![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
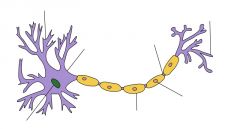
Neuron |
a specialized, impulse-conducting cell that is the functional unit of the nervous system, consisting of the cell body and its processes, the axon and dendrites. Dictionary.com
|
|
|
Neg. feedback mech. |
A mechanism that lower hormones so that the levels can't Go too high |
|
|
Post. Feedback mech. |
A mechanism that sends hormones levels way up |
|
|
C.N.S |
Central nervous system(consists of brain a spinal cord |
|
|
P.N.S |
The peripheral nerves include the 12 cranial nerves, the spinal nerves and roots, and what are called the autonomic nerves. The autonomic nerves are concerned with automatic functions of the body. Specifically, autonomic nerves are involved with the regulation of the heart muscle, the tiny muscles lining the walls of blood vessels, and glands.-medicalnet.com
|
|
|
Axon |
A long fiber of a nerve cell (a neuron) that acts somewhat like a fiber-optic cable carrying outgoing (efferent) messages. Medicalnet.com
|
|
|
Axon terminal |
Axon terminals (also called synaptic boutons) are distal terminations of the branches of an axon. Wikipedia
|
|
|
Dendrite |
a short branched extension of a nerve cell, along which impulses received from other cells at synapses are transmitted to the cell body. Wikipedia
|
|
|
Cell body |
The body of the cell |
|
|
Thyroid |
The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland that sits low on the front of the neck. Your thyroid lies below your Adam’s apple, along the front of the windpipe. The thyroid has two side lobes, connected by a bridge (isthmus) in the middle. When the thyroid is its normal size, you can’t feel it. Webmd
|
|
|
Parathyroid |
Parathyroid glands control the amount of calcium in our blood and bones
|
|
|
Hypothalamus |
a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamus is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland (hypophysis).
|
|
|
Metabolism |
the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms.
|
|
|
Adrenal gland |
The gland that produce the hormone adrenaline |
|
|
Pituitary gland |
In vertebrate anatomy, the pituitary gland, or hypophysis, is an endocrine gland about the size of a pea and weighing 0.5 grams (0.018 oz) in humans. It is a protrusion off the bottom of the hypothalamus at the base of the brain. Wiki
|
|
|
Pineal gland |
The pineal gland, also known as the pineal body, conarium or epiphysis cerebri, is a small endocrine gland in the vertebrate brain. It produces melatonin, a serotonin derived hormone, which affects the modulation of sleep patterns in both seasonal and circadian rhythms.
|
|
|
Cerebrum |
The cerebrum is a large part of the brain containing the cerebral cortex (of the two cerebral hemispheres), as well as several subcortical structures, including the hippocampus, basal ganglia, and olfactory bulb.
|
|
|
Cerebellum |
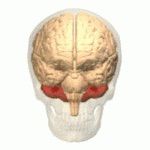
The cerebellum (Latin for "little brain") is a region of the brain that plays an important role in motor control
|
|
|
Brain stem |
the brainstem (or brain stem) is the posterior part of the brain, adjoining and structurally continuous with the spinal cord.
|
|
|
Impulse |
The sudden movement of electricity |
|
|
Endocrine system |
The endocrine system refers to the collection of glands of an organism that secrete hormones
|
|
|
Hormone |
A hormone (from Greek ὁρμή, "impetus") is any member of a class of signaling molecules produced by glands in multicellular organisms that are transported by the circulatory system to target distant organs to regulate physiology and behaviour.
|
|
|
Gland |
A gland is an organ in an animal's body that synthesizes a substance such as hormones for release into the bloodstream (endocrine gland) or into cavities inside the body or its outer surface (exocrine gland).
|
|
|
Thymus |
The thymus is a specialized primary lymphoid organ of the immune system. Within the thymus, T cells or T lymphocytes mature.
|
|
|
Pancreas |
An organ that regulates blood sugar |
|
|
Ovaries |
The female sex organ |
|
|
Pupil |
A part of the eye that lets in light |
|
|
Iris |
The muscle in the eye allowing it to expand and contract |
|
|
Lens |
The clear almost marble in the eye that helps the cornea refract light. |
|
|
Thanks |
Bye |

