![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
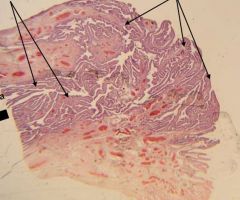
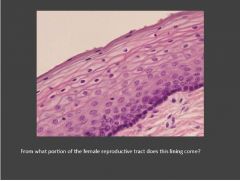
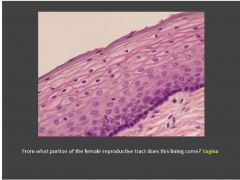
Identify the tissue/organ and the structures indicated
|
Infundibulum (of oviduct). The right arrows indicate the fimbriae and left arrows indicate the mucosal folds (near ampulla region).
|
|
|
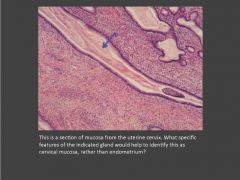
Describe the composition of the fimbriae?
|
Loose connective tissue core, some smooth muscle, lined by mucosal epithelium.
|
|
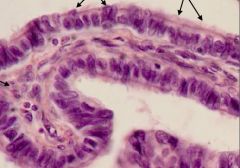
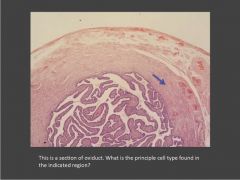
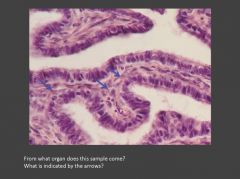
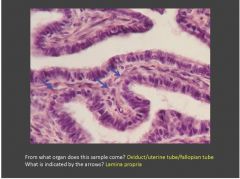
Identify the tissue/structure? What kind of epithelium is present? Identify the cells indicated with arrows?
|
Mucosal folds in the oviduct; Mucosal epithelium is simple columnar. Central lamina propria. Left arrows indicate secretory (aka peg) cells; Right arrows indicate ciliated cells (note they rest on basal bodies).
|
|
|
What effect does estrogen have on the ciliated and secretory (peg) cells?
|
Estrogen stimulates both cell types to hypertrophy. It stimulates elongation of the cilia, and promotes increased secretion. Loss of estrogen reverses these effects.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
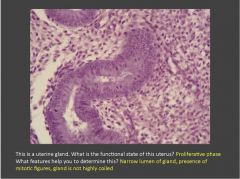
|
|

|

What cell layer is not found in thin skin? Stratum lucidum
|
|
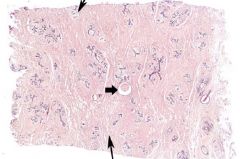
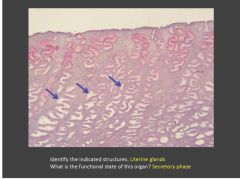
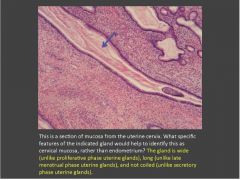
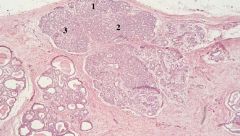
Identify the tissue and structures denoted by thin arrows. What pathological structure is indicated by the thick arrow?
|
Breast-Inactive mammary gland; Main features: parenchyma is mainly duct elements. Stroma (in lobule) is loose CT. Interlobular stroma is DICT. Top arrow-intralobular stroma; Bottom arrow-interlobular stroma (aka extralobular stroma); Pathology: macrocyst;
|
|
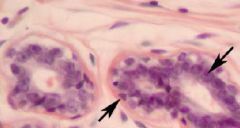
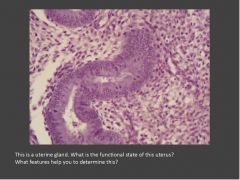
Identify the structures indicated in this section of mammary tissue? Is it active or inactive? What type of epithelium is characteristic of this glandular epithelium?
|
Myoepithelial cell (triangle shaped nuclei); Duct epithelial cell; This tissue is inactive. Simple cuboidal to low columnar epithelial cells characterize this tissue.
|
|
|
True or false: in the inactive mammary gland, alveoli are present?
|
False. There are no alveoli in the inactive mammary gland.
|
|
|
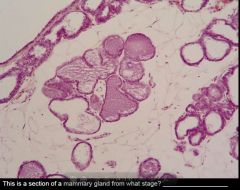
Describe the changes in the mammary gland during the first half of pregnancy. What hormones are responsible for these changes?
|
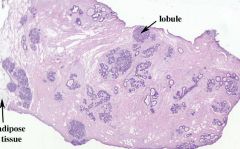
-Proliferation of intralobular ducts; Mammary tissue darker (basophilic) and looks more "crowded" with duct elements.
-Formation of end buds that hollow out to form alveoli. -You will also see some mitotic figures -Estrogen is main hormone required for duct and alveolar growth. |
|
|
Describe the changes in the mammary gland during the second half of pregnancy. What hormones are responsible for these changes?
|
The alveoli differentiates and fat and protein droplets appear in alveolar cells. In some alveoli you may see a characteristic "apocrine snout." You will also see fat accumulation in the apical cytoplasm. Overall appearance is really crowded lobules that have an almost "squished" appearance. The intralobular stroma is highly vascularized the epithelium is often tall columnar. Progresterone is the main hormone needed for alveolar differentiation.
|
|
|
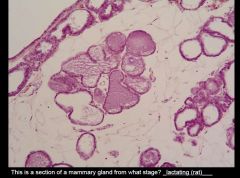
What features are present that are NOT typical of a human lactating mammary gland? Adipose tissue among the lobules.
|
|

