![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Nutrients |
A nourishing substance required for growth and repair by biotic organisms |
1. There are six _________ needed for organisms to stay healthy. 2. _______ are needed to make more and stronger cells during the growth process. |
|
|
Heterotrophs |
Acquire the nutrients and energy they need from consuming living or dead organisms |
1. a.k.a. Consumers |
|
|
Autotrophs |
Acquire the nutrients and energy they need from nonliving sources |
1. Sunlight, minerals, and air are nutrients for _______. 2. Needed for Heterotrophs to survive. |
|
|
Photoautotrophs |
Captures the energy needed from sunlight or photosynthesis |
1. Creates organic compounds from sunlight or carbon dioxide and water 2. Some energy from photosynthesis is stored as chemical energy |
|
|
Photosynthesis |
The process of capturing sunlight to create carbon dioxide and water |
1. Photoautotrophs use __________ to capture energy. 2. Most plants and other organisms use _____________ to create CO2 and H2O. |
|
|
Chemoautotrophs |
Autotrophs that obtain their energy from inorgainc substances |
1. Use Chemosynthesis to obtain energy 2. All are bacteria |
|
|
Chemosynthesis |
The process of capturing energy from inorganic substances |
1. Captures energy to store it as chemical energy for their cells. 2. Inorganic reactions creates energy |
|
|
Cell Respiration |
Released energy created from chemical reactions by heterotrophs and autotrophs |
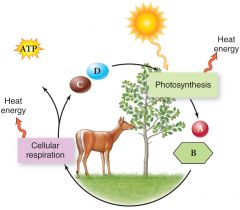
1. Energy is passed between autotrophs and heterotrophs, causing oxygen and carbon dioxide to cycle between them. |
|
|
Producers |
Produces food for heterotrophs to consume |
1. a.k.a. Autotrophs 2. Produces food through photosynthesis |
|
|
Consumers |
Obtains autotrophs or other organisms for food |
1. a.k.a. Heterotrophs 2. Eat other animals and plants that have gotten the energy from the sun for their own nutrients |
|
|
Decomposers |
Certain heterotrophs that can consume dead animals and plants for food |
1. Bacteria, Fungi, Heterotrophs 2. Some heterotrophs, or _______, eat dead, biotic organisms for food. |
|
|
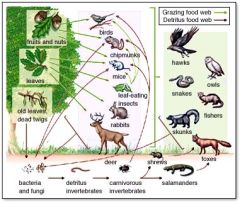
Food Web |
A cycle of reactions between producers, consumers, and decomposers for nutrients and energy |
1. Energy and nutrients are passed between all organisms in a cycle of life. 2. A chart to show the transfer of energy and nutrients to all organisms |
|
|
Biotic |
Living organisms that have growth and development |
1. Respond to stimuli, uses energy, and have genetic information 2. Consume Abiotic organisms to stay alive |
|
|
Abiotic |
All nonliving things that are depended upon by living organisms |
1. Soil, minerals, water, and weather 2. Biotic and _______ organisms make up an Ecosystem. |
|
|
Ecosystem |
An exact location with living and nonliving organisms together |
1. Forest, field, river 2. All organisms acting like a system to keep each other alive |
|
|
Habitats |
A certain part of an ecosystem where similar organisms live |
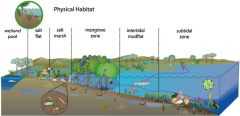
1. Top or bottom of a pond |
|
|
Biosphere |
All of the ecosystems on Earth |
1. Desert, coral reef, ocean 2. The _______ contains all the organisms on the planet. |
|
|
Energy |
Momentum and strength required to do daily tasks |
1. Ability to do work 2. Sugar is a great source of ______. |
|
|
Chemical Energy |
Energy that has been stored in molecules and is released through chemical reactions |
1. Get energy from eating other animals and autotrophs 2. Waste is released afterwards |
|
|
Free Energy |
Part of the Chemical Energy that can work |
1. Used for muscle contraction, growth, and tissue repair 2. During the chemical reaction, free energy is released to do work for the organisms cells |
|
|
Heat Energy |
Energy that is stored in atoms and is transferred through changes in temperature |
1. Only releases some energy as heat from a chemical reaction 2. During a conversion of chemical energy, it releases free energy and ___ ______. |
|
|
First Law of Thermodynamics |
Energy that can't be created or destroyed, but can change into different forms |
1. Energy is present in different form in an ecosystem 2. Total energy of the Earth remains constant |
|
|
Second Law of Thermodynamics |
Increases disorder in a system through it's surroundings |
1. More disorder when more free energy is released 2. Organisms have to be organized in a certain way to stay alive and grow |
|
|
Entropy |
Increased disorder in a system and its surroundings |
1. Energy is needed to maintain a system from more disorder than needed 2. Systems usually change so ______ is increased in the system and surroundings |
|
|
Enzymes |
Proteins that allow a faster reaction by lowering the activation energy |
1. All are catalysts 2. Shape of ______ is linked to its function |
|
|
Catalysts |
Chemicals that lower the activation energy, allowing a faster reaction |
1. Not all are enzymes 2. Depending on the structure of its tertiary structure, there can only be a couple of specific reactions |
|
|
Active Site |
Specific reactions caused by tertiary structure of an enzyme |
1. Shape that resembles the starting molecule(s) 2. Requires less activation energy |
|
|
Substrate |
Beginning molecule of a chemical reaction |
1. Activation site brings the substrate and enzyme closer together 2. Products formed more easily |
|
|
Metabolism |
All chemical reactions and changes that happen inside a cell or organism |
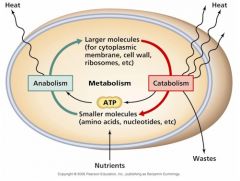
1. Chemical reactions occur all the time in organisms |
|
|
Synthesis |
A type of metabolism that form larger, complex biomolecules from biosynthesis reactions |
1. "building-up" reactions 2. Biosynthesis reaction: starch to glucose |
|
|
Decomposition |
A type of metabolism that takes larger molecules and breaks them down into smaller molecules |
1. "breaking-down" reactions 2. Breakdown reaction: glycogen to glucose within muscle cells |
|
|
Biosynthesis |
Process of building proteins from amino acids to create muscles and blood |
1. Synthesis reaction 2. Requires free energy to create |
|
|
Oxidation |
Process of decomposition that removes electrons from a molecule |
1. Decomposition reaction 2. Some bonds can be broken and rearranged |
|
|
ATP |
Free energy released follows electron transfers and turns into a molecule |
1. Adenosine Triphosphate 2. "Energy currency" of living cells |
|
|
ADP |
ATP molecule gives up one phosphate group |
1. Adenosine diphosphate 2. Energy carrier between cell release and reactions that require energy |

