally be found on? |
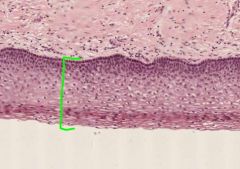
This is Stratified Squamous Epithelium.
It is located in the Ectocervical Epithelium, on the anterior (outside) side of the cervical Os. |
|
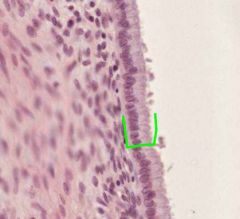
What type of epithelial cells are shown here?
Where in the cervix would they be normally found? |
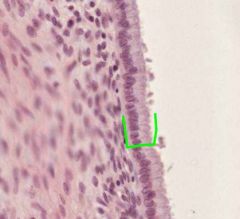
These are Simple Columnar Epithelium (mucus secreting).
They are normally found in the Endocervical Canal. |
|
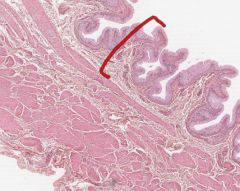
What layer is indicated by the red bracket on this bladder cross section?
|
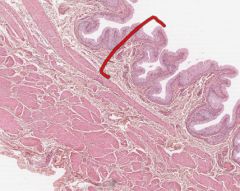
The Tunica Mucosa (inner layer) of the bladder.
The epithelium here is referred to as urothelium. The other histological layers of the bladder are the Tunica Muscularis and the outer Serosa. |
|
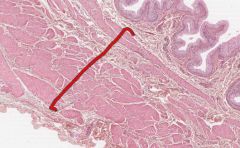
What layer of the urinary bladder is indicated by the red bracked?
|
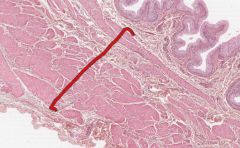
The Tunica Muscularis.
It is a smooth muscle middle layer. |
|
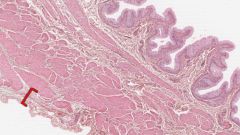
What layer of the urinary bladder is indicated by the red bracket?
|
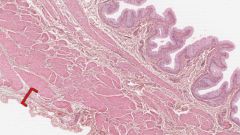
The Tunica Serosa is the outer layer of the bladder, composed of loose connective tissue.
|
|
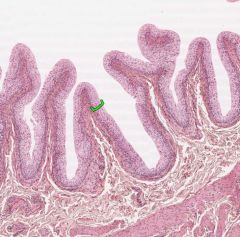
What is the name of this epithelium in the bladder?
|
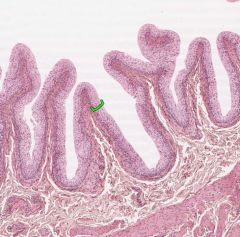
Urothelium, or transitional epithelium is only found in the urinary tract.
It changes structure with stretching. |
|
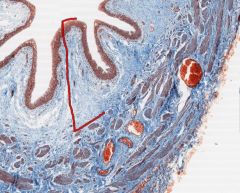
In this cross-section of a ureter, what type of epithelial cells are in the centre.
What type of muscle is in the wall? What is the ureter's relationship to the peritoneum? |
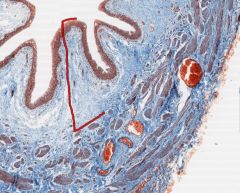
The ureter has urothelium similar to the bladder.
Like the bladder, the ureter is surrounded by smooth muscle. The ureter is retroperitoneal. |
|
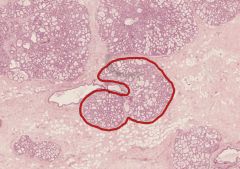
What structure in a female mammary gland is shown circled in red?
Is this breast tissue lactating? |
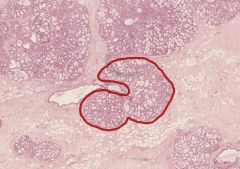
Lobule of Mammary Gland.
It is lactating (you can tell from the budding alveoli, apparently), but I don't think that's a fair question! |
|
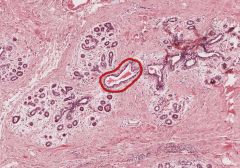
What is the mammary structure outlined in red?
|
Interlobular Lactiferous Duct
You can see it is surrounded by Mammary Glands (i.e. below left). This slide is from an inactive mammary gland. The pink tissue surrounding everything is collagenous connective tissue. The white cell deposits are adipose tissue, the largest portion of an inactive mature breast. |

