![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
92 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What does the skeletal system composed of |
bones -joints -cartilages and -ligaments |
|
|
How many bones that a baby have |
276 bones |
|
|
How many bones does an adult have |
206 bones |
|
|
Why do the bones of a human decrease as they grow |
Because their bones fuse together |
|
|
Functions of the Skeletal System |
Support Protection Movements Storage Blood Cell Production |
|
|
Tough ropelike CHON that makes cartilages tough |
Collagen |
|
|
Large molecules of polysaccharides attached to CHONs |
Proteoglycans |
|
|
Types of bones according to SHAPE |
1. Long bones 2. Short bones 3. Flat bones 4. Irregular bones |
|
|
Parts of the long bone |
Diaphysis Epiphyses Periosteum Articular Cartilage Epiphyseal Plate Epiphyseal Line Medullary Cavity |
|
|
True or False. Adults have more red marrow than children |
False |
|
|
What does the yellow marrow composed of? |
Adipose tissue |
|
|
What does the RED marrow consists of |
Blood-forming cells |
|
|
Outermost layer of a bone |
Periosteum |
|
|
Innermost layer of the bone |
Endosteum |
|
|
Bone-forming cells that fxn in the formation of bone, |
Osteoblast |
|
|
Thin sheets. of EC matrix where bone is formed |
Lamellae |
|
|
Spaces b/w the lamellae where osteocytes can be found |
Lacunae |
|
|
2 basic types of bone tissue |
Compact Bone Spongy Bone |
|
|
Sets of concentric ring that contain the blood vessels supplying the bone tissue |
Haversian Canal |
|
|
Consist of interconnecting rods or plates of bones called Trabeculae resembling scaffoldings |
Spongy Bone |
|
|
The formation of bone by osteoblasts. |
Bone Ossification |
|
|
A mature bone cell |
Osteocyte |
|
|
2 types of ossification |
Intramembranous Ossification Endochondral ossification |
|
|
Cartilage cells |
Chondrocytes |
|
|
Increase in bone width or diameter |
Appositional Growth |
|
|
Where bone growth in length occurs &leads to increase in height |
Epiphyseal Plate |
|
|
Occurs by the deposition of new bone lamellae onto existing bone or connective tse by the osteoblasts |
Bone Growth |
|
|
Involves the removal of existing bones by osteoclasts & deposition of new bone by osteoblasts |
Bone Remodeling |
|
|
Decreases osteoclastic activity thus, Ca+ levels in the blood will be decreased |
Calcitonin (Thyroid Gland) |
|
|
Indirectly stimulates osteoclastic activity→ ↑bone breakdown and ↑blood Ca+ levels |
Parathyroid Hormone |
|
|
3 organs that work when there is HYPOCALCEMIA |
Parathyroid Gland Kidneys Small Intestine |
|
|
Two Divisions of the Skeletal System |
Axial Appendicular |
|
|
What composes the AXIAL Skeleton |
Skull Vertebral Column Rib Cage |
|
|
What composes the Appendicular Skeleton |
Pectoral Girdle Upper limb Pelvic Girdle Lower limb |
|
|
What comprises the Skull |
Braincase(Cranium) (8) Facial Bones (14) |
|
|
What comprises the Cranium |
Frontal bone Parietal bone (paired) Temporal bone (paired) Occipital bone Sphenoid bone Ethmoid bone |
|
|
Types of sinuses |
Frontal sinus Ethmoidal sinus Sphenoidal sinus Maxillary sinus |
|
|
Suture that joins the Parietal and the Frontal bone |
Coronal Suture |
|
|
Suture that joins the Temporal bone |
Squamous Suture |
|
|
Canal that leads to the eardrum and the middle ear |
External Auditory Meatus |
|
|
A sharp, needlelike structure located inferiorly to the EAM |
Styloid Process |
|
|
Suture that joins the Occipital and Parietal bones |
Lambdoid Suture |
|
|
Large opening at the base of occipital bone |
Foramen Magnum |
|
|
Located laterally to the foramen magnum which rest on the first vertebra of the vertebral column |
Occipital Condyles |
|
|
Butterfly- shaped bone that spans the width of the skull and forms part of the floor of the cranial cavity |
Sphenoid Bone |
|
|
Saddle-shaped structure at the central region of the sphenoid bone |
Sella Turtica |
|
|
What does the Sella Turtica contain |
Pituitary Gland |
|
|
Irregularly shaped bone that lies anterior to the sphenoid bone |
Ethmoid Bone |
|
|
Unpaired,U-shaped bone |
Hyoid Bone |
|
|
5 major functions of the Vertebral Column |
1. Supports the weight of the head &the trunk. 2. Protects the SC 3. Allows the spinal nerves toexit the SC 4. Site for muscle attachment. 5. Permits movement of thehead and trunk. |
|
|
What consists our Vertebral Column |
Cervical-7 Thoracic-12 Lumbar-5 Sacrum-1 Coccyx- 1 |
|
|
Posterior curvature(thoracic region;hunchback) |
Kyphosis |
|
|
Anterior curvature(lumbar region;swayback condition) |
Lordosis |
|
|
Lateral curvature |
Scoliosis |
|
|
First cervical vertebrae |
Atlas |
|
|
2nd cervical vertebrae |
Axis |
|
|
Sturdiest of vertebra |
Lumbar |
|
|
Function of the rib cage |
Protects the organs within the thorax |
|
|
What consist the rib cage |
1-7 TRUE RIBS 8-12 FALSE RIBS 11-12 FLOATING RIBS |
|
|
Also called the "breastbone" |
Sternum |
|
|
How many bones does the Appendicular Skeleton have |
126 bones |
|
|
What does the Appendicular consists of |
1. Pectoral Girdle 2. Upper Limbs 3. Pelvic girdles 4. Lower Limb |
|
|
What consist the Upper limbs |
Arm Forearm Wrist Hand |
|
|
2 bones of the forearm |
Radius and Ulna |
|
|
Lateral bone, on the thumb side of the forearm |
Radius |
|
|
Medial bone, on the little finger side of the forearm |
Ulna |
|
|
Place where the lower limbs attach to the body |
Pelvic Girdle |
|
|
3 bones that form a Coxal bone |
1. Ilium – most superior 2. Ischium – inferior and posterior “sitdown bone” 3. Pubis- inferior and anterior |
|
|
Thigh bone |
Femur |
|
|
Bones that composes your leg |
Tibia Fibula |
|
|
Bones that consists your feet |
Metatarsals Phalanges |
|
|
Functional Classification of Joints |
1. Synarthrosis – immovable joints 2. Amphiarthrosis – slightly movable joints 3. Diarthrosis – freely movable joints |
|
|
Structural classification of Joints |
Fibrous Cartilaginous Synovial |
|
|
Types of Fibrous joints |
Sutures Fontanels Syndesmoses Gomphoses |
|
|
Thin layer of cartiilage that cover the articular surfaces w/in the synovial joints |
Articulating Cartilage |
|
|
Encloses the cavity and helps hold the bones together&allows movement |
Joint Capsule |
|
|
Lines the cavity everywhere except over the articular cartilage |
Synovial Membrane |
|
|
Pocket or sac that is an extension of the synovial membrane |
Bursa |
|
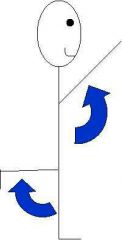
Movement in the sagittal plane that decreases the angle of the joint and brings two bones closer together |
Flexion |
|
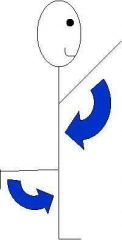
Movement in the sagittal plane that increases the angle of the joint or distance between two bones or parts of the body |
Extension |
|
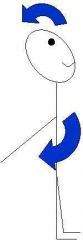
extension greater than 180 degrees |
Hyperextension |
|

