![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The National Party came into power In which year ? |
1948 |
|
|
What was apartheid based on |
Apartheid was based on racism And built on the idea that white people were superior to everyone else |
|
|
Universal |
Applies to everyone |
|
|
Ideology |
Set of beliefs values and ideas |
|
|
Apartheid |
Official government policy that lasted it from 1948 when the national party came to power to 1994 when the African national Congress won the.1st democratic election in South Africa. |
|
|
UNO |
United Nations Organization |
|
|
The aim of the UNO |
1. Keep peace among the world countries 2. Promote human rights 3. Improve living conditions in poorer parts of the world |
|
|
UDHR |
Universal declaration of human rights (1948) |
|
|
Example of human rights |
1.The right to liberty and personal security 2. Freedom from torture and degrading treatment 3. The right to equality before the law 4. The right to free trial 5. The right to privacy 6. Freedom of belief and religion 7. Freedom of peace assembly and association 8. Right to participate in government 9. The right to social security 10. The right to work 11. The right to adequate standards of living 12. The right to education |
|
|
The apartheid ideology |
Used skin color and other physical characteristics of South Africans to classify people into 'race groups' |
|
|
Racism |
The false idea or myth that certain groups of people are better than others |
|
|
Africans were referred to as |
Natives or Bantus |
|
|
Segregation |
The practice or policy of creating separate facilities within the same society for the use of a particular group. |
|
|
Examples of other racial segregation laws |
1. People living in the town's and cities had to live in separate suburbs and townships according to skin color 2. Africans in the cities were only allowed to stay as long as their labor was needed by whites. Pass laws controlled the movement of Africans. African men outside the Reserves had to carry "passes" which allowed them to work and live in the cities. The police would arrest anyone without a pass and they would be fined or send to jail 3. The job Color bar gave white people jobs rather than black people and A white person was paid more for doing the same job as a black person. A white skin was a better recommendation for a job than Ability 4. Black South Africans were not allowed to vote |
|
|
Born frees |
South Africas born after the end of apartheid after 1994 |
|
|
The Land Act of 1913 |
Stated that African people could only own 13% of land and the rest would be for the whites |
|
|
Main apartheid laws in broad outline |
After they came to power in 1948, the National Party passed 148 apartheid laws. These laws aimed to: • increase the power and living standards of whites • increase the separation of ‘races’ • control the movement of black people. |
|
|
Main apartheid laws |
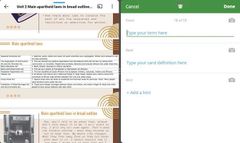
|
|
|
Group Areas Act of 1950 |
The Group Areas Act of 1950 determined where people could live on the basis of their ‘race’ |
|
|
SophiaTown before 1955 |
It was a racially mixed suburb that was home to about 70 000 people, most of them Africans |
|
|
Bantustan |
a negative word for the reserves where black people were meant to be citizens |

