![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
49 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Hypothesis |
Explanation for the questions you asked. Explanation of the experiment |
|
|
Null hypothesis |
Not supporting the hypothesis. No relationship between independent and dependent variables |
|
|
Alternative hypothesis |
Supporting hypothesis. There is a relationship between independent and dependent variables. |
|
|
Order the scientific method |
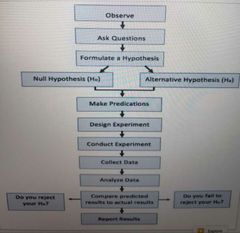
|
|
|
Independent variable |
What you're changing |
|
|
Dependent variable. |
Result of the change |
|
|
What does the dependent variable always depend on |
The independent variable |
|
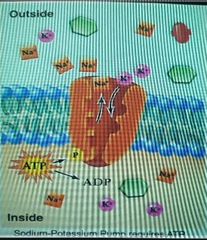
What is this an example of |
Active transport |
|
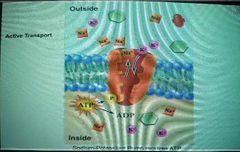
What is the pump here |
The red/orange protein |
|
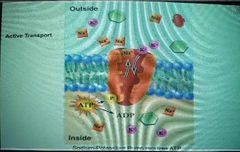
What does the pump do |
Takes 2 potassium ions and brings them into the cell while taking 3 sodium ions and expelling them from the cell |
|
|
How is taking 2 potassium ions and bringing them into the cell while taking 3 sodium ions and expelling them from the cell an active transport? |
Because it requires energy and it's stock piling. There's already a lot of sodium outside the cell and already a lot of pottasium in the cell |
|
|
Metabolism |
All the chemical reactions that occur in a cell |
|
|
How many chemical reactions are occurring in our cells and how often? |
Thousands and thousands, 24/7, always while we're alive |
|
|
Chemical reactions that happen in our body can't happen outside the body without adding a lot more heat. How do they happen in our body at such a low temperature? |
Enzymes. They lower the activation energy so a particular reaction can occur |
|
|
Enzymes |
A protein that is capable of speeding up a specific chemical reaction by lowering the required activation energy |
|
|
Carbohydrates are made up of |
Sugars |
|
|
Nucleic acids are made up of |
Nucleotides |
|
|
Fats are made up of |
Lipids |
|
|
Proteins are made up of |
Amino acids |
|
|
What are the basic categories of biomolecules |
Sugars, fats, proteins, and nucleic acids |
|
|
What are proteins used for |
Structural purposes inside of cells and they are enzymes |
|
|
What are enzymes made up of |
Amino acids |
|
|
How many different amino acids do we have available |
20 |
|
|
What determines the function of the protein and how it folds |
The type of amino acid and their placement in a long string of amino acids |
|
|
When a protein folds what does that determine |
What that protein is able to work on |
|
|
Active site |
Surface of the enzyme where substrate binds and reaction occurs |
|
|
Substrate |
Starting material. Before a reaction is done you need your starting material, and after the reaction occurs you have your product |
|
|
Objective lense |
Magnifies with different levels of magnification |
|
|
Ocular |
To be able to see the image of the cells or what you're looking at. The lens you're looking into |
|
|
Stage |
Where you put the slide on a microscope |
|
|
Diaphragm |
Controls the amount of light that comes in |
|
|
Arm |
Supports everything and that's how you carry it and support it by the base |
|
|
How do you control the stage? |
Mechanical stage controls can make it go back and forth or left and right |
|
|
Coarse and fine adjustment knobs |
Coarse - find what you're trying to look at. fine- slightly adjust. both help to bring the stage closer to the lense |
|

What microscope is this |
Compound light |
|
|
Cover labels and name parts |

|
|
|
Substage light |
Light that comes through so you can see the cells |
|
|
Rheostat |
Controls amount of light. Adjusts it |
|
|
How do you get total magnification |
Magnification of Ocular lens times magnification of objective lens |
|
|
Coarse |
Allows you to move stage quickly closer or away from the lenses |
|
|
Fine |
Small adjustments to the position of the stage |
|

|
Cover up and name parts |
|
|
P- wave |
Depolarization of atria in response to SA node triggering |
|
|
T-wave |
Ventricular repolarization |
|
|
QRS Complex |
Depolarization of ventricles, triggers main pumping contractions |
|
|
1st sound of heart and cause |
Lub. Closure of atrioventeicular valves following atrial systole |
|
|
2nd sound of heart and cause |
Dub. Caused by closure of the semilunar valves following ventricle systole |
|
|
Red blood cells appear red because |
Hemoglobin, respiratory pigment |
|
|
5 types of white blood cells |
Never let monkeys eat bananas (most to least common) Neutrophil, Lymphocyte, Monocytes, Eosinophil, Basophil |