movement of a bone around its longitudinal axis |
Rotation |
|

moving a limb away in the frontal plane from the median plane of the body, spreading the fingers apart |
Abduction |
|

opposite of abduction; movement of a limb toward the body midline |
Adduction |
|
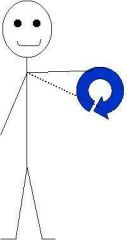
|
Circumduction |
|
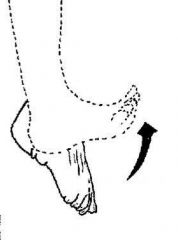
|
Dorsiflexion |
|
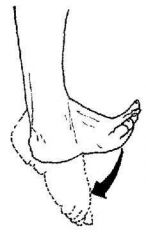
|
Plantarflexion |
|
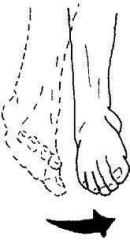
|
Inversion |
|
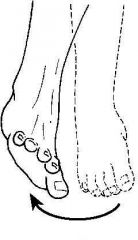
|
Eversion |
|
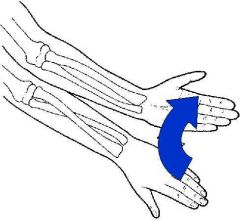
|
Supination |
|
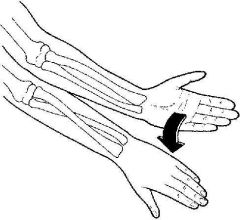
|
Pronation |
|
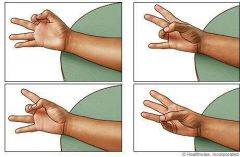
|
Opposition |