|

|
|
|
Describe the parenchyma and stroma of the inactive breast.
|
Parenchyma is mostly duct elements whereas the stroma is loose connective tissue.
|
|
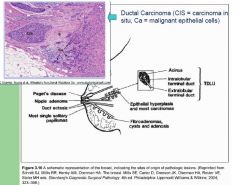
What is the medical importance of the terminal duct lobular unit?
|
It is the site from which most breast cancer arises.
|
|
|
What is the difference breast secretion of mil proteins and milk lipids?
|
Milk protein is secreted by merocrine secretion. Milk lipids are secreted by apocrine secretion.
|
|
|
What is the primary function of colostrum?
|
It provides the baby with passive immunity--it has a high concentration of antibodies and proteins.
|
|
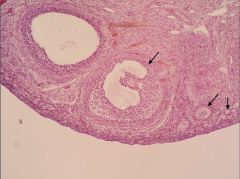
Identify the organ and structures indicated by the arrows.
|
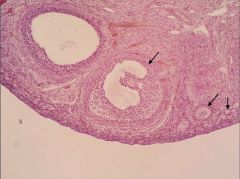
Ovary; Ovarian follicles
|
|
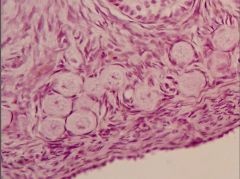
Identify the organ and round structures in the foreground.
|
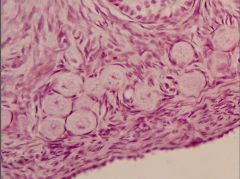
Ovary; these are primordial follicles.
|
|
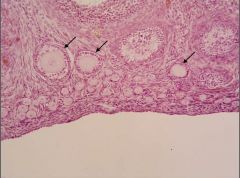
Identify the structures indicated. What features help you make this identification.
|
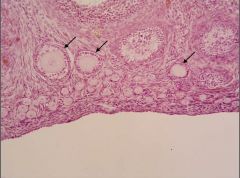
Two unilaminar primary follices; one developing multilaminar primary follicle.
|
|
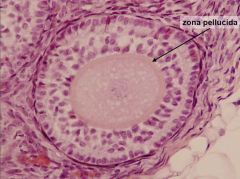
What follicle type is this? Describe features that help make this ID?
|
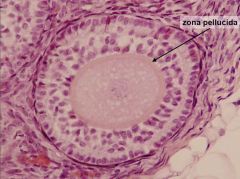
Multilaminar primary follicle; stratified cuboidal epithelium (aka granulosa); NO fluid filled antrum; zona pellucida
|
|
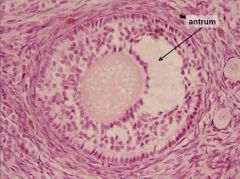
What follicle type is this? Describe features that help make this ID?
|
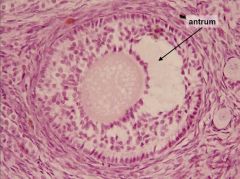
Secondary follicle; stratified cuboidal epithelium (aka granulosa), fluid filled antrum; zona pellucida;
|

